Modeling and analysis of mode conversion process for STOVL propulsion system
-
摘要:
在通过对离合器组件的动力学分析建立离合器动态性能计算模型的基础上,根据短距起飞/垂直降落(STOVL)推进系统各部件在不同工作状态下的耦合关系,建立了STOVL推进系统模式转换过程的共同工作方程组,即其动态性能仿真模型,并提出了STOVL推进系统短垂模式与常规模式相互转换的控制策略,对比了不同离合器接合速度下模式转换过程中的性能参数特点。结果表明:建立的仿真模型在模式转换过程中与国外文献数据相比最大误差为3.76%;提出的控制策略可保证模式转换过程中STOVL推进系统无超温、超转现象,且喘振裕度变化在0.1%以内;模式转换过程中离合器接合时间越短,其瞬时摩擦产热量越大,但总产热量越小。
-
关键词:
- 短距起飞/垂直降落(STOVL) /
- 离合器 /
- 升力风扇 /
- 动态性能 /
- 模式转换
Abstract:Based on the clutch dynamic performance calculation model established by the dynamic analysis of the clutch components, the co-working equations of STOVL propulsion system mode conversion process, namely its dynamic performance simulation model, were set up, according to the coupling relationship of short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL) propulsion system components in different working states. The control strategies for the conversion between STOVL mode and conventional mode were proposed, and the characteristics of the performance parameters during the conversion process under different clutch engagement speeds were compared. Results showed that the maximum error of the simulation model was 3.76% compared with the foreign research data in the process of mode conversion. In the process of mode conversion, the proposed control strategy can ensure that there was no overlimit of temperature and speed of STOVL propulsion system, and the surge margin change was less than 0.1%. In the process of mode conversion, the shorter clutch engagement time of mode conversion process, the greater instantaneous frictional heat generation, but the lower total heat generation.
-
Key words:
- short takeoff and vertical landing (STOVL) /
- clutch /
- lift fan /
- dynamic performance /
- mode conversion
-
表 1 STOVL推进系统平衡方程
Table 1. Equilibrium equations of STOVL propulsion system
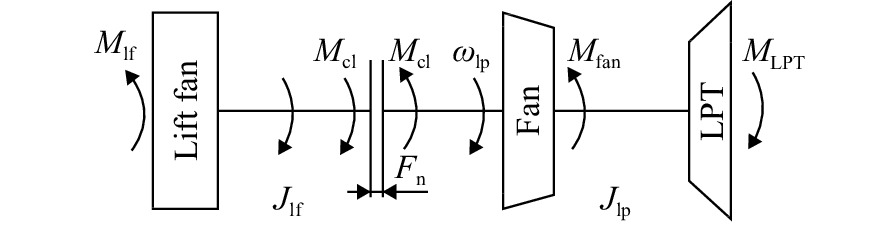
序号 离合器状态 滑动状态 锁定状态 1 ${q_{m,{\text{fan,in}}}} = {q_{m{\text{,fan,map}}}}$ 2 ${q_{m,{\text{com,in} } } } = {q_{m,{\text{com,map} } } }$ 3 ${q_{m,{\text{HPT,in} } } } = {q_{m,{\text{HPT,map} } } }$ 4 ${q_{m,{\text{LPT,in} } } } = {q_{m,{\text{LPT,map} } } }$ 5 ${p_{{\text{s,mixinner}}}} = {p_{{\text{s,mixouter}}}}$ 6 ${q_{m,{\text{nozz,in}}}} = {q_{m{\text{,nozz,cap}}}}$ 7 ${M_{ {\text{HPT} } } } = {M_{ {\text{com} } } } + {J_{ {\text{hp} } } }\dfrac{ { {\text{d} }{\omega _{ {\text{hp} } } } } }{ { {\text{d} }t} }$ 8 ${M_{ {\text{LPT} } } } = {M_{ {\text{fan} } } } + {M_{ {\text{cl} } } } + {J_{ {\text{lp} } } }\dfrac{ { {\text{d} }{\omega _{ {\text{lp} } } } } }{ { {\text{d} }t} }$ 9 ${q_{m{\text{,rollnozz,in}}}} = {q_{m,{\text{rollnozz,cap}}}}$ 10 ${q_{m{\text{,lf,in}}}} = {q_{m{\text{,lf,map}}}}$ 11 ${q_{m,{\text{lfnozz,in}}}} = {q_{m,{\text{lfnozz,cap}}}}$ 12 ${M_{ {\text{cl} } } } = {M_{ {\text{lf} } } } + {J_{ {\text{lf} } } }\dfrac{ { {\text{d} }{\omega _{ {\text{lf} } } } } }{ { {\text{d} }t} }$ 表 2 短垂模式地面静止工作点性能参数
Table 2. Performance parameters of ground static operating point in STOVL mode
参数 仿真结果 文献[18]数据 涡轮前温度/K 2197.7 2200 涵道比 0.645 0.645 巡航发动机推力/kN 78.1 78.1 升力风扇推力/kN 81.5 81.1 滚转喷管推力/kN 18.1 17.9 表 3 常规模式高空巡航工作点性能参数
Table 3. Performance parameters of high altitude cruising point in conventional mode
参数 仿真结果 文献[18]数据 涡轮前温度/K 2198.7 2200 涵道比 0.55 0.55 净推力/kN 64.5 65.0 -
[1] 郭捷,杨琳,郑宁,等. 短距/垂直起落战斗机升力风扇关键技术的探讨[J]. 航空科学技术,2008,20(2): 30-35.GUO Jie,YANG Lin,ZHENG Ning,et al. Investigation of critical technology for lift fan[J]. Aeronautical Science and Technology,2008,20(2): 30-35. (in Chinese) [2] 朱大明. F-35B/F135一体化控制系统[J]. 国际航空,2014,59(1): 66-68.ZHU Daming. Integration control system of F-35B/F135[J]. International Aviation,2014,59(1): 66-68. (in Chinese) [3] BEVILAQUA P. Inventing the F-35 joint strike fighter[R]. AIAA-2009-1650, 2009. [4] MADDOCK I, HIRSCHBERG M, HIRSCHBERG M, et al. The quest for stable jet borne vertical lift: ASTOVL to F-35 STOVL[R]. AIAA-2011-6999, 2011. [5] BEVILAQUA P. Future application of the JSF variable cycle[R]. AIAA-2003-2614, 2003. [6] GOEBEL J E. Design of a lift fan engine for a heavy lift aircraft[D]. Monterey, US: Naval Postgraduate School, 2003. [7] WIEGAND C. F-35 air vehicle technology overview[R]. AIAA-2018-3368, 2018. [8] WALKER G, ALLEN D. X-35B STOVL flight control law design and flying qualities[R]. AIAA-2002-6018, 2002. [9] 梁春华. F135发动机的升力风扇联轴器[J]. 航空发动机,2004,30(1): 39.LIANG Chunhua. Lift fan coupling of F135 engine[J]. Aeroengine,2004,30(1): 39. (in Chinese) [10] 郭健. 短距起飞/垂直降落战斗机发展及关键技术分析[J]. 飞机设计,2016,36(5): 19-28.GUO Jian. Analysis of development and key technique for short take off and vertical landing fighter[J]. Aircraft Design,2016,36(5): 19-28. (in Chinese) [11] COX C F. F-35B auxiliary air inlet analysis and design maturation[R]. AIAA-2013-0218, 2013. [12] WURTH S P. F-35 propulsion system integration, development and verification[R]. AIAA-2018-3517, 2018. [13] WALKER G P, FULLER J W, WURTH S P. F-35B integrated flight-propulsion control development[R]. AIAA-2013-4243, 2013. [14] BEVILAQUA P M. Joint strike fighter dual-cycle propulsion system[J]. Journal of propulsion and power,2005,21(5): 778-783. doi: 10.2514/1.15228 [15] BEVILAQUA P M. The shaft driven lift fan propulsion system for the joint strike fighter[R]. Virginia Beach, US: American Helicopter Society Annual, 1997. [16] 刘帅,王占学,蔡元虎,等. 升力风扇和涡扇发动机组合动力系统性能模拟与分析[J]. 航空动力学报,2013,28(5): 1095-1100.LIU Shuai,WANG Zhanxue,CAI Yuanhu,et al. Simulation and analysis of performance for combination of lift fan and turbofan engine power system[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2013,28(5): 1095-1100. (in Chinese) [17] ARNULFO L,PILIDIS P,YIN J,et al. Remote lift-fan engines[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers: Part G Journal of Aerospace Engineering,2001,215(3): 155-163. doi: 10.1243/0954410011533149 [18] VARELIS A. Variable cycle engine for combat STOVL aircraft[D]. Bedfordshire, UK: Cranfield University, 2007. [19] 任冰涛,李秋红,亢岚,等. 短距起飞/垂直降落发动机建模技术研究[J]. 航空动力学报,2015,30(10): 2531-2538.REN Bingtao,LI Qiuhong,KANG Lan,et al. Research of short take off and vertical landing engine modeling techniques[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2015,30(10): 2531-2538. (in Chinese) [20] 符大伟,张海波. 带升力风扇的垂直起降推进系统建模研究[J]. 推进技术,2018,39(3): 685-694.FU Dawei,ZHANG Haibo. Modeling of a STOVL propulsion system with a lift fan[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2018,39(3): 685-694. (in Chinese) [21] 袁长龙,李瑞军,顾嫄媛,等. 基于常规发动机发展STOVL推进系统的总体性能方案[J]. 燃气涡轮试验与研究,2019,32(2): 7-11,6.YUAN Changlong,LI Ruijun,GU Yuanhui,et al. General performance scheme of developing STOVL aircraft propulsion system based on conventional turbofan engine[J]. Gas Turbine Experiment and Research,2019,32(2): 7-11,6. (in Chinese) [22] 张海明,骆广琦,孟龙,等. STOVL型战斗机变循环发动机性能数值模拟[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版),2011,12(6): 13-17.ZHANG Haiming,LUO Guangqi,MENG Long,et al. Numerical simulation on performance of a variable cycle engine for STOVL fighter[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition),2011,12(6): 13-17. (in Chinese) [23] VISSER W P, BROOMHEAD M J. GSP a generic object-oriented gas turbine simulation environment[R]. ASME Paper 2000-GT-0002, 2000. [24] 张晓博,王占学,蔡元虎. 面向对象的航空发动机性能仿真系统研究[J]. 机械设计与制造,2010,48(11): 133-135.ZHANG Xiaobo,WANG Zhanxue,CAI Yuanhu. A study of object-oriented aero-engine performance simulation system[J]. Machinery Design and Manufacture,2010,48(11): 133-135. (in Chinese) [25] WALSH P P, FLETCHER P. Gas turbine performance[M]. Hoboken, US: John Wiley and Sons, 2004. [26] 廉筱纯, 吴虎. 航空发动机原理[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 2005. -








 下载:
下载: