Multi-objective optimization design of supersonic wind-tunnel nozzle cooling structure
-
摘要:
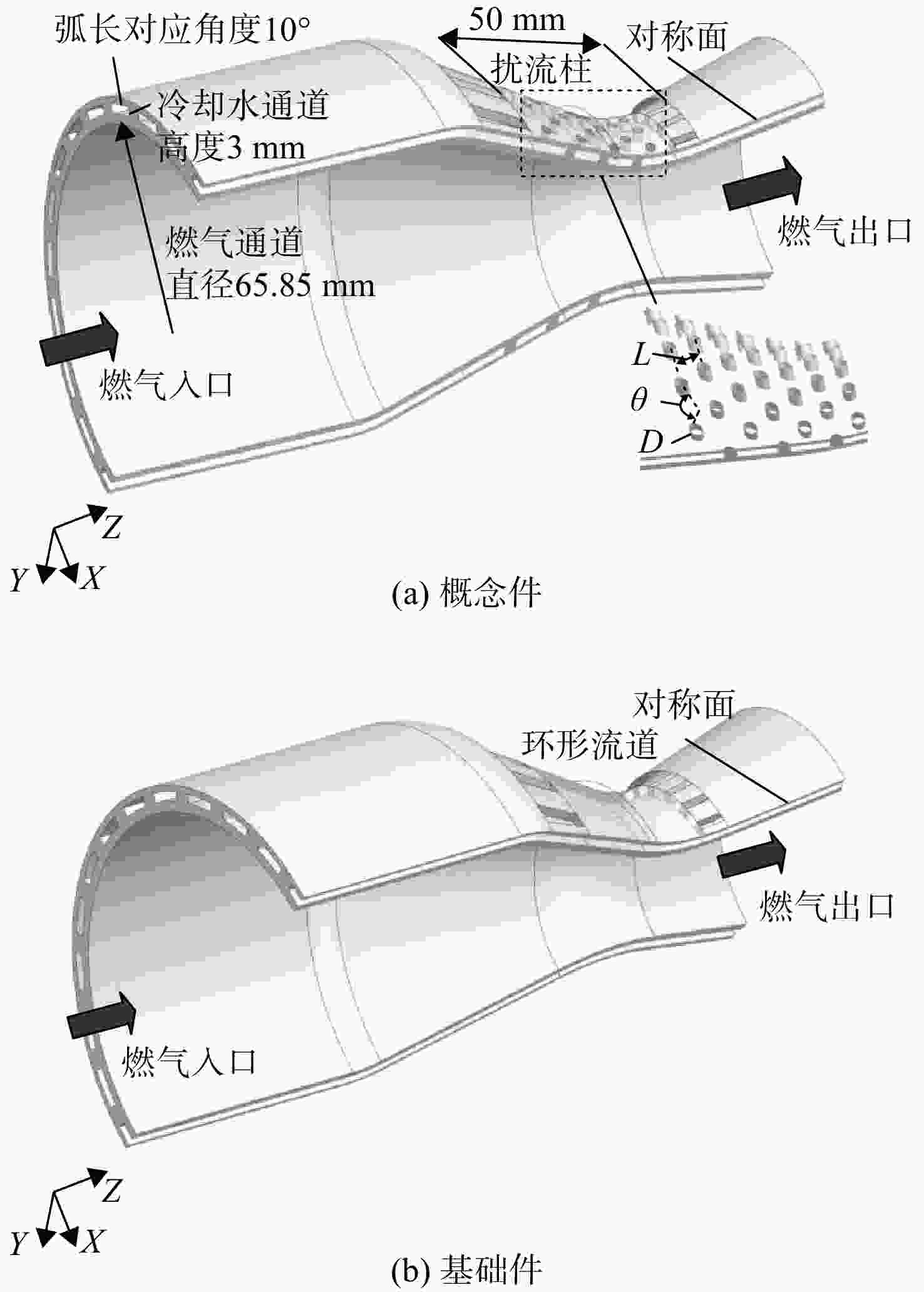
针对某风洞喷管提出了一种水冷结构,即在喷管前后段壁内设置了24组流道,而在喉部区域壁内错排布置扰流柱阵列。采用气热耦合-结构热分析的数值模拟方法对喷管整体结构的流动、换热、刚度性能进行了计算和分析。计算结果表明:冷却水量为1 kg/s时,与基础件相比,提出的冷却结构的概念件平均冷却效率提升0.68%,喉部等效应变减小5%左右。采用了响应面模型近似方法和多岛遗传算法对概念件进行了多目标优化计算,结果表明:冷却水量为2.1429 kg/s时,与概念件对比,优化件壁面最高温度可以降低1.6 K左右,喉部等效应变减小约10%。喷管冷却结构设计及其多目标优化方法为风洞喷管型面有效的热防护设计提供一定的参考。
-
关键词:
- 超声速风洞喷管 /
- 多流道冷却结构 /
- 气热耦合-结构热分析 /
- 多目标优化设计 /
- 响应面模型近似方法
Abstract:A cooling structure for nozzle of a wind tunnel was proposed, that is: 24 channels were set on walls of anterior and posterior segments of the nozzle while staggered pin-fin structure was set on wall of nozzle throat area. The numerical simulation method of the conjugated heat transfer-structural thermal analysis was used to calculate and analyze the fluid flow, heat transfer, and stiffness performances of the overall nozzle structure. The calculation results showed that under the cooling water mass flow rate of 1 kg/s, the averaged cooling efficiency of the proposed cooling structure of the conceptual nozzle was 0.68% higher than that of the basic structure, and equivalent elastic strain of throat area of the nozzle was reduced by around 5%. The response surface model approximation method and multi island genetic algorithm were used to perform multi-objective optimization calculation of the conceptual nozzle. The results showed that the maximum wall temperature of the optimized structure was about 1.6 K lower than that of the conceptual one under the cooling water mass flow rate of 2.142 9 kg/s, and equivalent elastic strain of throat area of the nozzle was reduced by around 10%. The cooling structure design of the nozzle and its multi-objective optimization method may provide a reference for an effective thermal protection design of nozzle of wind tunnel.
-
表 1 喷管气热耦合计算边界条件及其湍流模型
Table 1. Boundary conditions and turbulence model of the coupled heat transfer calculation for nozzle
参数 数值及说明 燃气入口压力/105 Pa 5.171 燃气入口温度/K 844.3 外壁面温度 式(1) 喷管出口 超声速出口 入口燃气密度/(kg/m3) 2.1306 燃气动力黏度 Sutherland方程 湍流模型 RNG k-ε 表 2 中心复合实验设计方案下气热耦合数值模拟计算结果
Table 2. Coupled heat transfer numerical simulation results of central composite experimental design schemes
运行序 Q/
(kg/s)θ/
(°)D/
mmL/
mmη Tmax/K f 1 2.75 20 3 6 0.8929 400.9 0.00452 2 2.75 15 3 6 0.8929 400.4 0.00425 3 2.75 15 5 6 0.8929 401.9 0.00460 4 2.75 10 3 6 0.8933 399.5 0.00432 5 5.00 15 3 6 0.8997 395.9 0.00399 6 2.75 15 3 5 0.8929 400.6 0.00427 7 2.75 15 3 7 0.8931 400.1 0.00391 8 0.50 15 3 6 0.8426 437.0 0.00525 9 2.75 15 3 6 0.8929 400.4 0.00425 10 2.75 15 1 6 0.8923 402.5 0.00381 11 5.00 20 5 5 0.8995 398.4 0.00435 12 2.75 15 3 6 0.8929 400.4 0.00425 13 2.75 15 3 6 0.8929 400.4 0.00425 14 0.50 20 5 7 0.8444 430.4 0.00541 15 5.00 10 1 5 0.8993 396.8 0.00388 16 0.50 10 5 5 0.8472 418.2 0.00525 17 0.50 10 1 7 0.8389 449.9 0.00539 18 5.00 10 5 7 0.8988 398.5 0.00576 19 0.50 20 1 5 0.8341 468.5 0.00506 20 5.00 20 1 7 0.8995 396.2 0.00319 21 0.50 20 5 5 0.8449 425.4 0.00553 22 5.00 10 1 7 0.8995 396.8 0.00377 23 0.50 10 1 5 0.8391 447.1 0.00584 24 5.00 10 5 5 0.8988 400.7 0.00486 25 2.75 15 3 6 0.8929 400.4 0.00425 26 5.00 20 5 7 0.8995 398.0 0.00398 27 2.75 15 3 6 0.8929 400.4 0.00425 28 0.50 20 1 7 0.8381 452.5 0.00456 29 5.00 20 1 5 0.8953 414.4 0.00347 30 0.50 10 5 7 0.8479 419.0 0.00614 表 3 拟合公式系数表
Table 3. Table of fitting formula coefficient
多项式
分项分项
系数系数值 η Tmax f 常数项 c0 8.19×10−1 4.57×102 3.13×10−3 x1 c1 3.71×10−2 −2.68×101 −8.14×10−4 x2 c2 −8.63×10−4 3.64×100 −1.15×10−4 x3 c3 4.00×10−3 −1.56×101 −4.27×10−4 x4 c4 1.58×10−3 −2.20×100 1.43×10−3 x12 c11 −4.35×10−3 3.25×100 8.34×10−5 x22 c22 −1.93×10−6 8.00×10−3 8.88×10−6 x32 c33 −1.27×10−4 5.50×10−1 2.96×10−6 x42 c44 −1.40×10−4 3.50×10−1 −1.04×10−4 x1·x2 c12 4.90×10−5 −1.58×10−1 −6.78×10−6 x1·x3 c13 −4.34×10−4 1.62×100 4.41×10−5 x1·x4 c14 1.02×10−5 −3.72×10−1 8.06×10−6 x2 x3 c23 3.44×10−5 −1.57×10−1 −8.36×10−7 x2·x4 c24 8.73×10−5 −3.87×10−1 −3.13×10−5 x3·x4 c34 −2.53×10−4 1.08×100 8.21×10−5 表 4 响应面模型拟合公式的精度
Table 4. Accuracy of response surface model fitting formula
响应参数 R2/% η 99.91 Tmax 97.77 f 93.05 表 5 喷管的流动换热性能对比
Table 5. Flow and heat transfer performances comparison of nozzle
流动换热指标 概念件 基础件 最高温度Tmax/K 416.0 426.7 平均冷却效率η 0.8716 0.8648 摩擦因数f 0.00479 0.00351 表 6 优化计算和仿真验算结果的比较
Table 6. Comparison of optimization calculation and simulation verification results
结果比较 输入参数 响应参数 Q/(kg/s) θ/(°) D/mm L/mm η Tmax/K f 优化件的优化计算结果 2.1429 10.0233 3.3222 5.8480 0.8850 401.8 0.00493 优化件的仿真验算结果 2.1429 10.0233 3.3222 5.8480 0.8896 401.4 0.00453 误差/% 0.52 0.10 8.11 概念件的仿真验算结果 2.1429 15 3 6 0.8890 403.0 0.00437 -
[1] MEYER O,NITSCHE W. Update on progress in adaptive wind tunnel wall technology[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences,2004,40(3): 119-141. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2004.02.001 [2] OWEN F K,OWEN A K. Measurement and assessment of wind tunnel flow quality[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences,2008,44(5): 315-348. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2008.04.002 [3] MUNGIGUERRA S,MARTINO G D D,SAVINO R,et al. Characterization of novel ceramic composites for rocket nozzles in high-temperature harsh environments[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2020,163: 120492.1-120492.18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.120492 [4] 范志鹏,徐惊雷,吕郑,等. 型面旋转变马赫数风洞喷管的优化设计[J]. 航空学报,2014,35(5): 1216-1225.FANG Zhipeng,XU Jinglei,LÜ Zheng,et al. Optimization design of variable mach number wind tunnel nozzle by rotating profile[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2014,35(5): 1216-1225. (in Chinese) [5] CHEN Pengfei,WU Feng,XU Jinglei,et al. Design and implementation of rigid-flexible coupling for a half-flexible single jack nozzle[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2016,29(6): 1477-1483. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2016.09.002 [6] 齐伟呈,徐惊雷,范志鹏,等. 马赫数2~4连续可调风洞数值模拟及静态标定试验[J]. 航空学报,2017,38(1): 86-94.QI Weicheng,XU Jinglei,FAN Zhipeng,et al. Numerical simulation and experimental calibration of continuously adjustable wind tunnel with Mach number 2 to 4[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2017,38(1): 86-94. (in Chinese) [7] LÜ Zheng. , XU Jinglei, WU Feng, et al. Design of a variable Mach number wind tunnel nozzle operated by a single jack[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology,2018,77: 299-305. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2018.03.011 [8] 金韶山,姜培学,孙纪国. 液体火箭发动机喷管发汗冷却研究[J]. 航空动力学报,2008,23(7): 1334-1340.JIN Shaoshan,JIANG Peixue,SUN Jiguo. Investigation on the transpiration cooling of a liquid rocket nozzle[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2008,23(7): 1334-1340. (in Chinese) [9] 金韶山. 液体火箭发动机推力室及钝体头锥发汗冷却研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2008.JIN Shaoshan. Research on transpiration cooling of liquid rocket thrust chamber and blunt nose cone[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2008. (in Chinese) [10] 张宏伟,陶文铨,何雅玲,等. 再生冷却推力室耦合传热数值模拟[J]. 航空动力学报,2006,21(5): 148-154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8055.2006.05.025ZHANG Hongwei,TAO Wenquan,HE Yaling,et al. Numerical study on coupled heat transfer of thrust chamber with regenerative cooling[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2006,21(5): 148-154. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8055.2006.05.025 [11] 康玉东,孙冰. 气壁镀镍和冷却剂入口对再生冷却的影响[J]. 航空动力学报,2010,25(12): 2834-2838.KANG Yudong,SUN Bing. Effects of hot-gas wall nickelage and cooling channel inflow on regenerative cooling[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2010,25(12): 2834-2838. (in Chinese) [12] RALF S,CHLOÉ G,CHRISTIAN M,et al. Design of a film cooled dual-bell nozzle[J]. Acta Astronautica,2019,158: 342-350. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.05.056 [13] MAYANK V,NITISH A,ASHOKE D. Investigation of flow characteristics inside a dual bell nozzle with and without film cooling[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology,2020,99: 105741.1-105741.14. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105741 [14] KIM K S,LEE S H,NGUYEN V Q,et al. Ablation characteristics of rocket nozzle using HfC-SiC refractory ceramic composite[J]. Acta Astronautica,2020,173: 31-44. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.03.050 [15] BACK L H, MASSIER P F, GIER H L. Convective heat transfer in a convergent-divergent nozzle[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 1964, 7(5): 549-568. [16] 何宁,杨海波,孙冬柏. 高温长时间风洞喷管冷却结构CFD研究[J]. 工程科学学报,2016,38(4): 568-574.HE Ning,YANG Haibo,SUN Dongbai. CFD study on nozzle cooling structure for a wind tunnel of high temperature and long operation time[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering,2016,38(4): 568-574. (in Chinese) [17] 黄祯君,张涛,王杰. 高焓高热流条件下半椭圆喷管冷却结构设计与分析[J]. 机械工程学报,2019,55(18): 157-164. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.18.157HUANG Zhenjun,ZHANG Tao,WANG Jie. Cooling structural design and thermodynamic analysis of semi-elliptic nozzle under high enthalpy and high heatflux conditions[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2019,55(18): 157-164. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.18.157 [18] PAL S, TUCKER K, LEHMAN M, et al. Experimental studies of the heat transfer to RBCC rocket nozzles for CFD application to design methodology[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd ASME/AIChE/ANS/AIAA National Heat Transfer Conference. Reston, US: AIAA, 1999: 168-177. [19] LIU Q Y,LUKE E A,CINNELLA P. Coupling heat transfer and fluid flow solvers for multidisciplinary simulations[J]. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer,2005,19(4): 417-427. doi: 10.2514/1.13522 -








 下载:
下载: