Phase transition characteristics of ice crystal particles in motion
-
摘要:
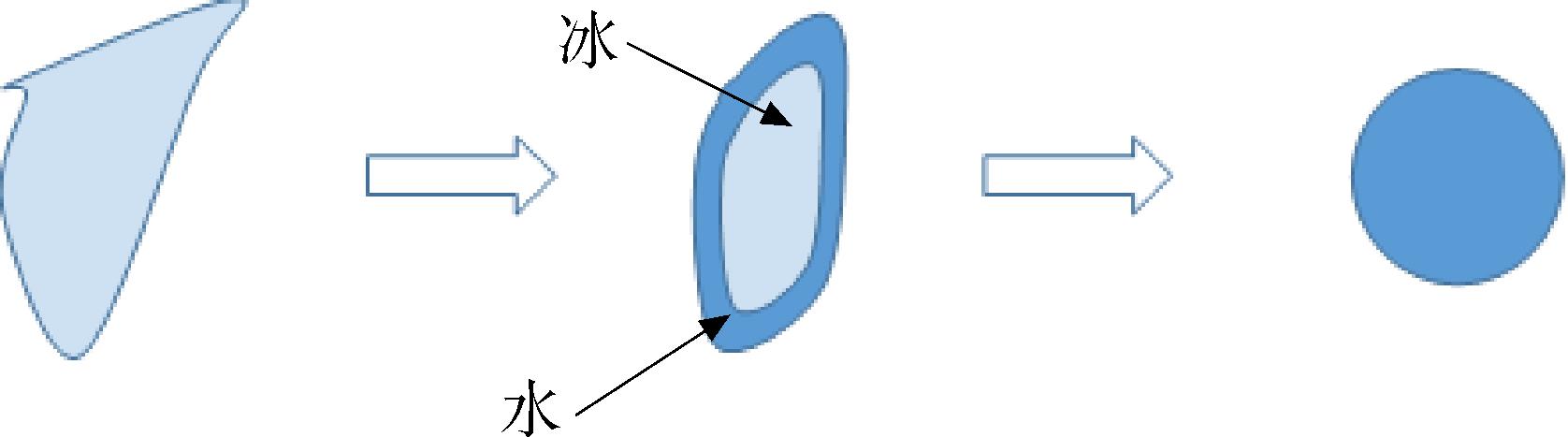
针对冰晶在温暖环境下运动时固液汽耦合的相变现象,基于欧拉法建立了冰晶粒子的运动相变模型和计算方法。计算了冰晶粒子在强迫对流环境下的融化相变过程,与实验结果对比验证了运动相变模型和计算方法的准确性。针对NACA0012翼型计算了冰晶绕流运动时的热力学特性,得到了冰晶粒子到达撞击表面时的融化状态与收集系数。研究了冰晶粒径大小、初始球形度、气流相对湿度和温度对运动相变的影响。结果表明:冰晶粒子运动相变模型可以有效地评估冰晶结冰风险,冰晶粒子的融化速率主要取决于粒子直径、球形度、气流温度、湿度等因素,环境温度为288 K时冰晶粒子的融化时间为27.5 s,而相同条件下环境温度为302 K时的融化时间仅有5.2 s。
Abstract:In view of the phase transition phenomenon of solid⁃liquid⁃vapor coupling when ice crystals moved in a warm environment,the phase transition model and calculation method of ice crystals were established based on Eulerian method.The melting phase transition processes of ice crystals under forced convection were calculated,and the comparison with the experimental results verified the accuracy of the movement phase transition model and calculation method.The thermodynamic characteristics of ice crystals moving around the NACA0012 airfoil were calculated,and the motion characteristics of ice crystals in a warm environment and the melting ratio were analyzed when they reached the impact surface.The influences of initial particle size,initial particle sphericity,air relative humidity and temperature on the movement phase transition were studied.The results showed that the ice crystal particle movement phase transition model can effectively evaluate the ice crystal icing risk,and the melting rate of ice crystal particles mainly counted on the particle diameter,sphericity,airflow temperature and humidity.When the air temperature was 288 K,the melting time of ice crystal particles was 27.5 s,while the melting time was only 5.2 s when the air temperature was 302 K under the same conditions.
-
Key words:
- ice crystal icing /
- two⁃phase flow /
- melting /
- phase transition /
- Eulerian method
-
表 1 Hauk实验条件
Table 1. Hauk's experimental conditions
算例 气流速度/(m/s) 气流温度/K 相对湿度/% 环境压力/Pa 初始温度/K 粒子球形度 粒径/μm 1 1 293.2 4 94 900 256.4 1 715 2 1 293.2 4 94 900 256.4 1 994 3 1 292.8 4 95 870 255.5 0.7 551 4 1 293.1 4 94 900 257 0.84 1 071 5 1.25 293.2 4 97 200 257 1 915 6 0.75 288.2 64 95 100 256.4 1 775 7 0.75 288.2 64 95 100 256.9 1 591 8 0.75 288.3 61 95 300 256 0.49 690 9 1 293.2 75 94 900 256.2 1 1 013 10 1 293.2 75 94 900 256.5 1 978 11 1 293.2 78 95 600 257.9 0.78 1 013 -
[1] MASON J G,STRAPP J W,CHOW P.The ice particle threat to engines in flight[R].AIAA 2006⁃206,2006. [2] 陈光.GEnx 发动机结冰问题初探[J].国际航空,2014(2):72⁃73.CHEN Guang.Discussion on GEnx engine icing[J].International Aviation,2014(2):72⁃73.(in Chinese) [3] MASON J G,CHOW P,FULEKI D M.Understanding ice crystal accretion and shedding phenomenon in jet engines using a rig test[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2011,133(4):1⁃8. [4] 刘增承.关于发动机内部结冰的探讨[R].北京:全国飞行技术和飞行安全研讨会,2000. [5] CURRIE T C,STRUK P M,TSAO J C,et al.Fundamental study of mixed⁃phase icing with application to ice crystal accretion in aircraft jet engines[R].AIAA 2012⁃2035,2012. [6] CURRIE T C,FULEKI D,MAHALLATI A.Experimental studies of mixed⁃phase sticking efficiency for ice crystal accretion in jet engines[R].AIAA 2014⁃3049,2014. [7] STRUK P M,BARTKUS T,TSAO J C,et al.Ice accretion measurements on an airfoil and wedge in mixed⁃phase conditions[R].SAE Paper 2015⁃01⁃2116,2015. [8] CURRIE T C,FULEKI D.Experimental results for ice crystal icing on hemispherical and double wedge geometries at varying mach numbers and wet bulb temperatures[R].AIAA 2016⁃3740,2016. [9] LIBBRECHT K G.The physics of snow crystals[J].Reports on Progress in Physics,2005,68(4):855⁃895. [10] HAUK T,ROISMAN I V,TROPEA C D.Investigation of the melting behaviour of ice particles in an acoustic levitator[R].AIAA 2014⁃2261,2014. [11] HAUK T,BONACCURSO E,VILLEDIEU P,et al.Theoretical and experimental investigation of the melting process of ice particles[J].Journal of Thermophysics & Heat Transfer,2016,30(4):946⁃954. [12] HAUK T.Investigation of the impact and melting process of ice particles[D].München,Germany:Technische Universität Darmstadt,2016. [13] AYAN E,OZGEN S,MURAT C,et al.Prediction of ice crystal accretion with TAICE[R].SAE Paper 2015⁃01⁃2148,2015. [14] GRIFT E,NORDE E,DER E,et al.Computational method for ice crystal trajectories in a turbofan compressor[R].SAE Paper 2015⁃01⁃2139,2015. [15] AOUIZERATE G,CHARTON V,BALLAND M,et al.Ice crystals trajectory calculations in a turbofan engine[R].AIAA 2018⁃4130,2018. [16] 卜雪琴,李皓,黄平,等.二维机翼混合相结冰数值模拟[J].航空学报,2020,41(12):200⁃210.BU Xueqin,LI Hao,HUANG Ping,et al.Numerical simulation of mixed phase icing on two⁃dimensional airfoil[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2020,41(12):200⁃210.(in Chinese) [17] IULIANO E,MONTREUI E,NORDE E,et al.Modelling of non⁃spherical particle evolution for ice crystals simulation with an Eulerian approach[R].SAE Paper 2015⁃01⁃2138,2015. [18] VILLEDIEU P,TRONTIN P,CHAUVIN R.Glaciated and mixed phase ice accretion modeling using ONERA 2D icing suite[R].AIAA 2014⁃2199,2014. [19] TRONTIN P,BLANCHARD G,VILLEDIEU P.A comprehensive numerical model for mixed⁃phase and glaciated icing conditions[R].AIAA 2016⁃3742,2016. [20] NORDE E,SENONER J M,VAN D,et al.Eulerian and Lagrangian ice⁃crystal trajectory simulations in a generic turbofan compressor[J].Journal of Propulsion and Power,2019,35(1):26⁃40. [21] NORDE E.Eulerian method for ice crystal icing in turbofan engines[D].Enschede,The Netherlands:University of Twente,2017. [22] GANSER G H.A rational approach to drag prediction of spherical and nonspherical particles[J].Powder Technology,1993,77(2):143⁃152. [23] MASON B J.On the melting of hailstones[J].Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society,1956,82(352):209‑216. [24] CROWE C T,SOMMERFELD M,TSUJI Y.Multiphase flows with droplets and particles[M].Boca Raton,US:CRC Press,2011. [25] SONNTAG D.Important new values of the physical constants of 1986,vapour pressure formulations based on the ITS⁃90,and psychrometer formulae[J].Zeitschrift für Meteorologie,1990,40(5):340⁃344. [26] 杨胜华,林贵平,申晓斌.三维复杂表面水滴撞击特性计算[J].航空动力学报,2010,25(2):284⁃290.YANG Shenghua,LIN Guiping,SHEN Xiaobin.Calculation of water droplet impact characteristics on three⁃dimensional complex surface[J].Journal of Aeronautical power,2010,25(2):284⁃290.(in Chinese) [27] 申晓斌,林贵平,杨胜华.三维发动机进气道水滴撞击特性分析[J].北京航空航天大学学报,2011,37(1):1⁃5.SHEN Xiaobin,LIN Guiping,YANG Shenghua.Analysis of water droplet impact characteristics in three⁃dimensional engine inlet[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2011,37(1):1⁃5.(in Chinese) -








 下载:
下载: