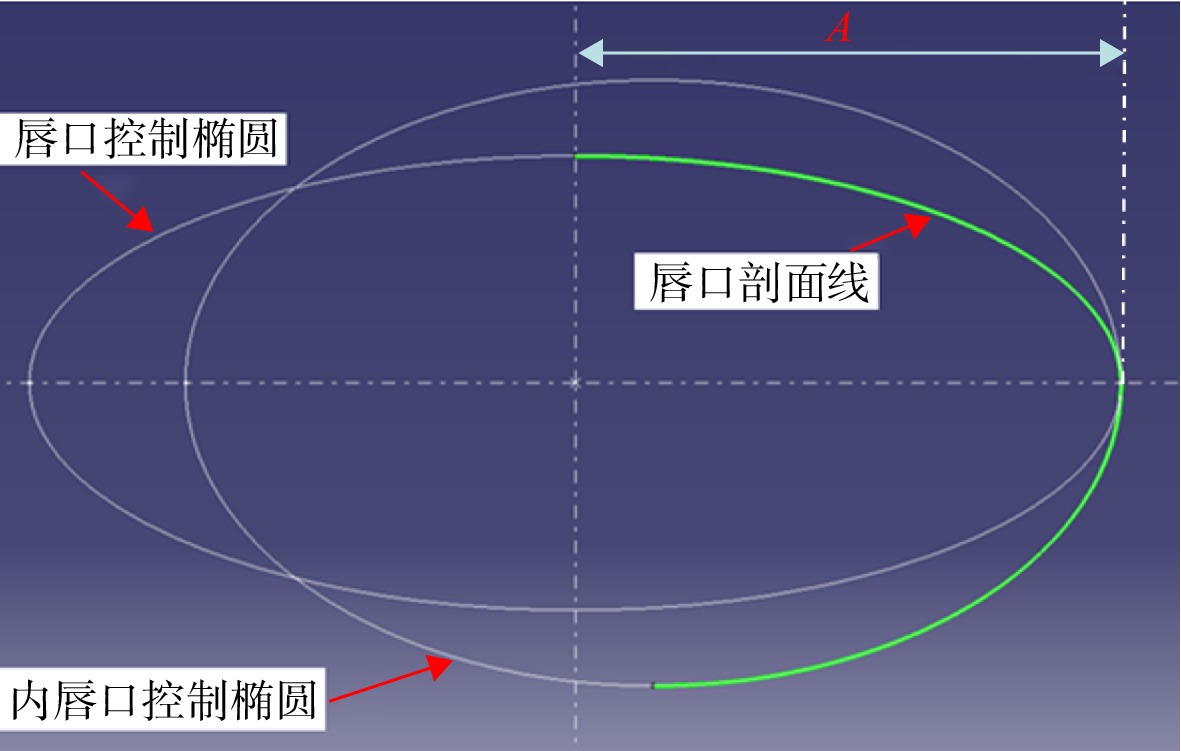
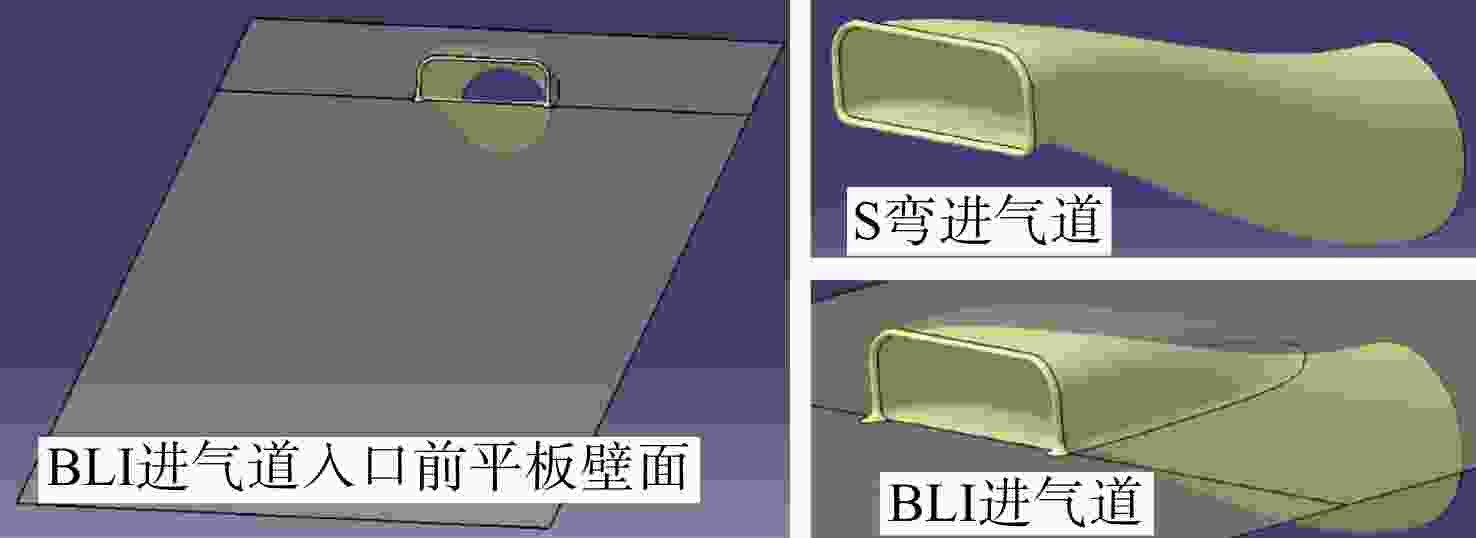
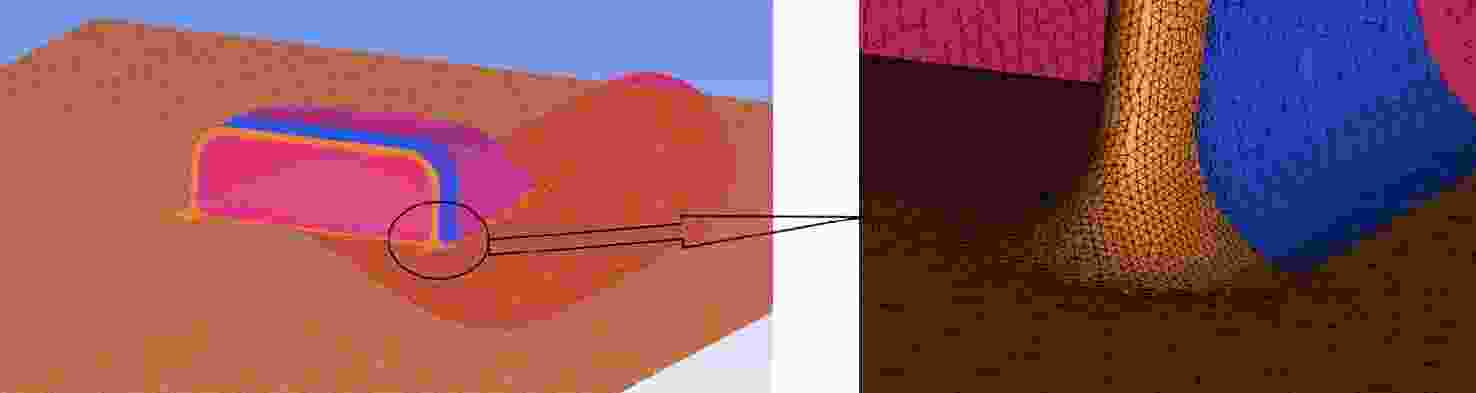
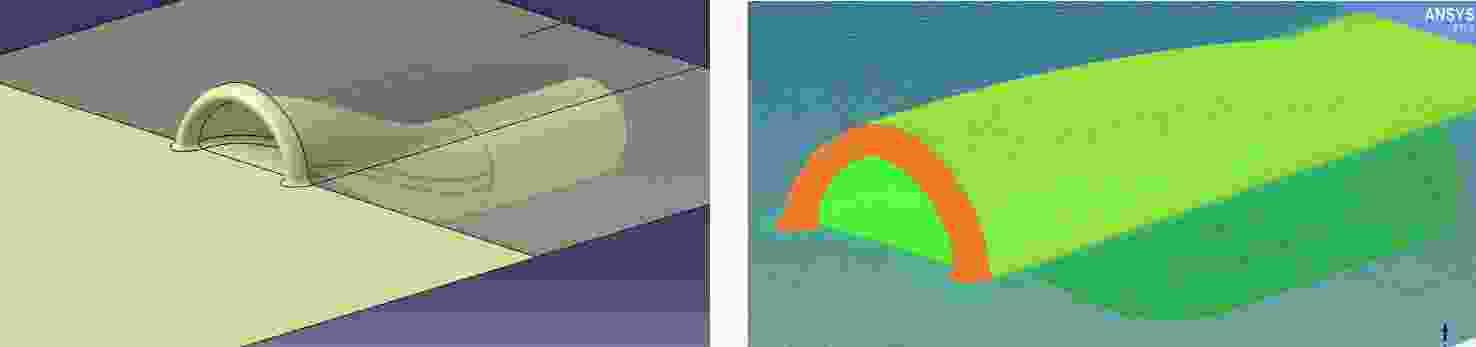
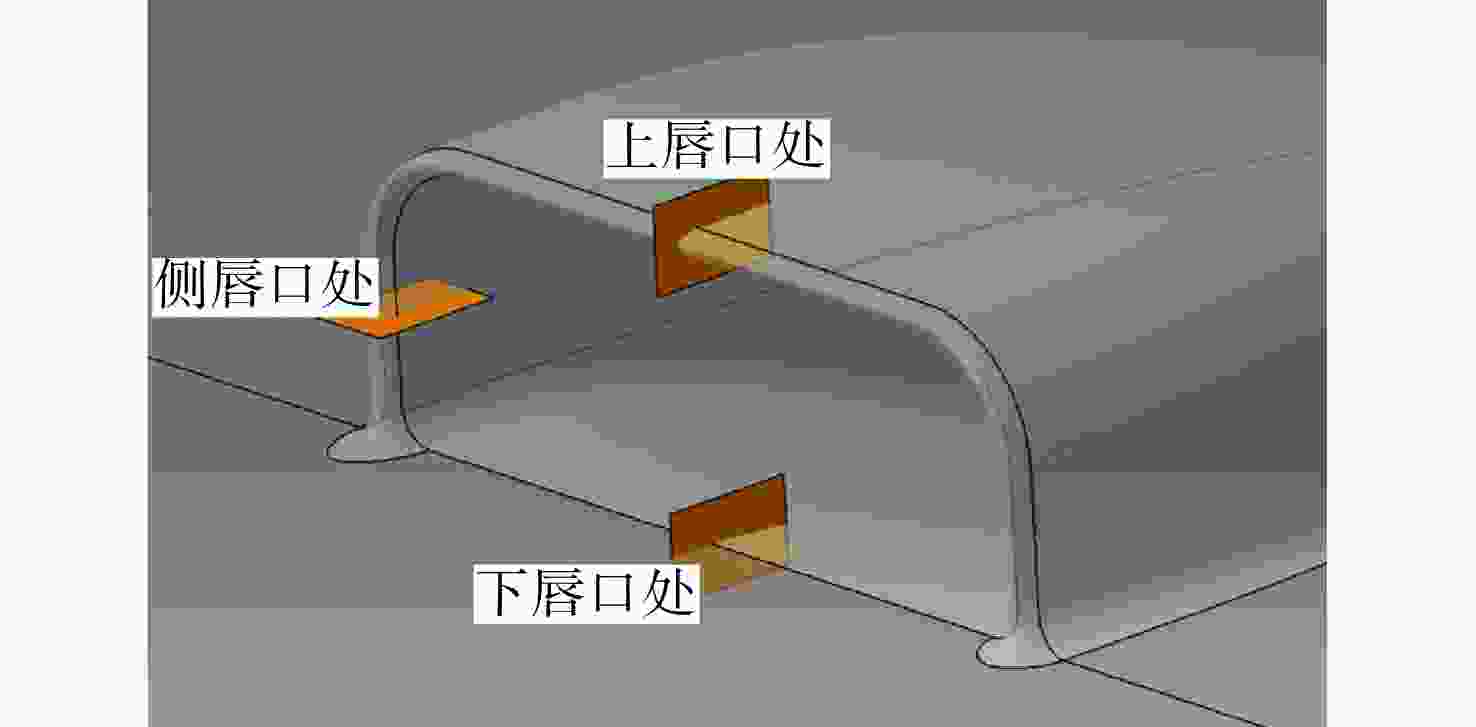
Flow losses characteristics of BLI inlet
-
摘要:
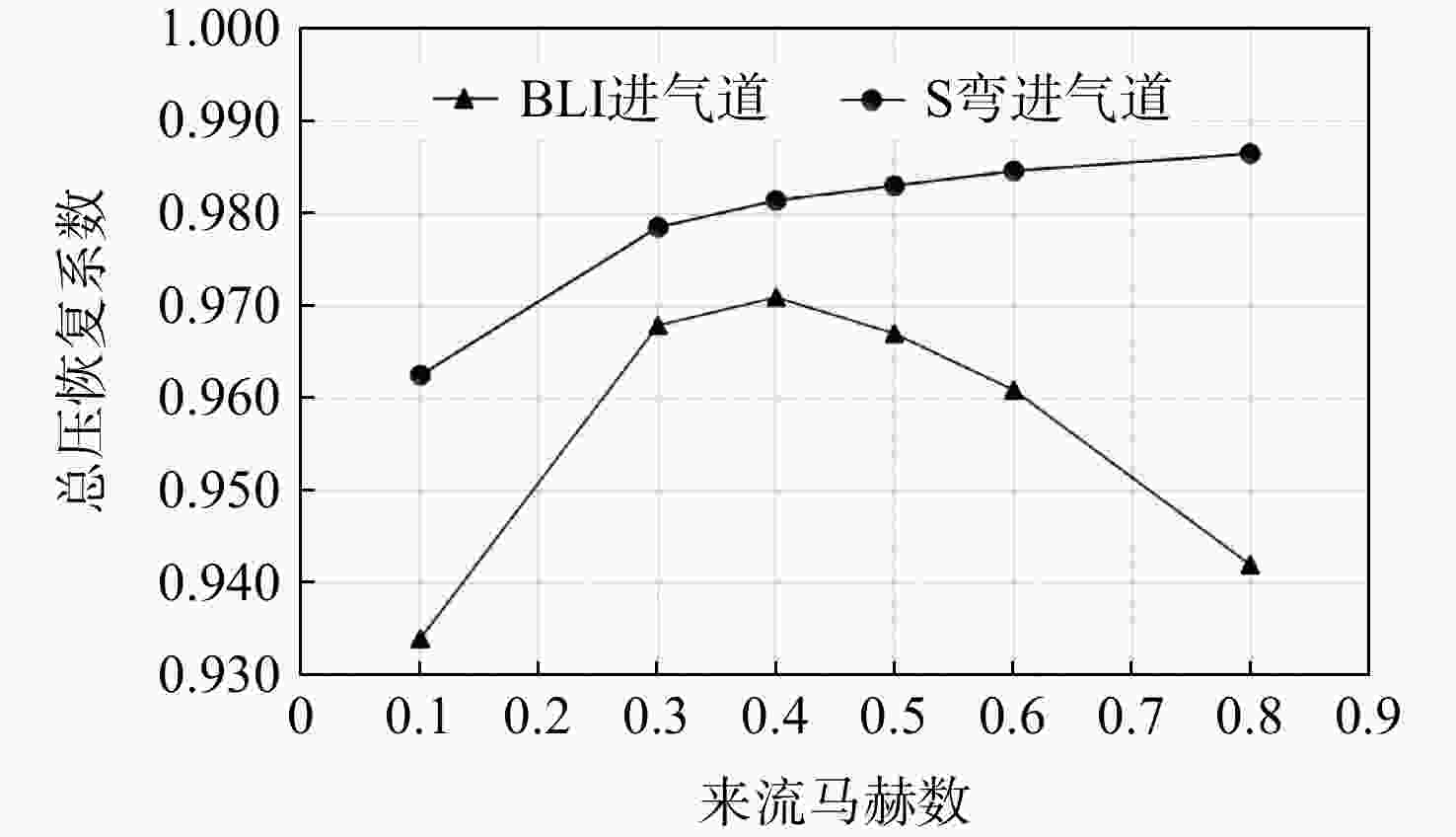
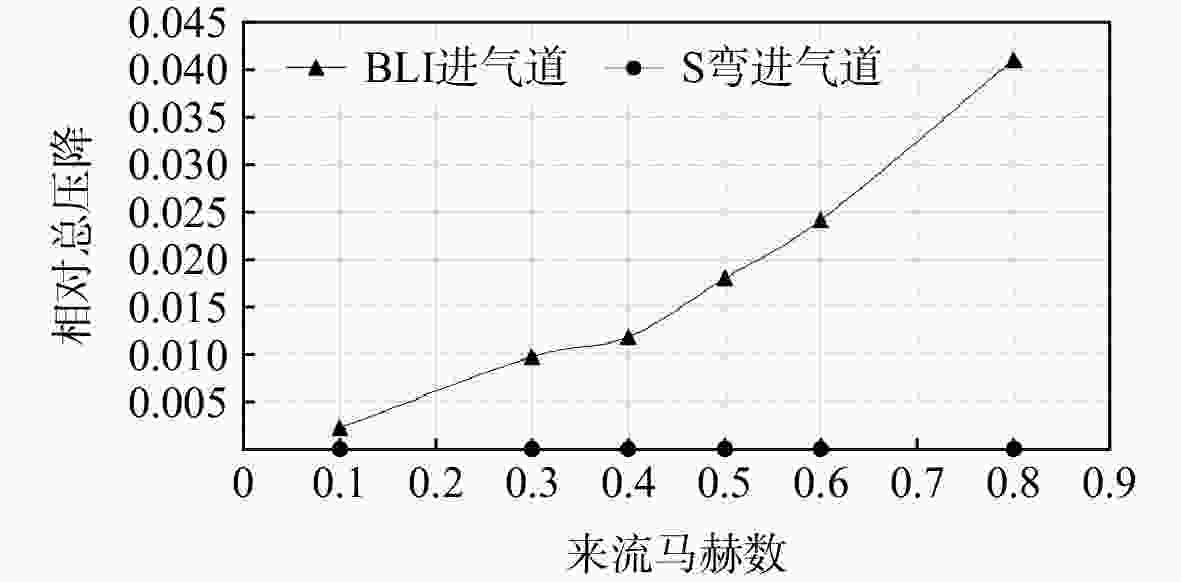
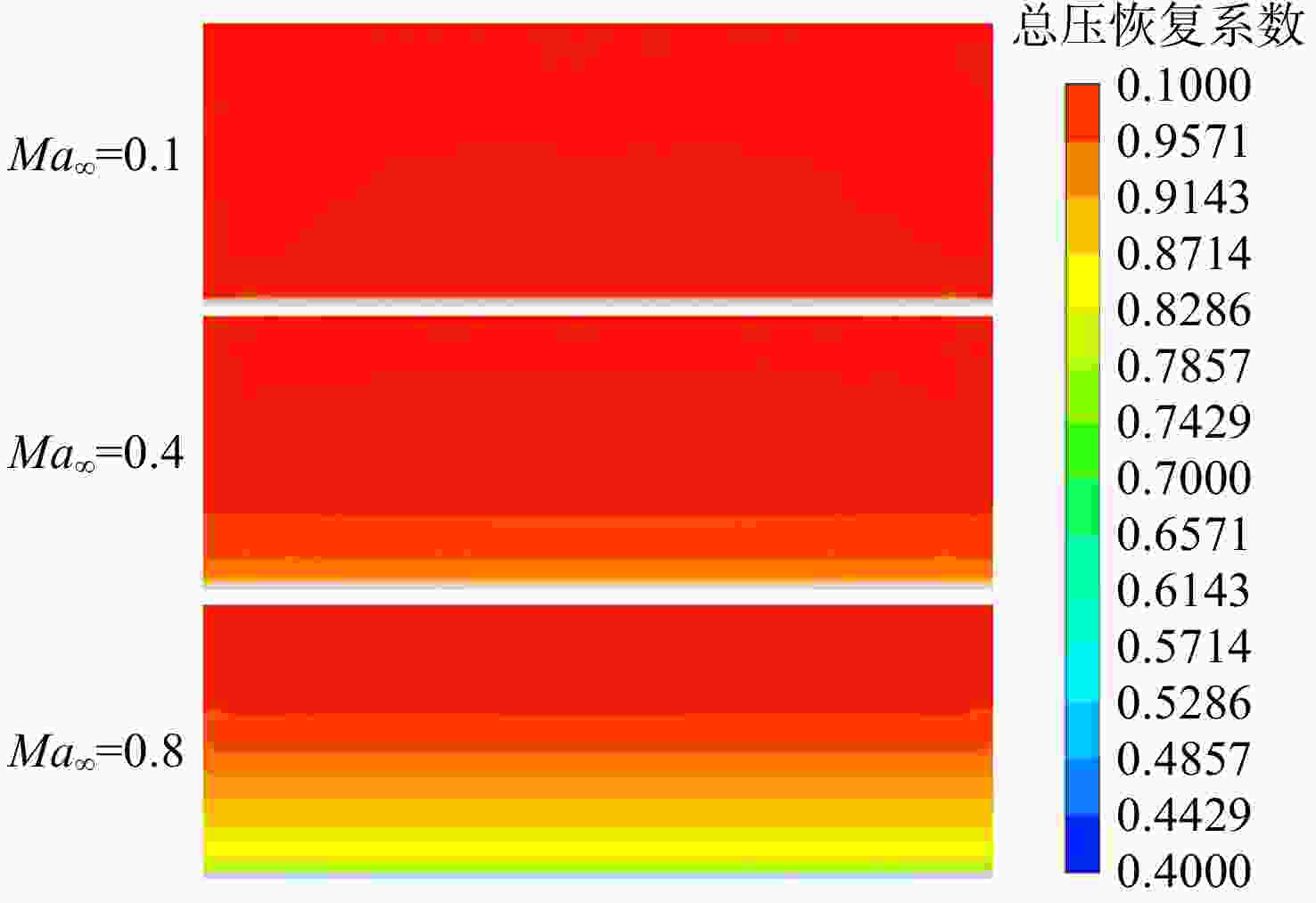
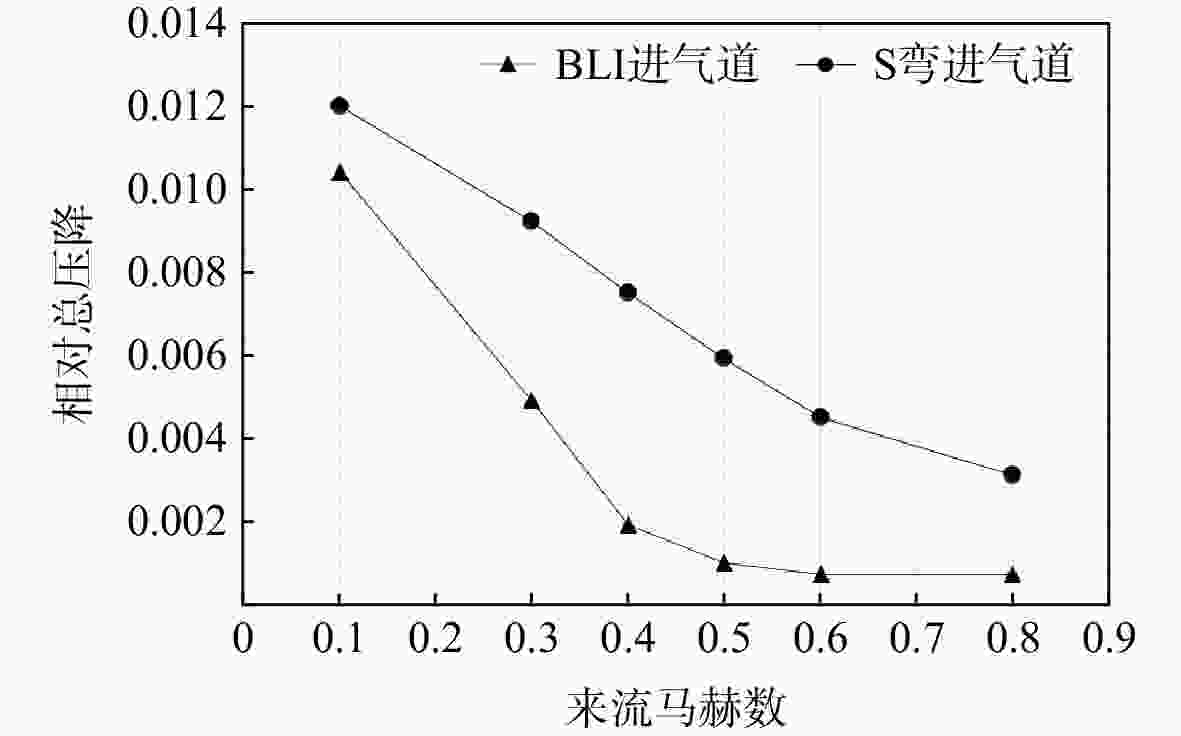
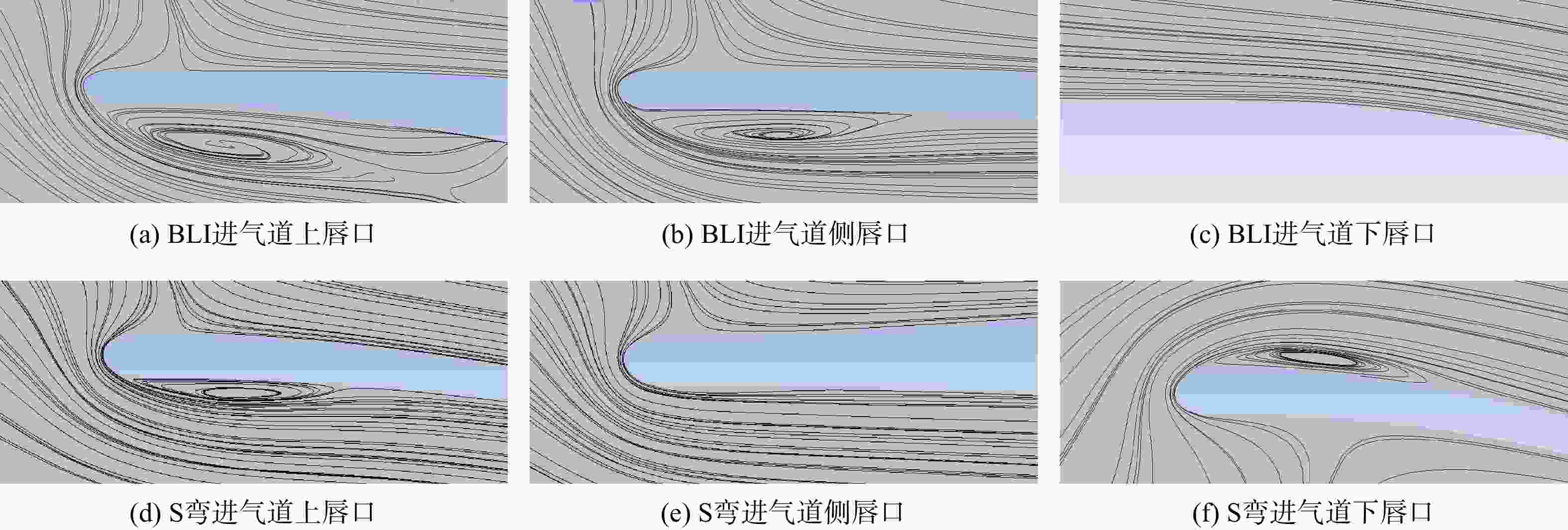
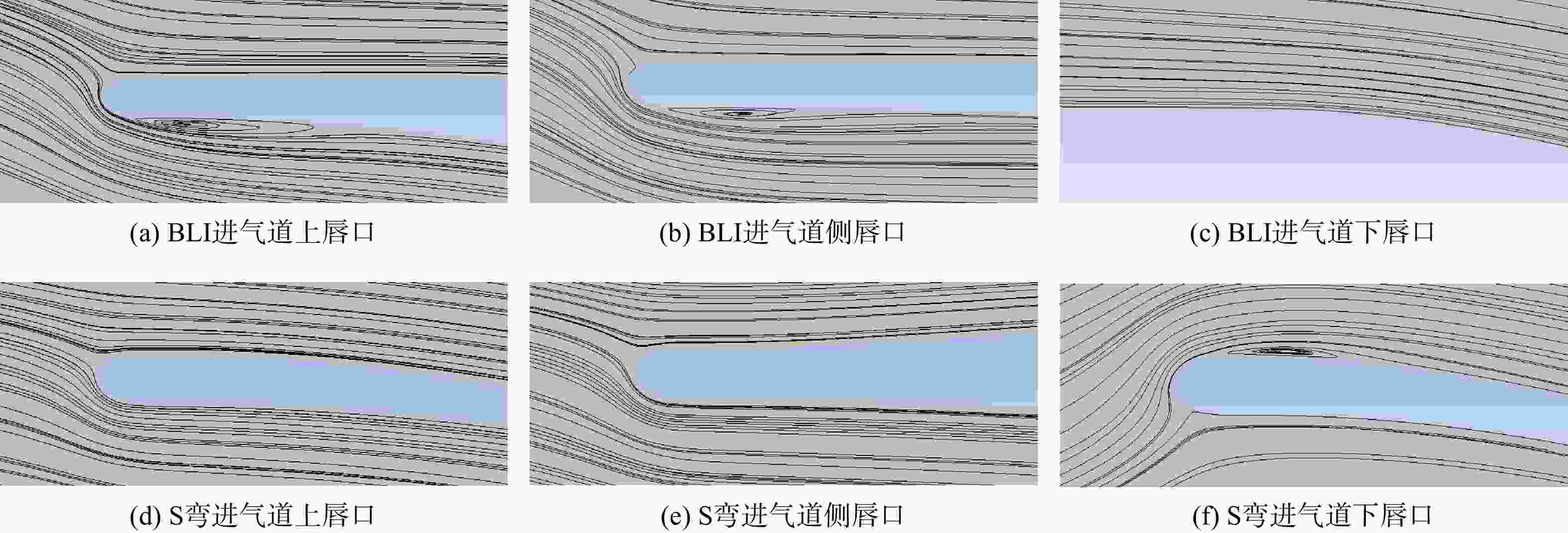
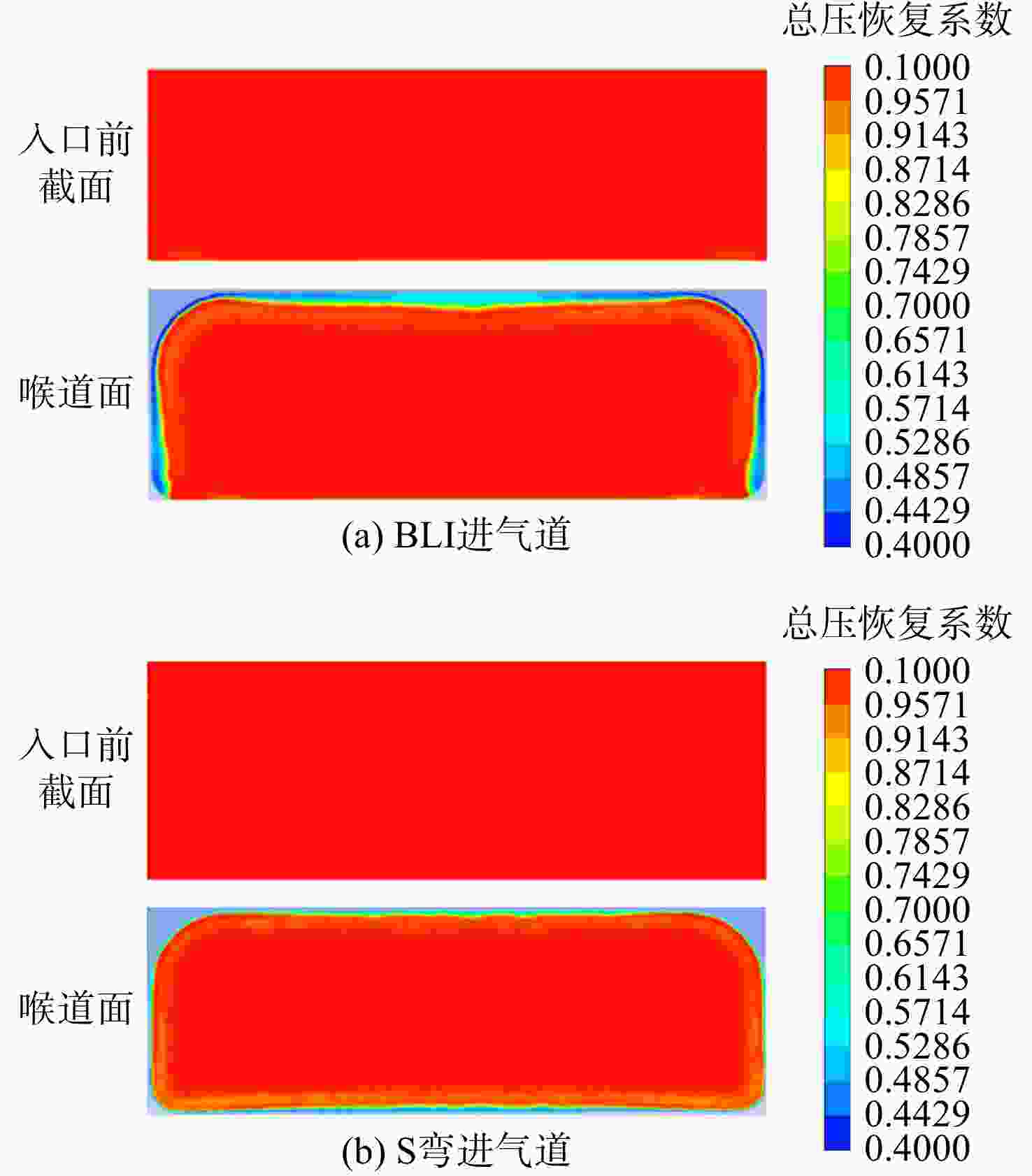
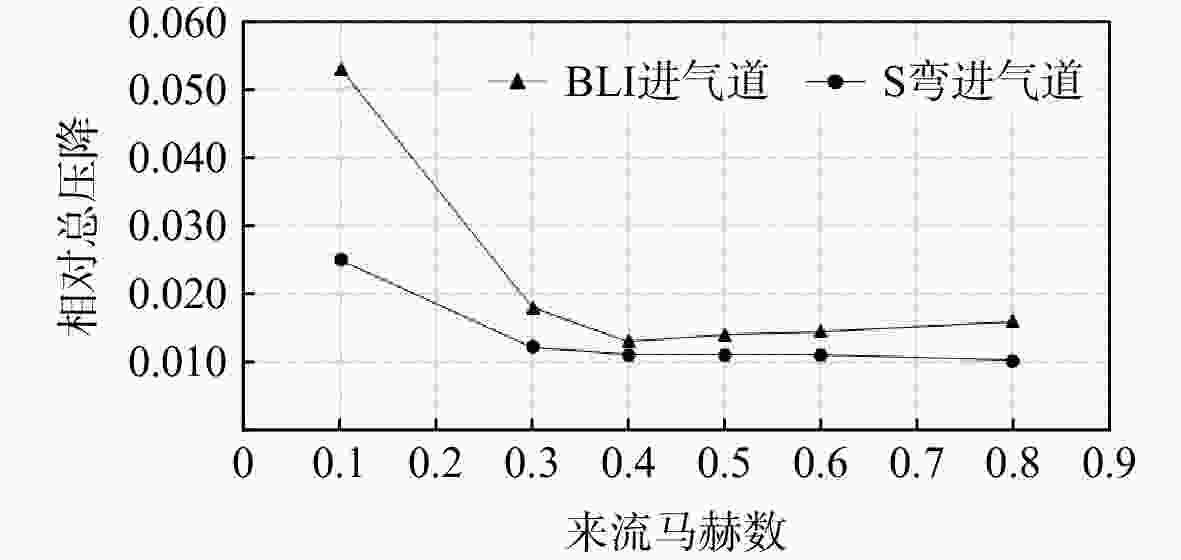
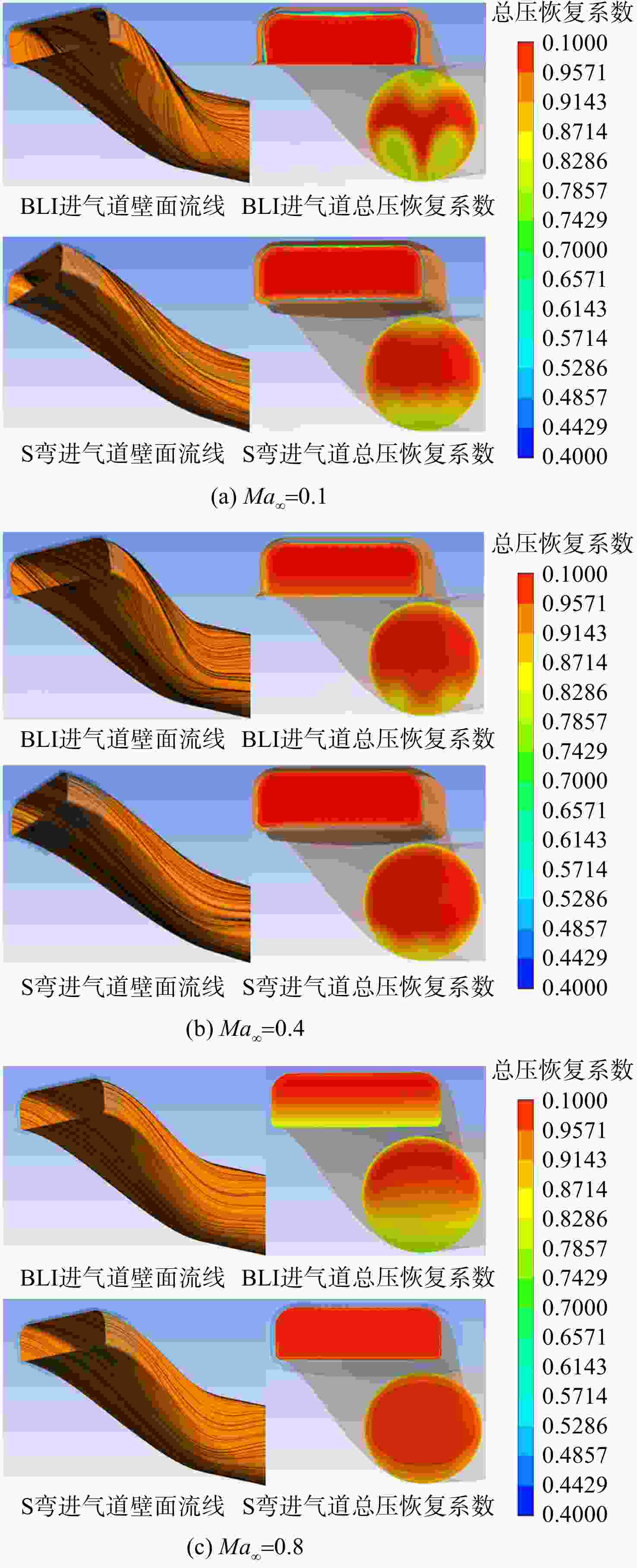
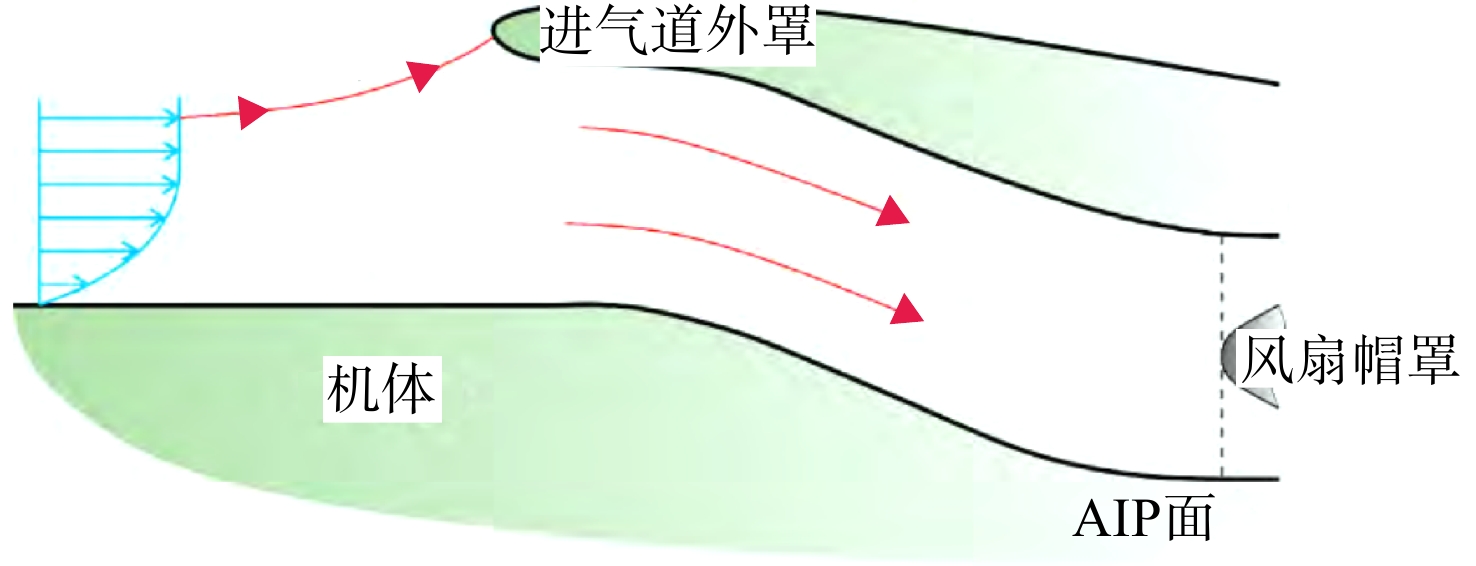
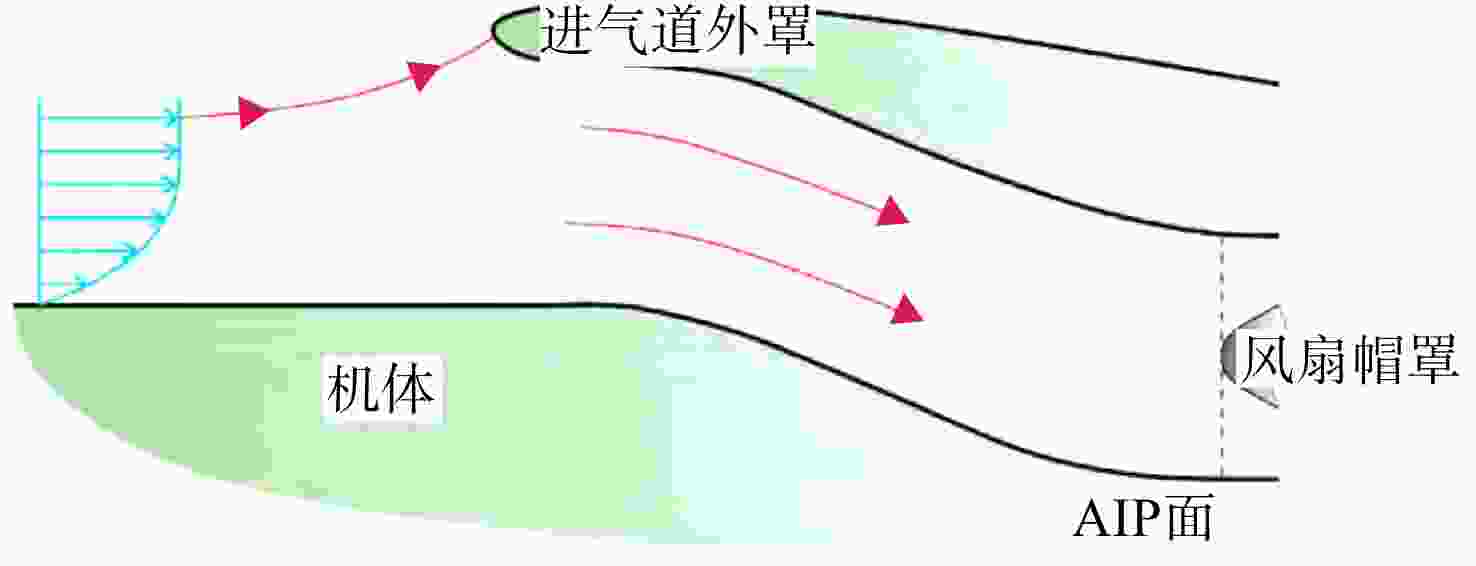
用数值仿真手段,对进气道内流总压损失采用逐段对比分析的方法,研究了附面层吸入式(BLI)进气道相对于常规S弯进气道的内流总压损失特性。结果表明:进气道出口马赫数不变,较低来流马赫数和较高来流马赫数工况下(方案对应马赫数0.3以下和马赫数0.6以上),BLI进气道产生的流动损失比常规S弯进气道的大,差量达2.4%;中等来流马赫数工况下(本文方案对应马赫数0.3与马赫数0.6之间),BLI进气道产生的流动损失比常规S弯进气道的略小,差量在0.3%以内;流动损失特性间的差异是由于BLI进气道进口前壁面与进口低能附面流改变了进口段流动特性、及在S弯管道内发展的综合作用结果。
-
关键词:
- 附面层吸入式(BLI)进气道 /
- S弯进气道 /
- 飞/发一体化 /
- 附面层 /
- 流动损失
Abstract:In order to study the difference and mechanism of the internal flow total pressure loss between the boundary layer ingestion (BLI) inlet and the conventional S-shaped inlet, numerical simulation method was applied and step-by-step comparative analysis of the total pressure loss was carried out. The results showed that, when fan-face Mach number was kept unchanged, the flow loss of BLI inlet was larger than that of the conventional S-shaped inlet under the working conditions of relatively lower and higher Mach number of free-stream (corresponding to below 0.3 or above 0.6), and the maximum difference was 2.4 percent. Under the working condition of medium Mach number of free-stream (corresponding to between 0.3 and 0.6), the flow loss generated by the BLI inlet was slightly smaller than that of the conventional S-shaped inlet, and the maximum difference was 0.3 percent. The combined effect of the fore-wall of the BLI inlet and the low-energy boundary flow changed the flow characteristics in the inlet and developed rapidly in the diffuser of the S-shaped pipeline, leading to the difference in flow loss characteristics.
-
表 1 网格无关性计算结果(
$M{a_\infty } = 0.4$ )Table 1. Results of mesh independent calculation (
$M{{{a}}_\infty } = 0.4$ )网格数量/104 进气道出口总压恢复系数 436 0.9796 672 0.9733 825 0.9715 1078 0.9712 -
[1] 林鹏,左林玄,王霄,等. 未来作战飞机飞发一体化技术的思考[J]. 航空动力,2018(2): 52-57.LIN Peng,ZUO Linxuan,WANG Xiao,et al. Discussion on aircraft/engine integration technology of future combat aircraft[J]. Aerospace Power,2018(2): 52-57. (in Chinese) [2] 梁彩云,谢业平,李泳凡,等. 飞/发性能一体化技术在航空发动机设计中的应用[J]. 航空发动机,2015,41(3): 1-5.LIANG Caiyun,XIE Yeping,LI Yongfan,et al. Application of integrated aircraft/engine technology in aeroengine designing[J]. Aeroengine,2015,41(3): 1-5. (in Chinese) [3] GOLDBERG C, NALIANDA D, PILIDIS P, et al. Installed performance assessment of a boundary layer ingesting distributed propulsion system at design point[R]. AIAA 2016-4800, 2016. [4] GOLDBERG C, NALIANDA D, PILIDIS P, et al. Performance assessment of a boundary layer ingesting distributed propulsion system at off-design[R]. AIAA 2017-5055, 2017 [5] 高为民. 飞发一体化设计的关键技术[J]. 航空动力,2018(2): 58-62.GAO Weimin. Key technology for aircraft/engine integration design[J]. Aerospace Power,2018(2): 58-62. (in Chinese) [6] 陈逖, 邱名, 江雄. 附面层吸入式推进系统研究进展[C]//2017年(第三届)中国航空科学技术大会论文集. 北京: 中国空气动力研究与发展中心计算空气动力研究所, 2017: 22-32. [7] OCHS S S, ILLMAN G, JOO J, et al. CFD-based analysis of boundary layer ingesting propulsion[R]. AIAA 2015-3800, 2015. [8] SMITH L H. Wakeingestion propulsion benefit[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power,1993,9(1): 74-82. doi: 10.2514/3.11487 [9] SMITH A,ROBERTS H E. The jet airplane utilizing boundary layer air for propulsion[J]. Journal of the Aeronautical Sciences,1947,14(2): 97-109. doi: 10.2514/8.1273 [10] LIEBECK R H, PAGE M A, RAWDON B K. Blended-wing-body subsonic commercial transport[R]. AIAA 1998-0438, 1998. [11] DAGGET D L, KAWAI R, FRIEDMAN D. Blended wing body systems studies: boundary layer ingestion inlet swith active flow control[R]. NASA/CR-203-2126-70, 2004. [12] LEE B J, KUMANO T, LIOU M S. Design explaration for vortex genarators for boundary-layer-ingesting inlet[R]. AIAA 2010-9399, 2010. [13] FLOREA R V, MATALANIS C, HARDIN L W, et al. Parametric analysis and design for embedded engine inlets[R]. AIAA 2012-3994, 2012. [14] BERRIER B L, CARTER M B. High Reynolds number investigation of a flush-mounted S-duct inlet with large amounts of boundary layer ingestion[R]. NASA/TP-2005-213766, 2005. [15] ANABTAWA A J, BLACKWELDER R F, LISSAMAN P B S. An experimental investigation of boundary layer ingestion in a diffusing S-duct with and without passive flow control[R]. AIAA 1999-0739, 1999. [16] LEE B J, KUMANO T, LIOU M S. Design exploration for vortex generators for boundary-layer-ingesting inlet[R]. AIAA 2010-9399, 2010. [17] 宁乐. BLI进气道流动特性的地面模拟方法和初步试验研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2016.NING Le. Ground-based simulation method for the flow characteristics of BLI inlet and preliminary experiment[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016. (in Chinese) [18] 达兴亚,范召林,熊能,等. 分布式边界吸入推进系统的建模与分析[J]. 航空学报,2018,39(7): 113-121.DA Xingya,FAN Zhaolin,XIONG Neng,et al. Modeling and analysis of distributed boundary layer ingesting propulsion system[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2018,39(7): 113-121. (in Chinese) [19] 陈建华. 附面层吸入式进气道主动流动控制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009.CHEN Jianhua. Investigation of active flow control in a boundary layer ingesting offset inlet[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009. (in Chinese) [20] 桑振坤. 半埋入式S弯进气道优化设计及主动流动控制技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009.SANG Zhenkun. Optimal design and active flow control of half flush-mounted S-duck inlet[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009. (in Chinese) [21] GRAY J S. Design optimization of a Boundary Layer Ingestion propulsor using a coupled aeropropulsive model[D]. Michigan, US: University of Michigan, 2018. [22] KIM H J, LIOU M S. Optimal inlet shape design of N2B hybrid wing body configuration[R]. AIAA 2012-3917, 2012 [23] ALLAN B, OWENS L, LIN J. Optimal design of passive flow control for a boundary-layer-ingesting offset inlet using design-of-experiments[R]. AIAA 2006-1049, 2006 [24] 赵鹤书, 潘杰元. 飞机进气道气动原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1989. [25] 姜正行. 飞机内流空气动力学[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 1989. [26] 周慧晨,谭慧俊,李湘萍. 复杂变截面进气道的一种设计方法[J]. 航空动力学报,2009,24(6): 1357-1363.ZHOU Huichen,TAN Huijun,LI Xiangping. Unique design method of subsonic inlet with complex cross-sectional shape[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2009,24(6): 1357-1363. (in Chinese) [27] 潘俊杰. S形进气道内流场特性及流动控制研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2014.PAN Junjie. Research on the flow field characteristics and flow control of S-shaped inlet[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014. (in Chinese) [28] HIRSCHEL E H, RIZZI A, BREITSAMTER C, et al. Separated and vortical flow in aircraft wing aerodynamics[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2021. [29] 吴国钊. 附面层理论[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 1989. [30] NICHOLS D A, VUKASINOVIC B, GLEZER A. Characterization and control of nacelle inlet flow in crosswind[R]. AIAA 2019-3685, 2019. -







 下载:
下载: