Engine knock recognition based on wavelet domains denoising and convolutional neural network
-
摘要:
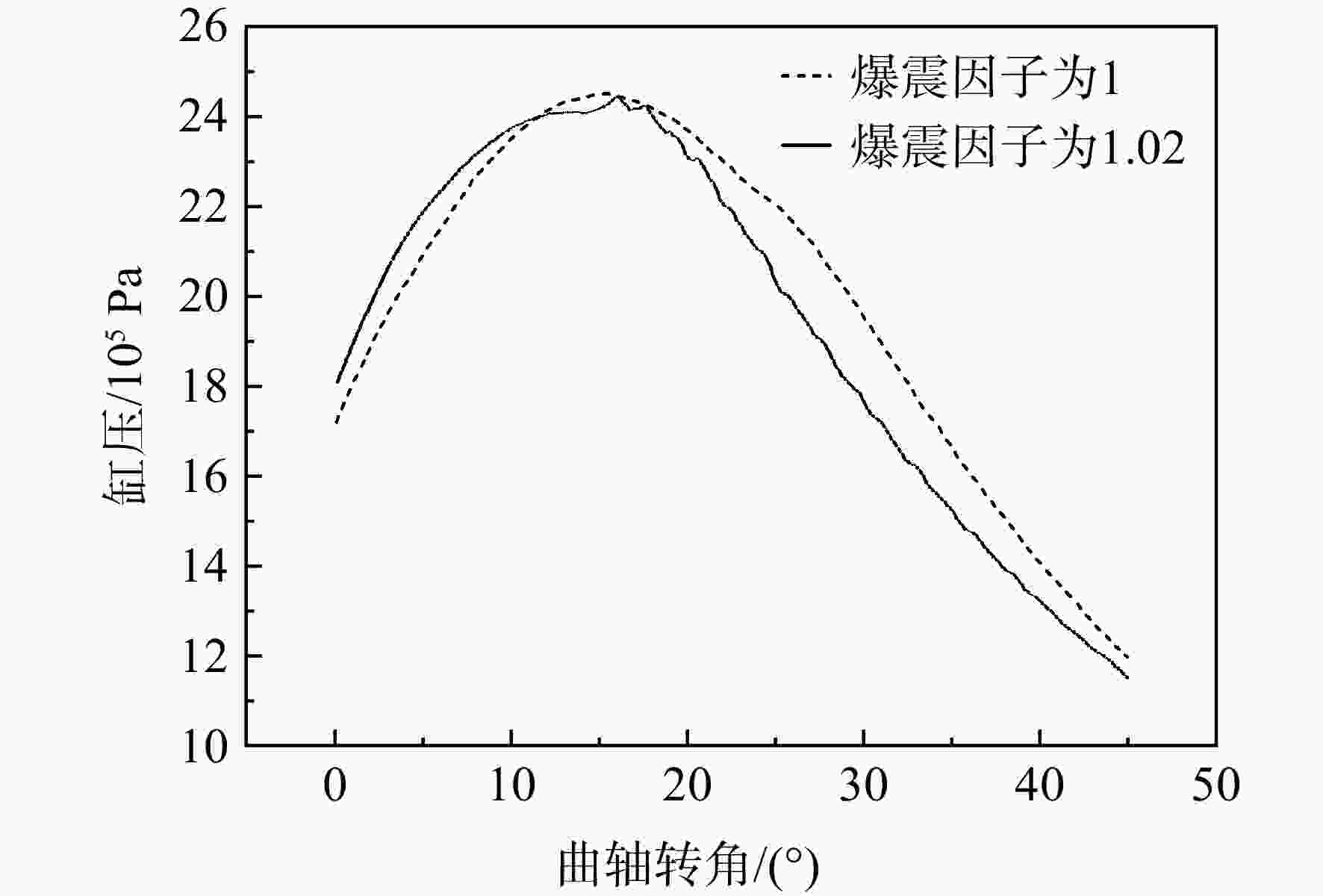
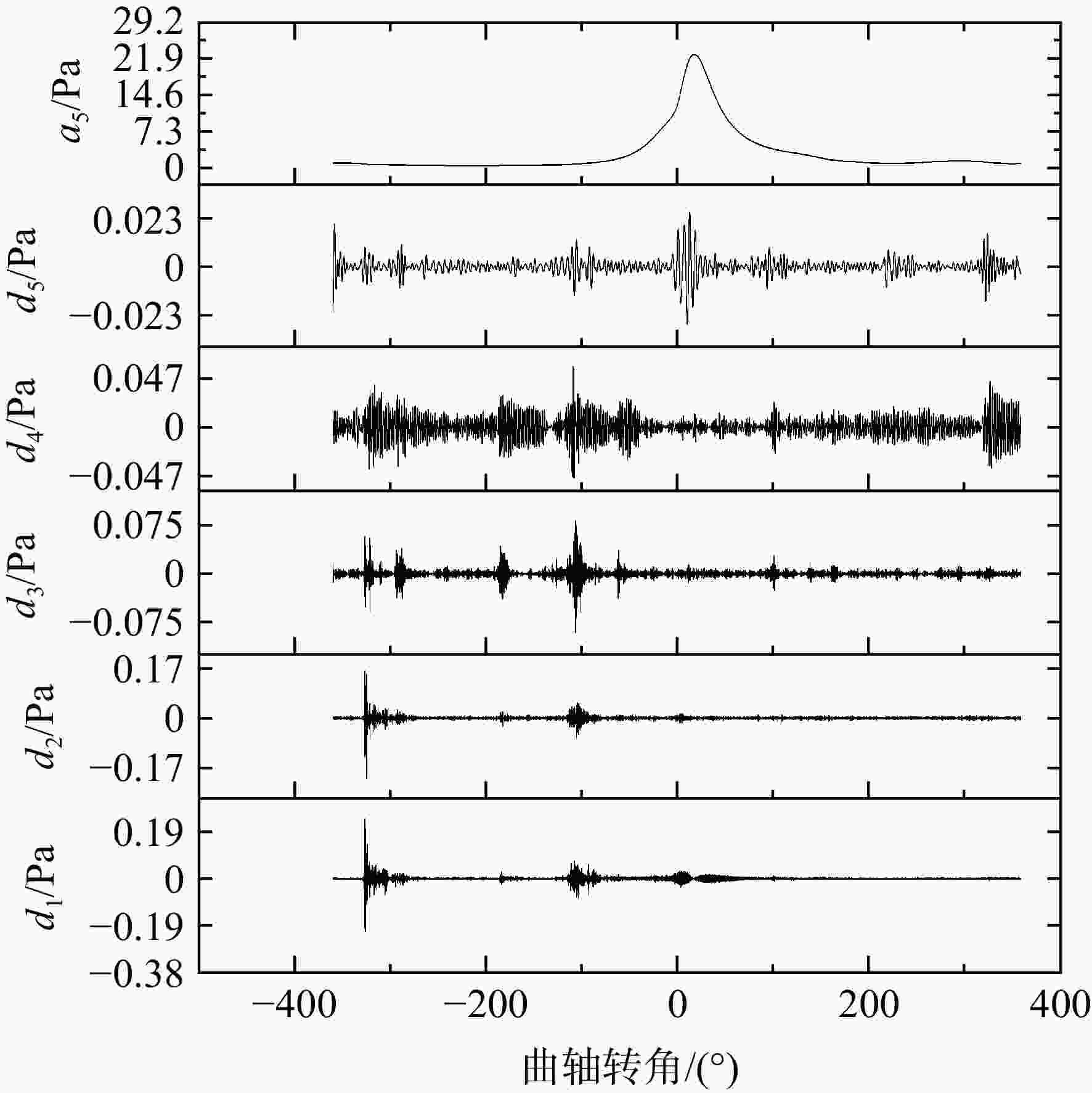
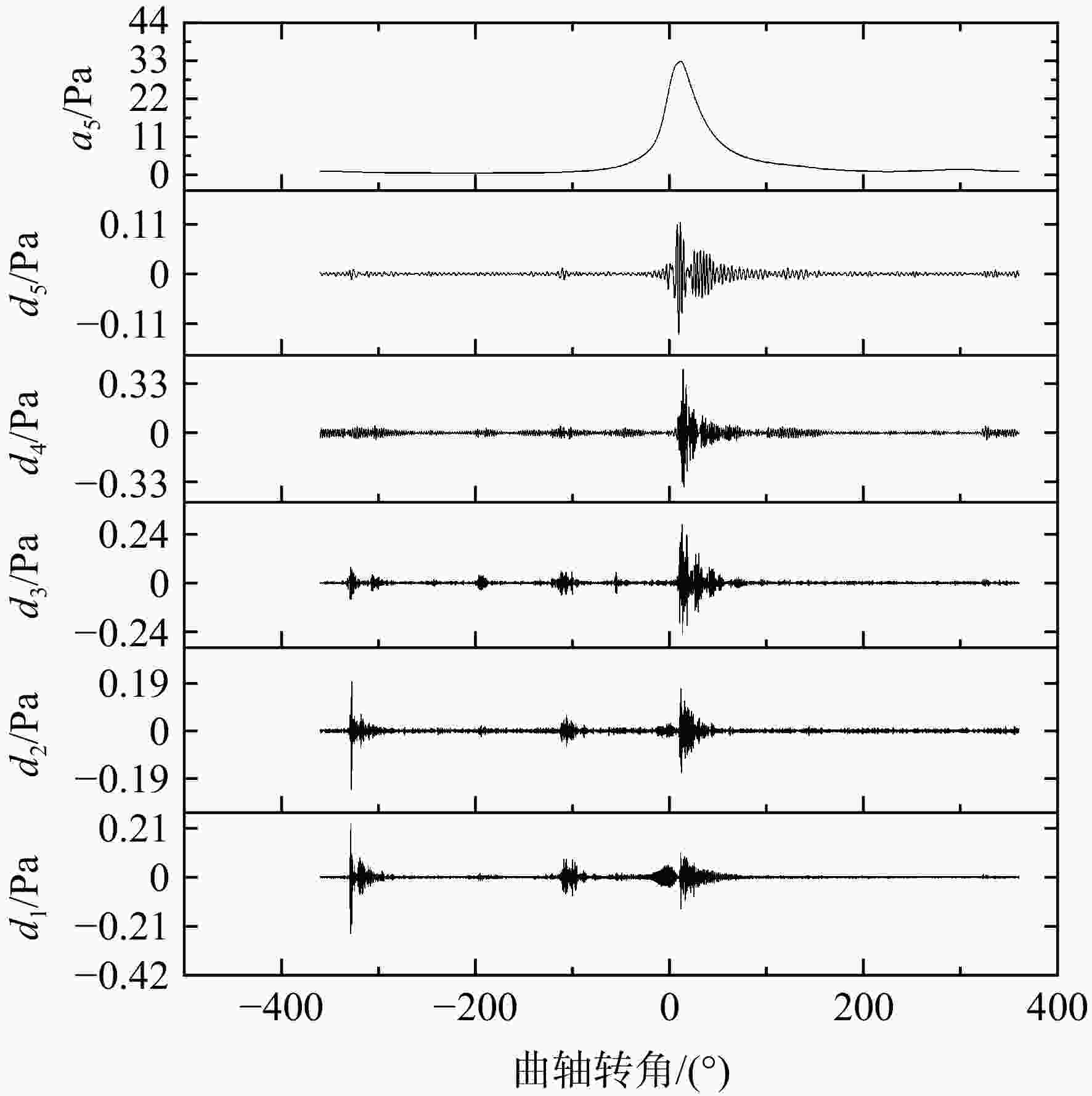
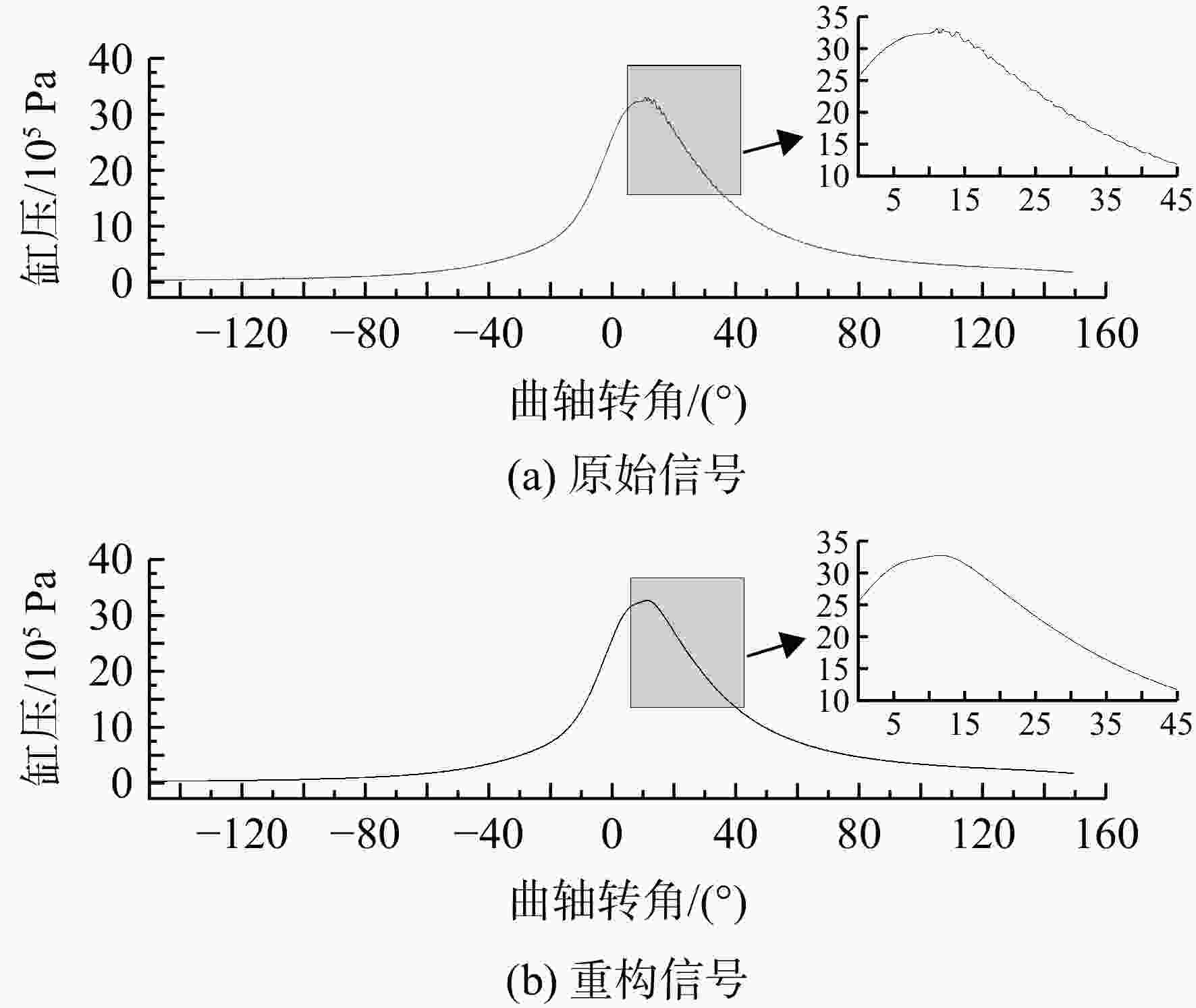
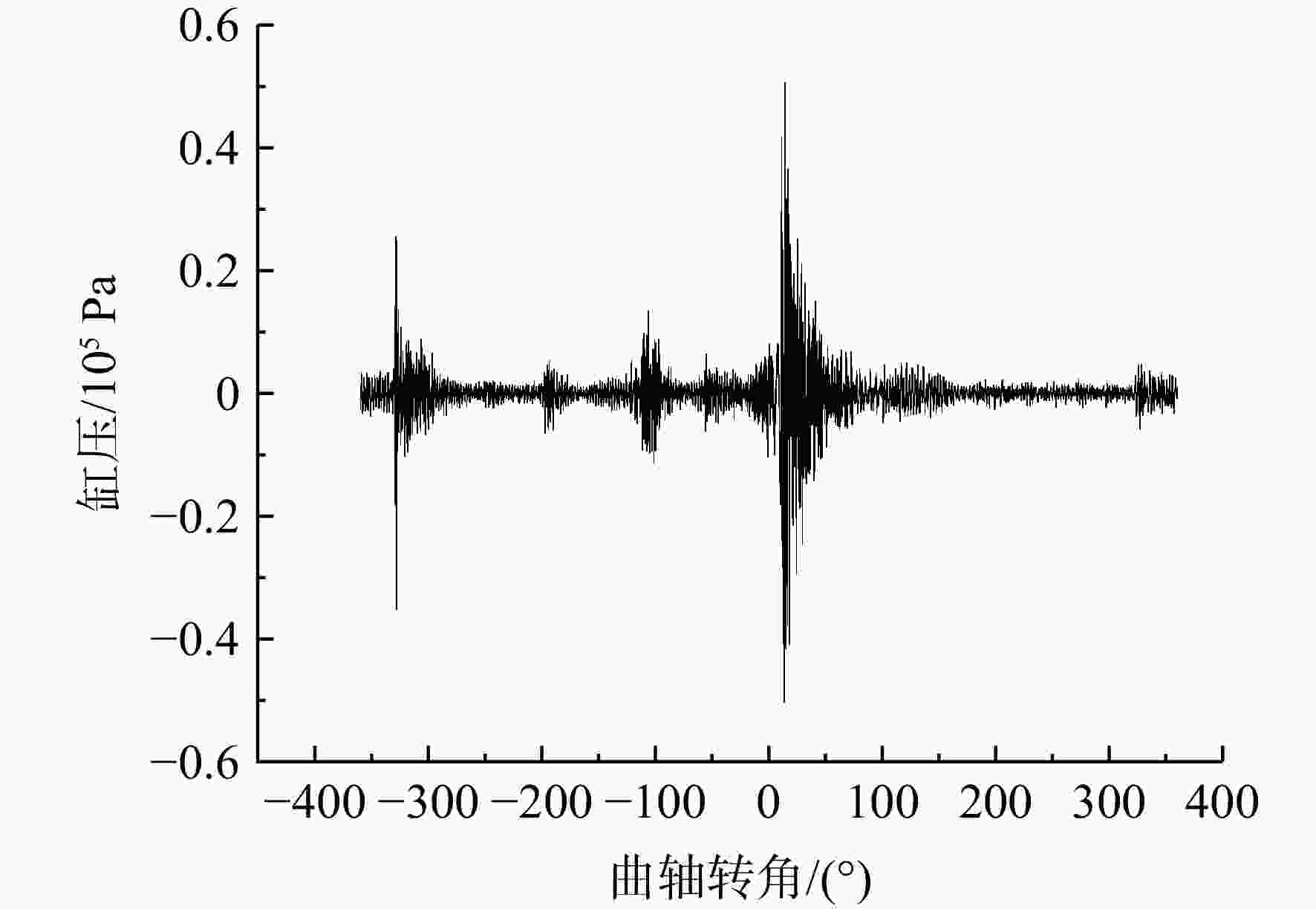
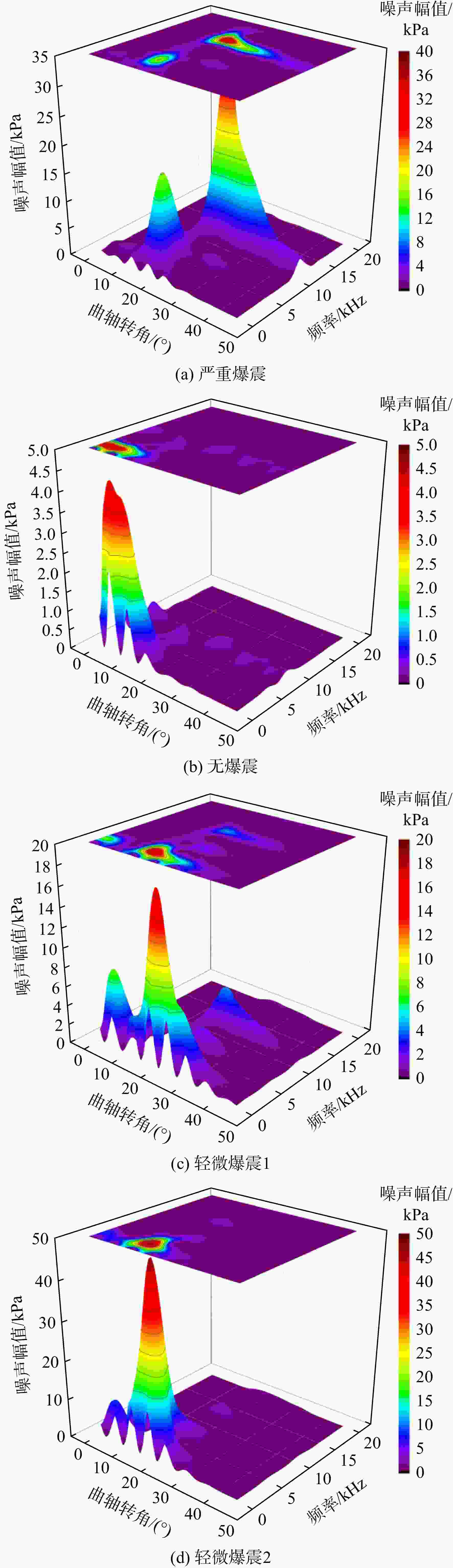
在活塞式航空煤油发动机上进行爆震试验研究,首先使用小波去噪对发动机缸压信号进行噪声提取,然后对0°~45°曲轴转角内的噪声信号进行快速傅里叶变换将一维时域噪声信号展开成二维时频域特征图,最后将特征图输入到训练好的卷积神经网络(convolutional neural networks, CNN)中进行爆震识别。验证结果表明:轻微和严重爆震都会在10°~30°曲轴转角内产生幅值较大噪声信号,与无爆震循环的时频域特征图有明显区别;在爆震特征提取上小波去噪要优于带通滤波,在爆震特征识别上CNN方法要优于支持向量机(support vector machine, SVM)方法;小波去噪和CNN结合的爆震识别方法对发动机4种不同运行工况的爆震识别准确率都能达到91%以上;小波去噪结合CNN方法对爆震循环的查准率为83.16%,查全率高达98.79%,能够准确地识别出发动机的爆震循环。
Abstract:Based on the method of wavelet domain denoising, the noise signals from in-cylinder pressure were extracted, at crank angle of 0°—45°, fast Fourier transform was used for simultaneous analysis of the noise signal in the time and frequency domains, then the feature map was outputted. The map was inputted into convolutional neural network (CNN) for identifying different features in order to distinguish non-knock and knock. The knock test was conducted on a direct injection engine fueled with aviation kerosene. The result revealed that: the time-frequency map was significantly different between knock and non-knock, because slight knocking and severe knocking both produced large-amplitude noise signals within crank angle of 10°—30°. Wavelet denoising was better than bandpass filtering in knocking feature extraction, while CNN was better than Support Vector Machine (SVM) in knocking feature recognition; under four different operating conditions, the knock recognition accuracy was all over 91% by wavelet domain denoising combining with CNN method; the precision and recall of the knock were 83.16% and 98.79%, respectively.
-
表 1 单缸活塞式航空煤油发动机试验参数
Table 1. Test parameters of single cylinder piston aviation kerosene engine
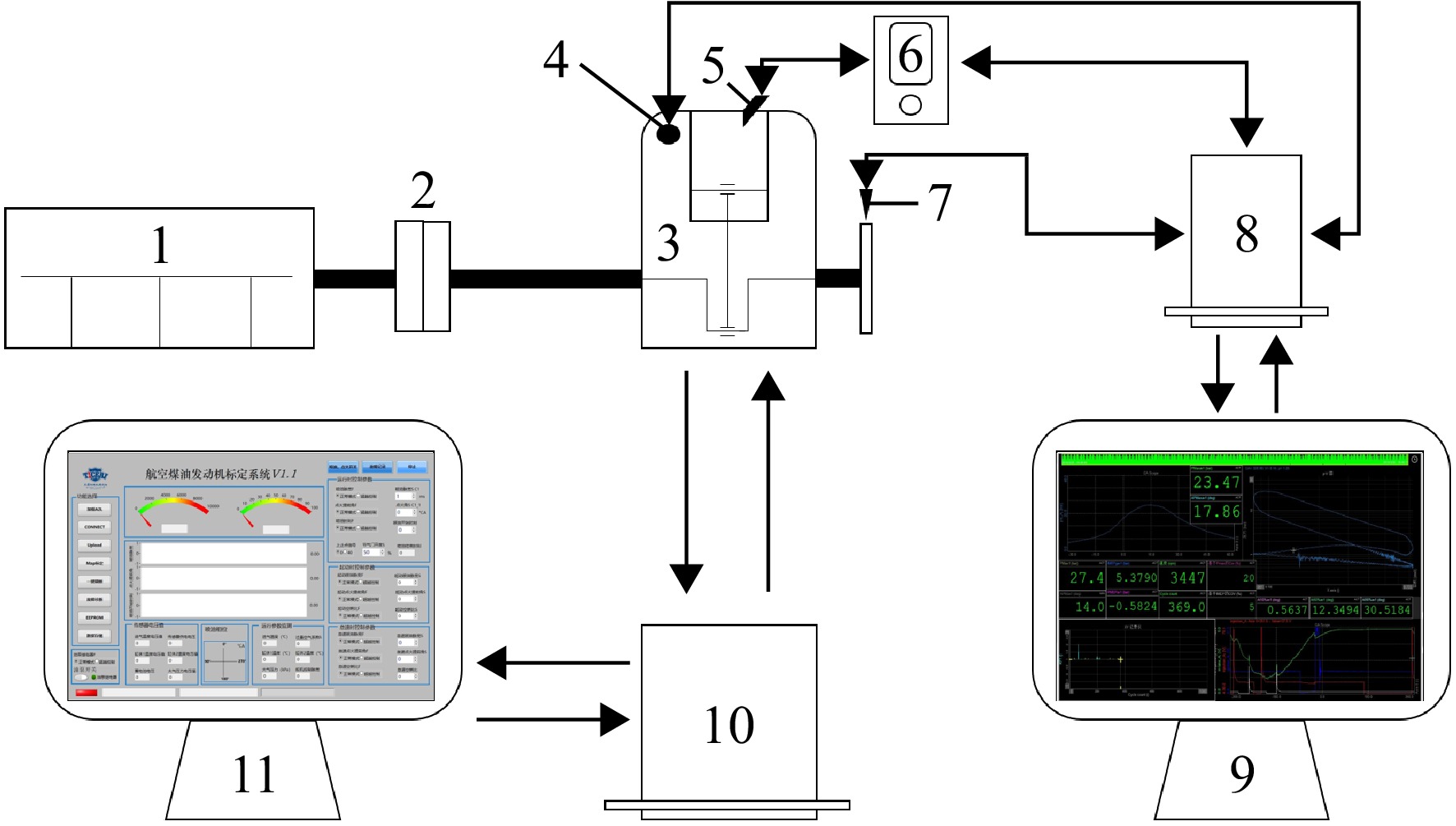
参数 数值或说明 排量/L 0.65 缸径/mm 100 连杆长度/mm 142.56 行程/mm 83 压缩比 9 气门数 2 活塞顶端形状 偏心球形 喷油方式 低压空气辅助直喷 冷却方式 缸头水冷、缸体风冷 表 2 发动机爆震试验典型工况参数
Table 2. Typical working parameters of engine knock test
参数 数值 转速/(r/min) 3500 节气门开度/% 30 点火提前角/(°) 27-39 喷油提前角/(°) 60 过量空气系数 1.0 冷却水温度/℃ 80 表 3 典型工况下爆震情况
Table 3. Knock situation under typical operating conditions
转速/(r/min) 点火提前角/(°) 循环数 爆震数 爆震率/% 3500 27 370 22 5.95 30 367 54 14.71 33 342 133 38.89 36 340 200 58.82 39 338 180 53.25 表 4 CNN架构
Table 4. CNN architecture
层 核大小 输出大小 参数说明 输入层 (450, 100, 1) 卷积层 2×2 (446, 96, 64) ReLU+SAME 池化层 2×2 (223, 48, 64) vaild 卷积层 3×3 (221, 46, 128) ReLU+SAME 池化层 2×2 (110, 23, 128) vaild 卷积层 3×3 (108, 21, 256) ReLU+SAME 池化层 2×2 (54, 10, 256) vaild 展开层 138240 密集层 128 ReLU Dropout 128 50% 密集层 64 ReLU Dropout 64 50% 密集层 32 ReLU Dropout 32 50% 输出层 2 softmax 表 5 测试工况参数说明
Table 5. Test condition parameter description
组别 点火提前角/(°) 转速/(r/min) 节气门开度/% 循环数 爆震数 爆震率/% 第1组 30 2500 20 324 58 17.9 第2组 4500 40 328 60 18.29 第3组 33 2500 20 391 117 29.92 第4组 4500 40 359 178 49.58 表 6 不同分类模型的识别正确率结果对比
Table 6. Comparison of recognition accuracy results of different classification models
模型 正确率/% 第1组 第2组 第3组 第4组 CNN a 93.2 94.21 91.3 95.82 b 87.65 88.11 88.23 87.74 SVM a 80.86 81.1 75.7 76.6 b 79.01 78.05 73.66 74.37 -
[1] 宗培越,胡春明,王书典. 活塞式航空煤油直喷发动机的爆震控制[J]. 航空动力学报,2018,33(3): 635-641. ZONG Peiyue,HU Chunming,WANG Shudian. Knocking control of direct injection piston-type aviation kerosene engine[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2018,33(3): 635-641. (in ChineseZONG Peiyue, HU Chunming, WANG Shudian. Knocking control of direct injection piston-type aviation kerosene engine[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2018, 33(3): 635-641. (in Chinese) [2] 周龙保. 内燃机学[M]. 3版. 北京: 机械工业出版社,2011. [3] 吴华堂. 船用天然气发动机爆震检测与控制技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学,2021. WU Huatang. Technology research on knock detection and control of marine natural gas engine[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University,2021. (in ChineseWU Huatang. Technology research on knock detection and control of marine natural gas engine[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2021. (in Chinese) [4] SHAHLARI A J,GHANDHI J B. A comparison of engine knock metrics[R]. Warrendale,US: Small Engine Technology Conference & Exhibition,2012. [5] 张力,康健,徐凤雏,等. 基于爆震因子统计特性的爆震燃烧识别方法[J]. 内燃机学报,2011,29(2): 152-156. ZHANG Li,KANG Jian,XU Fengchu,et al. Knock diagnosis based on statistical characteristics of knock factor[J]. Transactions of CSICE,2011,29(2): 152-156. (in ChineseZHANG Li, KANG Jian, XU Fengchu, et al. Knock diagnosis based on statistical characteristics of knock factor[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2011, 29(2): 152-156. (in Chinese) [6] 刘颖,陶建峰,黄武涛,等. 小波包能量与CNN相结合的滚动轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 机械设计与制造,2021(11): 127-131. LIU Ying,TAO Jianfeng,HUANG Wutao,et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on the combination of wavelet packet energy and CNN[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture,2021(11): 127-131. (in ChineseLIU Ying, TAO Jianfeng, HUANG Wutao, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on the combination of wavelet packet energy and CNN[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2021(11): 127-131. (in Chinese) [7] 韩璞. 基于振动信号的汽油机爆震特征提取与强度评价研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学,2014. HAN Pu. Research on gasoline engine knock feature extraction and intensity evaluation using vibration signal[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University,2014. (in ChineseHAN Pu. Research on gasoline engine knock feature extraction and intensity evaluation using vibration signal[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2014. (in Chinese) [8] WANG Xuezhong. Electronic radar signal recognition based on wavelet transform and convolution neural network[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal,2022,61(5): 3559-3569. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2021.09.002 [9] 盛立,徐西龙,王维波,等. 基于时频分析和卷积神经网络的微地震事件检测[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2021,45(5): 54-63. SHENG Li,XU Xilong,WANG Weibo,et al. Detection of microseismic events based on time-frequency analysis and convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science),2021,45(5): 54-63. (in ChineseSHENG Li, XU Xilong, WANG Weibo, et al. Detection of microseismic events based on time-frequency analysis and convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2021, 45(5): 54-63. (in Chinese) [10] 陈德昊,林建恒,衣雪娟,等. 基于小波包时频图特征和卷积神经网络的水声信号分类[J]. 声学技术,2021,40(3): 336-340. CHEN Dehao,LIN Jianheng,YI Xuejuan,et al. Classification of underwater acoustic signals based on time-frequency map features of wavelet packet and convolutional neural network[J]. Technical Acoustics,2021,40(3): 336-340. (in ChineseCHEN Dehao, LIN Jianheng, YI Xuejuan, et al. Classification of underwater acoustic signals based on time-frequency map features of wavelet packet and convolutional neural network[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2021, 40(3): 336-340. (in Chinese) [11] 陈妍伶,程良伦,吴衡,等. 基于小波系数图和卷积神经网络的太赫兹光谱物质识别[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2021,41(12): 3665-3670. CHEN Yanling,CHENG Lianglun,WU Heng,et al. A method of terahertz spectrum material identification based on wavelet coefficient graph[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2021,41(12): 3665-3670. (in ChineseCHEN Yanling, CHENG Lianglun, WU Heng, et al. A method of terahertz spectrum material identification based on wavelet coefficient graph[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(12): 3665-3670. (in Chinese) [12] PENG Cenxin,CHENG Wei,SONG Zihao,et al. A noise-robust modulation signal classification method based on continuous wavelet transform[C]//2020 IEEE 5th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference. Piscataway,US: IEEE,2020: 745-750. [13] BORG J M,SAIKALIS G,OHO S,et al. Knock signal analysis using the discrete wavelet transform[R]. Warrendale,US: SAE World Congress,2006. [14] 刘成材,高青,金英爱,等. 基于小波包分析提取汽油机爆震特征[J]. 内燃机学报,2012,30(2): 161-165. LIU Chengcai,GAO Qing,JIN Ying’ai,et al. Feature extraction in knocking detection of gasoline engine based on wavelet packet transform[J]. Transactions of CSICE,2012,30(2): 161-165. (in ChineseLIU Chengcai, GAO Qing, JIN Ying’ai, et al. Feature extraction in knocking detection of gasoline engine based on wavelet packet transform[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2012, 30(2): 161-165. (in Chinese) [15] 李宁,周瑞. 基于非线性小波变换的汽油机爆震强度识别[J]. 内燃机学报,2018,36(1): 83-89. LI Ning,ZHOU Rui. Knock intensity identification for a gasoline engine based on nonlinear wavelet transform[J]. Transactions of CSICE,2018,36(1): 83-89. (in ChineseLI Ning, ZHOU Rui. Knock intensity identification for a gasoline engine based on nonlinear wavelet transform[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2018, 36(1): 83-89. (in Chinese) [16] BORG J M,CHEOK K C,SAIKALIS G,et al. Wavelet-based knock detection with fuzzy logic[C]//CIMSA 2005 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Measurement Systems and Applications. Piscataway,US: IEEE,2005: 26-31. [17] CHO S,PARK J,SONG C,et al. Prediction modeling and analysis of knocking combustion using an improved 0D RGF model and supervised deep learning[J]. Energies,2019,12(5): 844. doi: 10.3390/en12050844 [18] PETRUCCI L,RICCI F,MARIANI F,et al. Engine knock evaluation using a machine learning approach[R]. Warrendale,US: Conference on Sustainable Mobility,2020. [19] MAURYA R K. Knocking and combustion noise analysis[M]//Reciprocating engine combustion diagnostics. Cham,Germany: Springer,2019: 461-542. [20] ZHEN Xudong,WANG Yang,XU Shuaiqing,et al. The engine knock analysis-an overview[J]. Applied Energy,2012,92: 628-636. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.11.079 [21] LEE J H,HWANG S H,LIM J S,et al. A new knock-detection method using cylinder pressure,block vibration and sound pressure signals from a SI engine[R]. Warrendale,US: SAE International Fuels and Lubricants Meeting and Exposition,1998. [22] 文莉,刘正士,葛运建. 小波去噪的几种方法[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2002,25(2): 167-172. WEN Li,LIU Zhengshi,GE Yunjian. Several methods of wavelet denoising[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science),2002,25(2): 167-172. (in ChineseWEN Li, LIU Zhengshi, GE Yunjian. Several methods of wavelet denoising[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2002, 25(2): 167-172. (in Chinese) [23] DONOHO D L. De-noising by soft-thresholding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,1995,41(3): 613-627. doi: 10.1109/18.382009 [24] JAIN S,CHAUHAN R. Handwritten digit recognition using DNN,CNN and RNN[C]//Advances in computing and data sciences: Second International Conference in Computing and Data Sciences. Dehradun,India: ICACDS,2018: 239-248. [25] MALLAT S G. A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,1989,11(7): 674-693. doi: 10.1109/34.192463 [26] 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社,2016. -








 下载:
下载: