Design and dynamic performance analysis of multi-degree-of-freedom flapping wing driving mechanism
-
摘要:
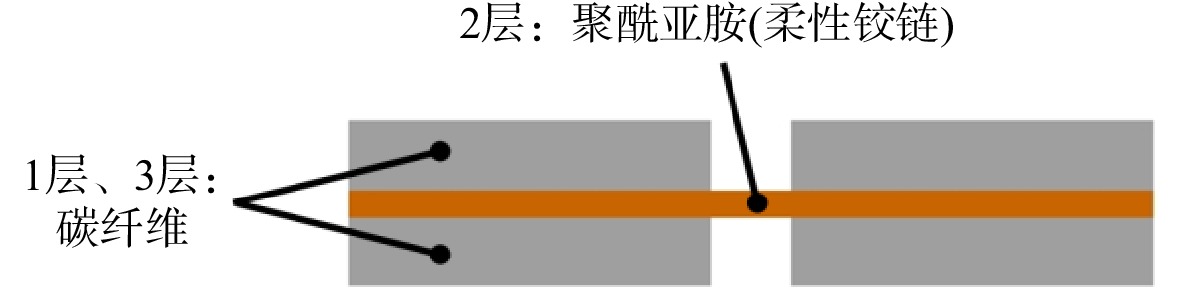
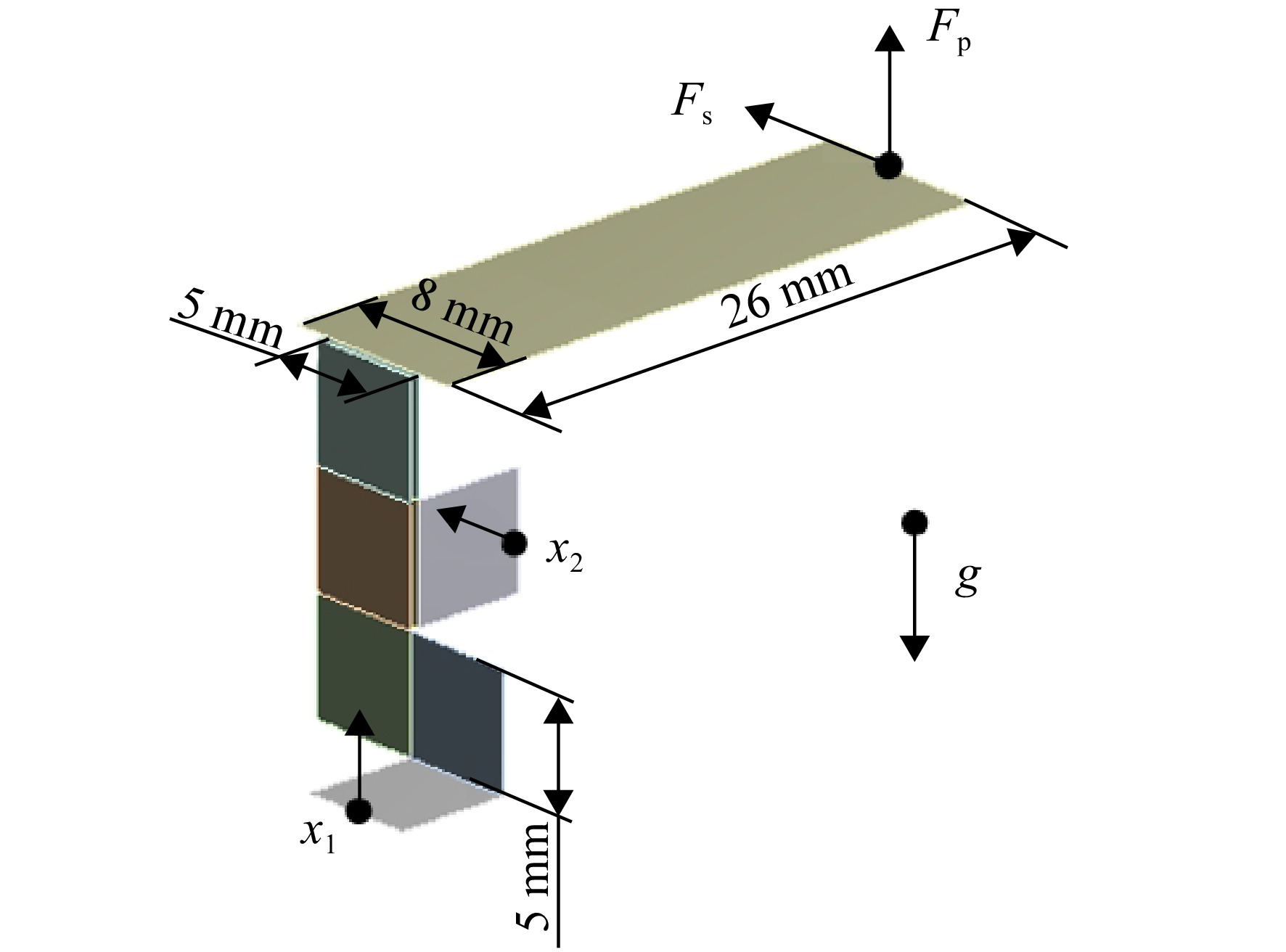
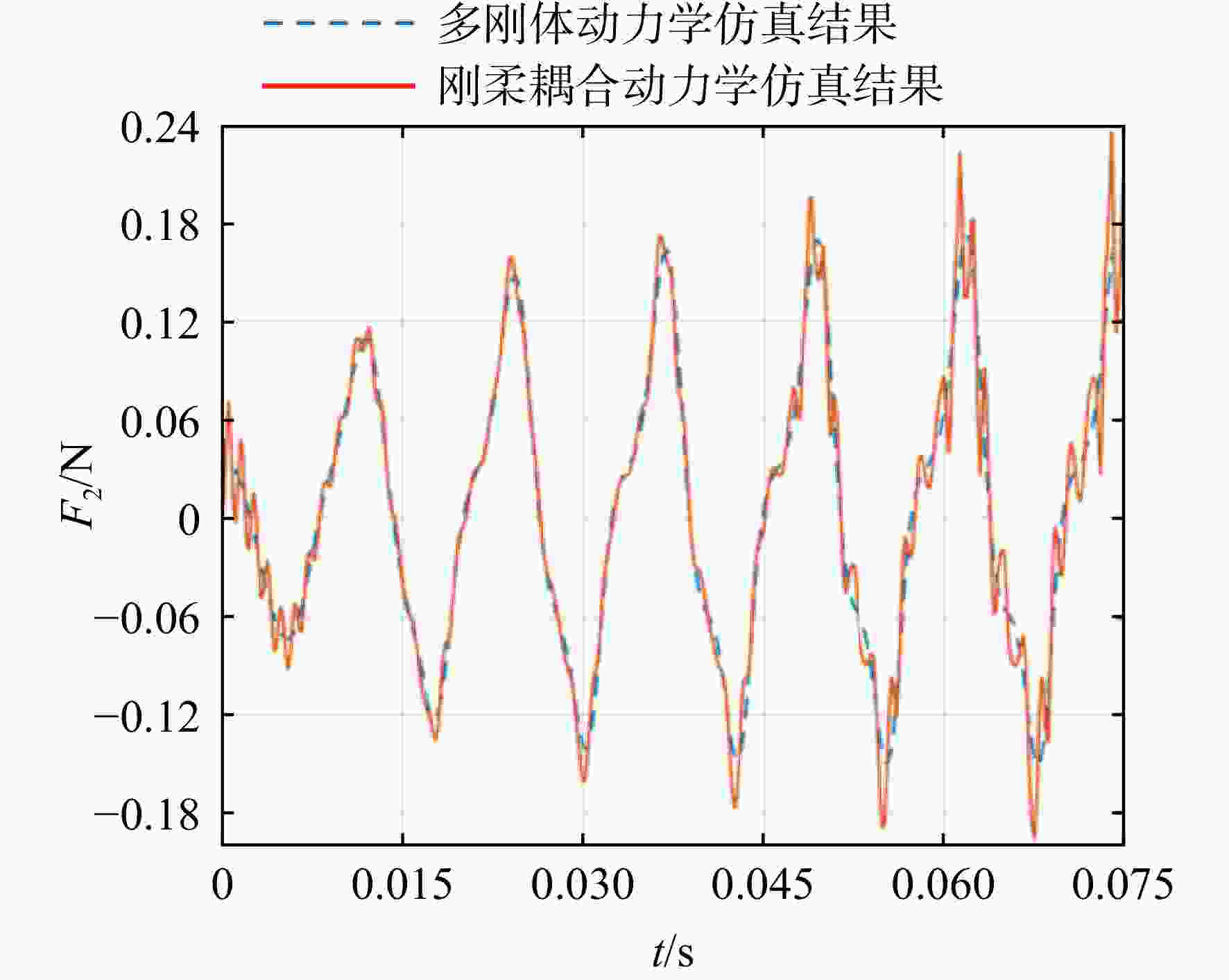
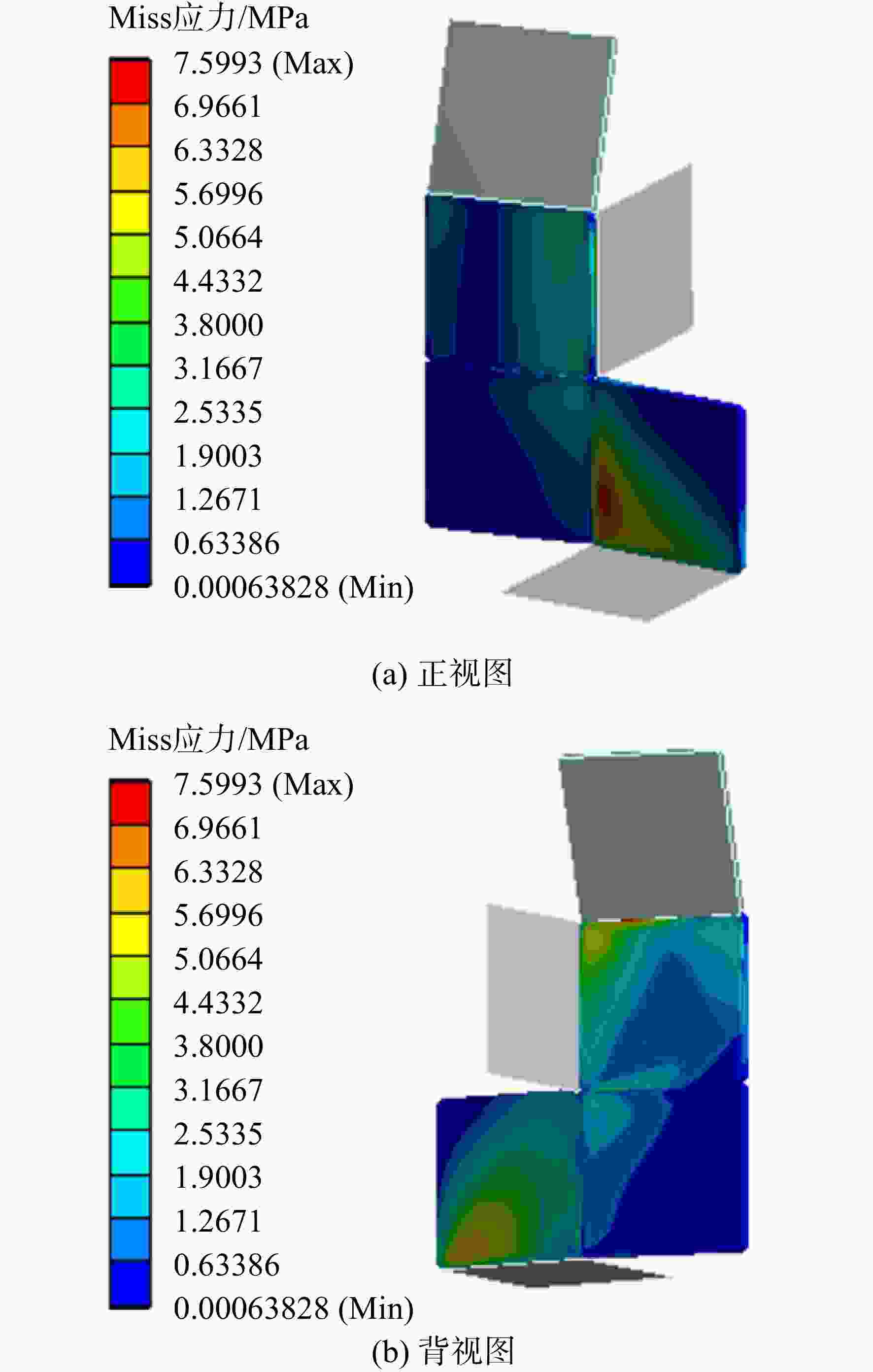
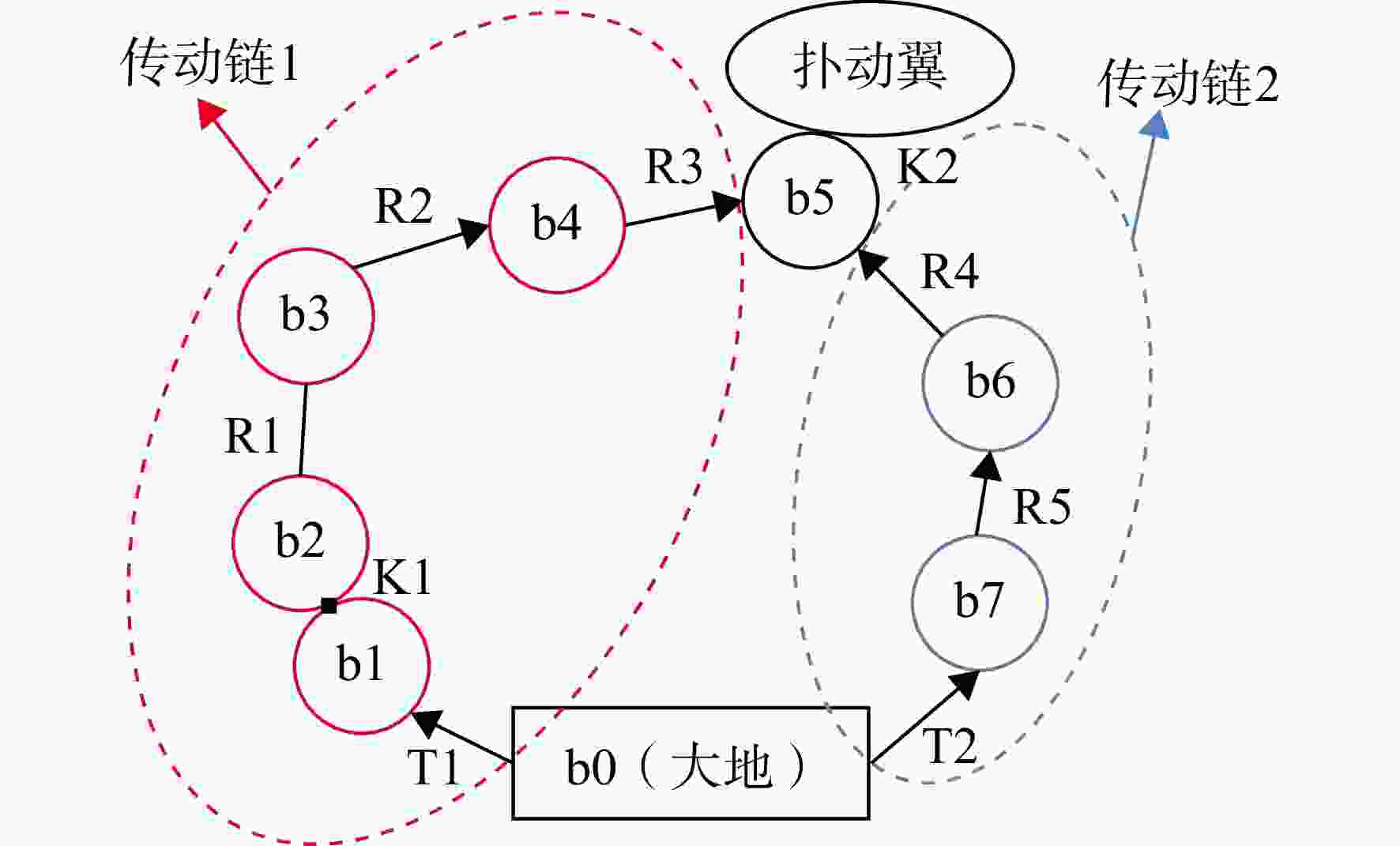
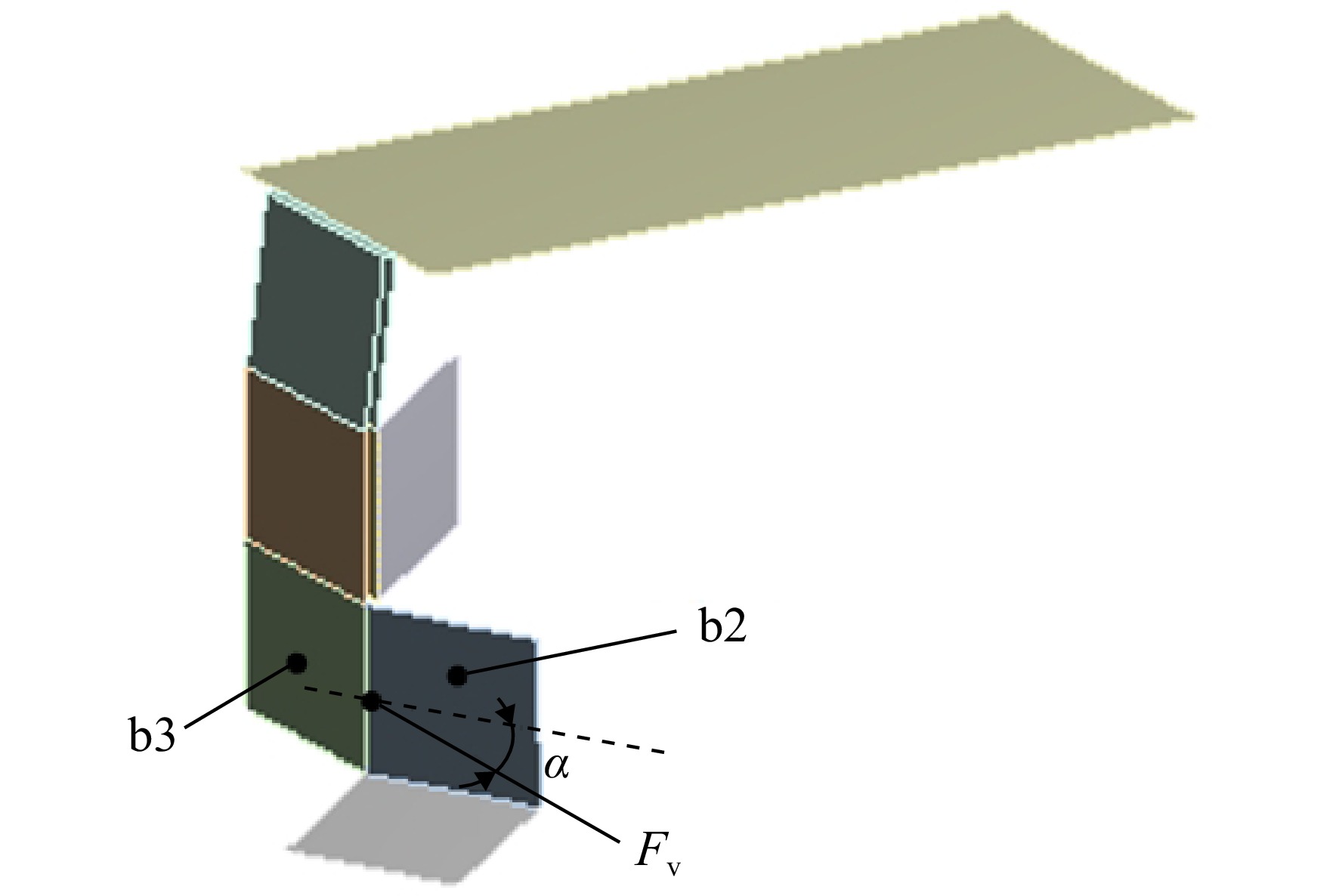
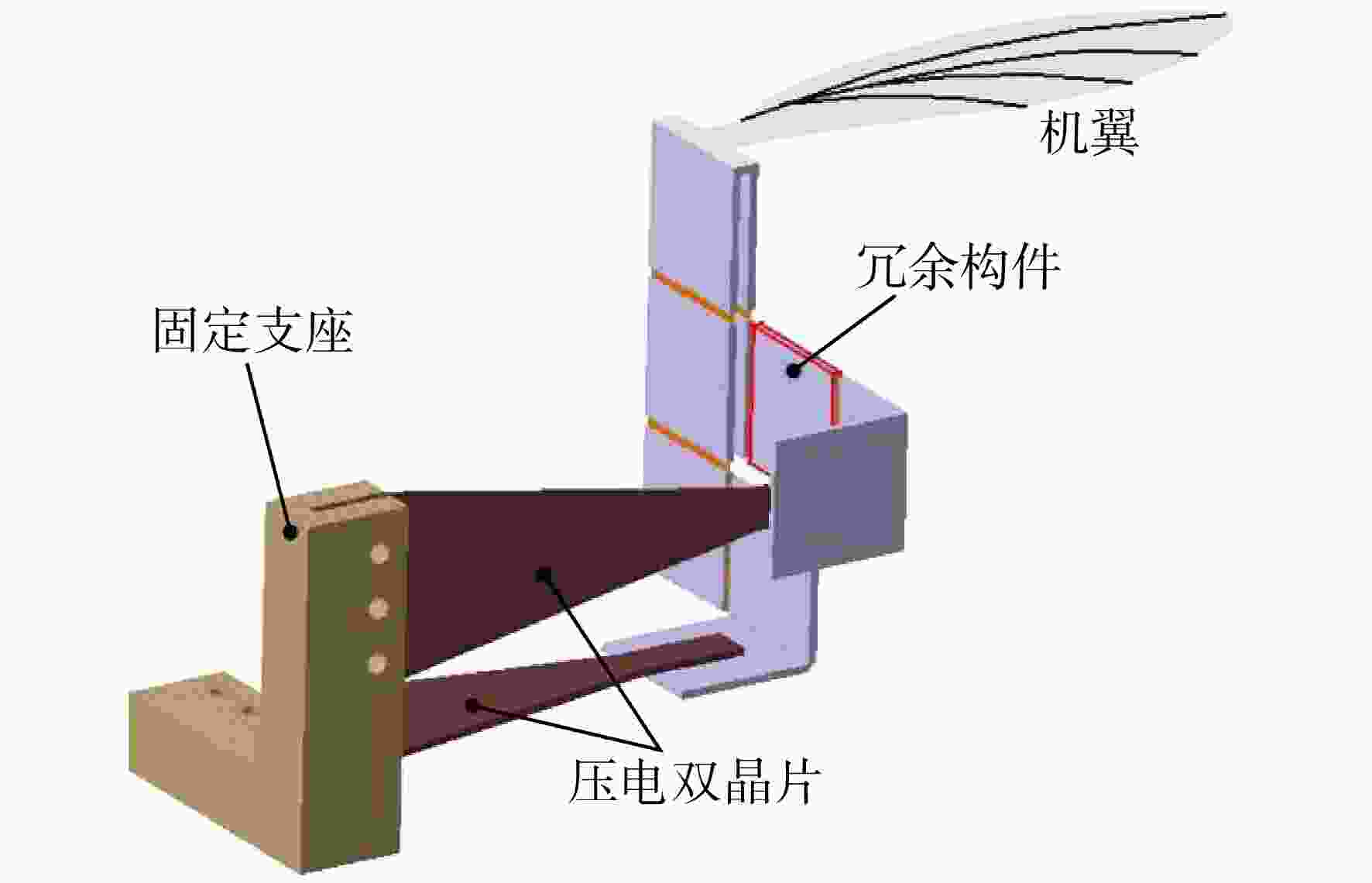
为实现微型扑翼飞行器的扑动翼沿复杂轨迹运动,设计了一种扑动—扫掠多自由度扑翼驱动机构。针对该机构在高频运动过程中各传动构件的惯性力与弹性变形对原动机驱动力造成影响的问题,建立了该机构的刚柔耦合动力学模型,同时提出可对原动机实际所需驱动力与其理想值之间差异进行量化处理的动力学性能因子,结合正交试验研究了机构中各薄板构件的厚度对机构动力学性能的影响规律。结果表明:受面外载荷的薄板构件对驱动机构动力学性能的影响较大,且所在传动链的传力路径越长、位置越靠近原动机,其影响越显著;驱动机构的扑动运动性能强于扫掠运动性能;此外驱动机构的动力学性能并非与薄板构件厚度呈正相关的关系。
Abstract:In order to realize the movement of the micro flapping-wing aircrafts’ wings along the complex trajectory, a flap-sweep multi-degree-of-freedom flapping-wing driving mechanism was designed. In view of the problem that the inertial force and elastic deformation of the mechanism’s transmission components affect the actuators’ driving force during the high-frequency motion, a rigid-flexible coupling dynamic model of the mechanism was established. At the same time, a dynamic performance factor that can quantify the difference between the driving force required by the actuators and its ideal value was proposed. Finally, combined with the orthogonal experiment, the influence of each thin-plate-component’s thickness on the dynamic performance of the mechanism was studied. The research results showed that the thin-plate-component subjecting to the out-of-plane load had a great influence on the dynamic performance of the driving mechanism, and the longer transmission chain’s force-transmission-path and the closer position to the actuators indicated the more significant impact; the flapping motion performance of the driving mechanism was stronger than the sweeping motion performance; In addition, the dynamic performance of the driving mechanism was not positively related to the thin-plate-component’s thickness.
-
表 1 正交试验的因素水平表
Table 1. Factor-level table of orthogonal experiments
mm 因素 水平 1 2 3 b2板件厚度A 0.13 0.23 0.33 b3板件厚度B 0.13 0.23 0.33 b4板件厚度C 0.13 0.23 0.33 b6板件厚度D 0.13 0.23 0.33 表 2 扑动、扫掠同相运动正交试验方案与结果
Table 2. Orthogonal experiment scheme and results of flapping and sweeping in same phase
试验
序号正交试验方案(各因素水平组合方式) 正交试验结果 b2厚度A/mm b3厚度B/mm b4厚度C/mm b6厚度D/mm 扑动性能因子$ {Y_{{\text{s1}}}} $ 扫掠性能因子$ {Y_{{\text{s2}}}} $ 平均性能因子$ {\bar Y_{\text{s}}} $ 1 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.8312 0.4662 0.6487 2 0.13 0.23 0.23 0.23 0.9213 0.5840 0.7527 3 0.13 0.33 0.33 0.33 0.8805 0.3705 0.6255 4 0.23 0.13 0.23 0.33 0.8597 0.7866 0.8232 5 0.23 0.23 0.33 0.13 0.9033 0.8481 0.8757 6 0.23 0.33 0.13 0.23 0.9278 0.6338 0.7808 7 0.33 0.13 0.33 0.23 0.8587 0.8831 0.8709 8 0.33 0.23 0.13 0.33 0.9509 0.8819 0.9164 9 0.33 0.33 0.23 0.13 0.9254 0.8673 0.8963 表 3 扑动、扫掠同相驱动时平均性能极差分析
Table 3. Average performance range analysis for flapping and sweeping in same phase
分析指标 因素A 因素B 因素C 因素D $ {Q_{{\text{s1}}}} $ 2.0269 2.3428 2.3459 2.4207 $ {Q_{{\text{s2}}}} $ 2.4797 2.5448 2.4722 2.4044 $ {Q_{{\text{s3}}}} $ 2.6836 2.3026 2.3721 2.3651 $ {R_{\text{s}}} $ 0.6567 0.2422 0.1263 0.0556 表 4 扑动、扫掠差相运动正交试验方案与结果
Table 4. Orthogonal experiment scheme and results of flapping and sweeping in different phase
试验
序号正交试验方案(各因素水平组合方式) 正交试验结果 b2厚度A/mm b3厚度B/mm b4厚度C/mm b6厚度D/mm 扑动性能因子$ {Y_{{\text{d1}}}} $ 扫掠性能因子$ {Y_{{\text{d2}}}} $ 平均性能因子$ {\bar Y_{\text{d}}} $ 1 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.7100 0.2996 0.5048 2 0.13 0.23 0.23 0.23 0.8353 0.4309 0.6331 3 0.13 0.33 0.33 0.33 0.7586 0.2589 0.5088 4 0.23 0.13 0.23 0.33 0.9463 0.7450 0.8457 5 0.23 0.23 0.33 0.13 0.9547 0.7718 0.8633 6 0.23 0.33 0.13 0.23 0.9599 0.8028 0.8813 7 0.33 0.13 0.33 0.23 0.9601 0.8074 0.8838 8 0.33 0.23 0.13 0.33 0.9732 0.9121 0.9426 9 0.33 0.33 0.23 0.13 0.9763 0.8941 0.9352 表 5 扑动、扫掠差相驱动时平均性能极差分析
Table 5. Average performance range analysis for flapping and sweeping in different phase
分析指标 因素A 因素B 因素C 因素D $ {Q_{{\text{d1}}}} $ 1.6467 2.2343 2.3287 2.3033 $ {Q_{{\text{d2}}}} $ 2.5903 2.4390 2.4140 2.3982 $ {Q_{{\text{d3}}}} $ 2.7616 2.3253 2.2559 2.2971 $ {R_{\text{d}}} $ 1.1149 0.2047 0.1581 0.1011 -
[1] BONTEMPS A,VANNESTE T,PAQUET J B,et al. Design and performance of an insect-inspired nano air vehicle[J]. Smart Materials and Structures,2013,22(1): 014008.1-014008.13. [2] YAN Xiaojun,QI Mingjing,LIN Liwei. Self-lifting artificial insect wings via electrostatic flapping actuators[C]//2015 28th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems. Piscataway,US: IEEE,2015: 22-25. [3] 杨艺,车云龙. 毫米级静电微扑翼驱动器的结构设计、工艺与测试[J]. 传感器与微系统,2018,37(1): 91-95. YANG Yi,CHE Yunlong. Structure design,fabrication and testing of millimeter-scale electrostatic micro flapping-wing actuator[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies,2018,37(1): 91-95. (in Chinese doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2018)01-0091-05 YANG Yi, CHE Yunlong . Structure design, fabrication and testing of millimeter-scale electrostatic micro flapping-wing actuator[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies,2018 ,37 (1 ):91 -95 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2018)01-0091-05[4] PENG Yuxin,LIU Li,ZHANG Yangkun,et al. A smooth impact drive mechanism actuation method for flapping wing mechanism of bio-inspired micro air vehicles[J]. Microsystem Technologies,2018,24(2): 935-941. [5] PHILLIPS N,KNOWLES K. Positive and negative spanwise flow development on an insect-like rotating wing[J]. Journal of Aircraft,2013,50(5): 1321-1332. [6] ORLOWSKI C T,GIRARD A R. Dynamics,stability,and control analyses of flapping wing micro-air vehicles[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences,2012,51: 18-30. [7] 从梦磊,李君兰. 基于空间RURS机构的三维仿生扑翼机构设计与分析[J]. 航空动力学报,2019,34(3): 692-700. CONG Menglei,LI Junlan. Design and analysis of three-dimensional bio-inspired flapping wing mechanism based on spatial RURS linkage[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2019,34(3): 692-700. (in Chinese doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2019.03.022 CONG Menglei, LI Junlan . Design and analysis of three-dimensional bio-inspired flapping wing mechanism based on spatial RURS linkage[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2019 ,34 (3 ):692 -700 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.2019.03.022[8] DICKINSON M H,LEHMANN F O,SANE S P. Wing rotation and the aerodynamic basis of insect flight[J]. Science,1999,284(5422): 1954-1960. [9] BAIK Y S,BERNAL L P. Experimental study of pitching and plunging airfoils at low Reynolds numbers[J]. Experiments in Fluids,2012,53(6): 1979-1992. [10] BERMAN G J,WANG Z J. Energy-minimizing kinematics in hovering insect flight[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2007,582: 153-168. [11] DONG Haibo,LIANG Zongxian,HARFF M. Optimal settings of aerodynamic performance parameters in hovering flight[J]. International Journal of Micro Air Vehicles,2009,1(3): 173-181. [12] LIU Zhiwei,YAN Xiaojun,QI Mingjing,et al. Design of flexible hinges in electromagnetically driven artificial flapping-wing insects for improved lift force[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering,2019,29(1): 015011.1-015011.12. [13] 宗光华,贾明,毕树生,等. 扑翼式微型飞行器的升力测量与分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2005,41(8): 120-124. ZONG Guanghua,JIA Ming,BI Shusheng,et al. Measurement and analysis of lift of micro air robot with flapping wings[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2005,41(8): 120-124. (in Chinese doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2005.08.020 ZONG Guanghua, JIA Ming, BI Shusheng, et al . Measurement and analysis of lift of micro air robot with flapping wings[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2005 ,41 (8 ):120 -124 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2005.08.020[14] HINES L,ARABAGI V,SITTI M. Shape memory polymer-based flexure stiffness control in a miniature flapping-wing robot[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics,2012,28(4): 987-990. [15] WIDHIARINI S,PARK J H,YOON B S,et al. Bird-mimetic wing system of flapping-wing micro air vehicle with autonomous flight control capability[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering,2016,13(3): 458-467. [16] YOON S, KANG L, JO S. Development of air vehicle with active flapping and twisting of wing[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2011, 8(1): 1-9.YOON S,KANG L,JO S. Development of air vehicle with active flapping and twisting of wing[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering,2011,8(1): 1-9. [17] WOOD R J,AVADHANULA S,SAHAI R,et al. Microrobot design using fiber reinforced composites[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design,2008,130(5): 052304.1-052304.11. [18] SREETHARAN P S,WHITNEY J P,STRAUSS M D,et al. Monolithic fabrication of millimeter-scale machines[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering,2012,22(5): 055027.1-055027.6. [19] PHILLIPS N,KNOWLES K. Effect of flapping kinematics on the mean lift of an insect-like flapping wing[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers,Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering,2011,225(7): 723-736. [20] FINIO B M,WHITNEY J P,WOOD R J. Stroke plane deviation for a microrobotic fly[C]//2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway,US: IEEE,2010: 3378-3385. [21] WHITNEY J P,WOOD R J. Aeromechanics of passive rotation in flapping flight[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2010,660: 197-220. [22] 王大燕. 考虑弹簧和运动副间隙的微扑翼飞行器翅翼机构动力学研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学,2008: 23-26. WANG Dayan. Research on the dynamics of flapping-wing mechanism with spring and bearing clearance[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University,2008: 23-26. (in ChineseWANG Dayan. Research on the dynamics of flapping-wing mechanism with spring and bearing clearance[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2008: 23-26. (in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: