Analysis of mechanical properties of SiCp/Al composites based on three-dimensional random meso-model
-
摘要:
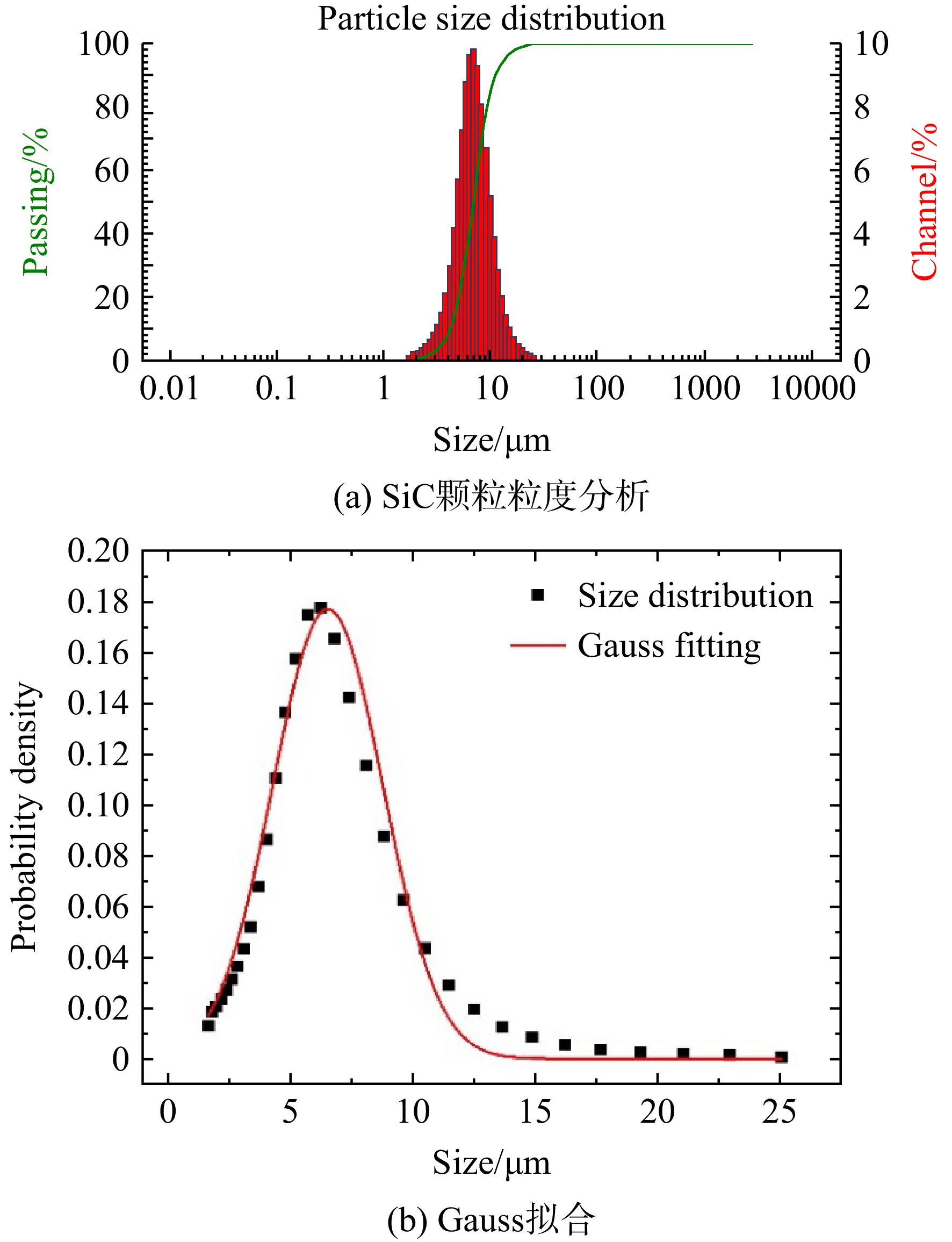
基于颗粒增强铝基复合材料的细观组成及结构特点,建立了考虑颗粒、基体、界面性能的三维随机细观颗粒增强复合材料分析模型和方法。在细观尺度上,分别采用立方颗粒、球形颗粒及三维随机多面体模型来表征颗粒的形状,根据颗粒原材料粒度分析获得的粒径分布数据,建立考虑颗粒空间分布的随机特性及粒径的概率分布特征的三维随机代表性体积单元。在Ludwik模型基础上考虑淬火硬化效应,描述铝基体的弹塑性本构关系,考虑了基体的韧性损伤、SiC颗粒的弹脆性破坏以及界面的拉伸-开裂行为,模拟了材料在单轴拉伸过程中的变形和损伤过程。开展SiCp/Al2009复合材料标准件的单轴拉伸试验验证,结果表明:弹性模量、屈服强度和拉伸强度的预测最大误差分别在5%、5%及11%以内;弹性模量的预测结果受颗粒形状影响较小;其中,三维随机多面体模型的拉伸强度预测精度最高,且能反映出颗粒增强复合材料拉伸断裂过程中的基体韧性断裂、颗粒脆性破坏以及界面脱黏的破坏模式;该模型和方法可为颗粒增强铝基复合材料的细观损伤机理及宏观力学性能分析提供有益的参考。
-
关键词:
- SiCp/Al复合材料 /
- 三维细观模拟 /
- 颗粒尺寸分析 /
- 颗粒形状 /
- 三维随机代表性体积单元 /
- 断口分析
Abstract:Based on the mesoscopic composition and structural characteristics of particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites, a three-dimensional random meso particle reinforced composites analysis model and method considering particle, matrix and interface properties are established. On the meso scale, cubic particle, spherical particle and three-dimensional random polyhedron models are used to characterize the shape of particles respectively. According to the particle size distribution data obtained from particle raw material particle size analysis, a three-dimensional random representative volume element considering the random characteristics of particle spatial distribution and the probability distribution characteristics of particle size is established. Based on Ludwik model, considering the quenching hardening effect, the elastic-plastic constitutive relationship of aluminum matrix is described. The ductile damage of matrix, the elastic-brittle failure of SiC particles and the tensile cracking behavior of interface are considered. The deformation and damage process of material in uniaxial tension are simulated. The uniaxial tensile test verification of SiCp/Al2009 composite standard parts is carried out. The results show that the maximum errors of elastic modulus, yield strength and tensile strength are less than 5%, 5% and 11% respectively; The prediction result of elastic modulus is less affected by particle shape; Among them, the three-dimensional random polyhedron model has the highest prediction accuracy of tensile strength, and can reflect the failure modes of matrix ductile fracture, particle brittle failure and interface debonding in the tensile fracture process of particle reinforced composites; The model and method can provide a useful reference for the analysis of meso damage mechanism and macro mechanical properties of particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites.
-
表 1 Al2009合金各组分含量
Table 1. Component content of Al2009 alloy
合金成分 Cu Si Fe Zn O 杂质 Al 质量
分数/%4.06 0.25 0.2 0.1 0.6 0.2 其余 表 2 组分的基本性能参数
Table 2. Basic performance parameters of components
β b/nm $\Delta {C_{{\mathrm{te}}}}$/℃−1 2.7 0.283 19.3×10−6 表 4 SiCp/Al2009复合材料单轴拉伸试验结果
Table 4. Uniaxial tensile test results of SiCp/Al2009 composites
应变速率 E/GPa ${\sigma _{0.2}}$/MPa ${\sigma _{\mathrm{b}}}$/MPa ${\varepsilon _{\mathrm{f}}}$/% 4×10−3/s 103 440 568 3.3 112 447 561 4.4 2×10−3/s 103 422 532 2.2 105 437 566 3.1 1×10−3/s 104 446 573 4.0 104 429 563 3.8 均值 105 437 560 3.5 表 5 不同RVE模型预测结果及试验对比
Table 5. Prediction results and test comparison of different RVE models
模型 E/GPa ${\sigma _{0.2}}$/MPa ${\sigma _{\mathrm{b}}}$/MPa ${\varepsilon _{\mathrm{f}}}$/% 试样数量 试验结果 105 437 560 3.5 6 RVE-Cube 103 448 503 2.3 3 RVE-Spherical 102 430 501 2.8 3 RVE-Su 102 452 508 2.2 3 -
[1] 王文明,潘复生,曾苏民. 碳化硅颗粒增强铝基复合材料开发与应用的研究现状[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程,2004,27(3): 61-67. WANG Wenming,PAN Fusheng,ZENG Sumin. Current status of development and application in SiCp/Al composites[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering,2004,27(3): 61-67. (in Chinese doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2004.03.016 WANG Wenming, PAN Fusheng, ZENG Sumin . Current status of development and application in SiCp/Al composites[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering,2004 ,27 (3 ):61 -67 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2004.03.016[2] 崔岩. 碳化硅颗粒增强铝基复合材料的航空航天应用[J]. 材料工程,2002,30(6): 3-6. CUI Yan. Aerospace applications of silicon carbide particulate reinforced aluminium matrix composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2002,30(6): 3-6. (in Chinese doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2002.06.001 CUI Yan . Aerospace applications of silicon carbide particulate reinforced aluminium matrix composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2002 ,30 (6 ):3 -6 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2002.06.001[3] 樊建中,肖伯律,徐骏,等. SiCp/Al复合材料在航空航天领域的应用与发展[J]. 材料导报,2007,21(10): 98-101. FAN Jianzhong,XIAO Bolyu,XU Jun,et al. Development and applications of SiCp/Al composites in aerospace field[J]. Materials Review,2007,21(10): 98-101. (in Chinese doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2007.10.026 FAN Jianzhong, XIAO Bolyu, XU Jun, et al . Development and applications of SiCp/Al composites in aerospace field[J]. Materials Review,2007 ,21 (10 ):98 -101 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2007.10.026[4] SRIVATSAN T S,IBRAHIM I A,MOHAMED F A,et al. Processing techniques for particulate-reinforced metal aluminium matrix composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1991,26(22): 5965-5978. doi: 10.1007/BF01113872 [5] 董翠鸽,王日初,彭超群,等. SiCp/Al复合材料研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报,2021,31(11): 3161-3181. DONG Cuige,WANG Richu,PENG Chaoqun,et al. Research progress in SiCp/Al composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2021,31(11): 3161-3181. (in Chinese DONG Cuige, WANG Richu, PENG Chaoqun, et al . Research progress in SiCp/Al composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2021 ,31 (11 ):3161 -3181 . (in Chinese)[6] 吕毓雄,毕敬,陈礼清,等. SiCp尺寸及基体强度对铝基复合材料破坏机制的影响[J]. 金属学报,1998,34(11): 1188-1192. LÜ Yuxiong,BI Jing,CHEN Liqing,et al. Effects of particle size and matrix strength on the failure mechanism of sicp reinforced aluminium matrix composites[J]. Acta Metallrugica Sinica,1998,34(11): 1188-1192. (in Chinese doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.1998.11.014 LÜ Yuxiong, BI Jing, CHEN Liqing, et al . Effects of particle size and matrix strength on the failure mechanism of sicp reinforced aluminium matrix composites[J]. Acta Metallrugica Sinica,1998 ,34 (11 ):1188 -1192 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.1998.11.014[7] 刘龙飞,戴兰宏,杨国伟. SiCP颗粒增强金属基6151Al复合材料中的增强颗粒尺寸效应[J]. 湘潭大学自然科学学报,2001,23(4): 46-50. LIU Longfei,DAI Lanhong,YANG Guowei. Reinforced particle dimension effect in SiCP particle reinforcing metal base 6151Al composite[J]. Natural Science Journal of Xiangtan University,2001,23(4): 46-50. (in Chinese LIU Longfei, DAI Lanhong, YANG Guowei . Reinforced particle dimension effect in SiCP particle reinforcing metal base 6151Al composite[J]. Natural Science Journal of Xiangtan University,2001 ,23 (4 ):46 -50 . (in Chinese)[8] 晏义伍. 颗粒尺寸对SiCp/Al复合材料性能的影响规律及其数值模拟[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学,2007. YAN Yiwu. Effect of particle size on properties of SiCp/Al composites and its numerical simulation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology,2007. (in ChineseYAN Yiwu. Effect of particle size on properties of SiCp/Al composites and its numerical simulation[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007. (in Chinese) [9] WANG Zhangwei,SONG Min,SUN Chao,et al. Effects of particle size and distribution on the mechanical properties of SiC reinforced Al–Cu alloy composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2011,528(3): 1131-1137. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.11.028 [10] DAI L H,LING Z,BAI Y L. Size-dependent inelastic behavior of particle-reinforced metal–matrix composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2001,61(8): 1057-1063. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(00)00235-9 [11] 原国森,李明科,王振永,等. 碳化硅体积分数对SiCP/6061Al复合材料组织和性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺,2018,47(16): 130-132. YUAN Guosen,LI Mingke,WANG Zhenyong,et al. Effect of Si C volume fraction on microstructure and properties of SiCP/6061Al composite[J]. Hot Working Technology,2018,47(16): 130-132. (in Chinese YUAN Guosen, LI Mingke, WANG Zhenyong, et al . Effect of Si C volume fraction on microstructure and properties of SiCP/6061Al composite[J]. Hot Working Technology,2018 ,47 (16 ):130 -132 . (in Chinese)[12] SONG Min. Effects of volume fraction of SiC particles on mechanical properties of SiC/Al composites[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2009,19(6): 1400-1404. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60040-6 [13] XIU Ziyang,CHEN Guoqin,WU Gaohui,et al. Effect of volume fraction on microstructure and mechanical properties of Si3N4/Al composites[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2011,21: 285-289. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61592-6 [14] NIE Junhui,FAN Jianzhong,ZHANG Shaoming,et al. Tensile and fracture properties of 15vol% SiCp/2009Al composites fabricated by hot isostatic pressing and hot extrusion processes[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters),2014,27(5): 875-884. doi: 10.1007/s40195-014-0127-2 [15] HONG S H,CHUNG K H. The effects of processing parameters on mechanical properties of SiCw/2124Al composites[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,1995,48(1/2/3/4): 349-355. [16] DONG Shanliang,ZHANG Bin,ZHAN Yuli,et al. Effect of extrusion temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCnw/2024Al composite[J]. Materials,2019,12(17): 2769-2782. doi: 10.3390/ma12172769 [17] ZHANG H Z,WANG H Y,LIU F F,et al. Investigation on femtosecond laser ablative processing of SiCp/AA2024 composites[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2020,49: 227-233. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.08.021 [18] SINGH P M,LEWANDOWSKI J J. Effects of heat treatment and reinforcement size[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A,1993,24(11): 2531-2543. doi: 10.1007/BF02646532 [19] WANG Tao,XIE Lijing,WANG Xibin. Simulation study on defect formation mechanism of the machined surface in milling of high volume fraction SiCp/Al composite[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2015,79(5): 1185-1194. [20] CHEN Shenggui,HASSANZADEH-AGHDAM M K,ANSARI R. An analytical model for elastic modulus calculation of SiC whisker-reinforced hybrid metal matrix nanocomposite containing SiC nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,767: 632-641. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.102 [21] GAO Xiang,ZHANG Xuexi,QIAN Mingfang,et al. Effect of reinforcement shape on fracture behaviour of SiC/Al composites with network architecture[J]. Composite Structures,2019,215: 411-420. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.02.067 [22] ZHANG J F,ANDRÄ H,ZHANG X X,et al. An enhanced finite element model considering multi strengthening and damage mechanisms in particle reinforced metal matrix composites[J]. Composite Structures,2019,226: 111281. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111281 [23] SEGURADO J,LLORCA J. Computational micromechanics of composites: the effect of particle spatial distribution[J]. Mechanics of Materials,2006,38(8/9/10): 873-883. [24] LI Mingshan,GHOSH S,ROUNS T N,et al. Serial sectioning method in the construction of 3-D microstructures for particle-reinforced MMCs[J]. Materials Characterization,1998,41(2/3): 81-95. [25] CHAWLA N,SIDHU R S,GANESH V V. Three-dimensional visualization and microstructure-based modeling of deformation in particle-reinforced composites[J]. Acta Materialia,2006,54(6): 1541-1548. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2005.11.027 [26] HAN W,ECKSCHLAGER A,BÖHM H J. The effects of three-dimensional multi-particle arrangements on the mechanical behavior and damage initiation of particle-reinforced MMCs[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2001,61(11): 1581-1590. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(01)00061-6 [27] YUAN Zhanwei,LI Fuguo,XUE Fengmei,et al. Analysis of the stress states and interface damage in a particle reinforced composite based on a micromodel using cohesive elements[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2014,589: 288-302. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.09.097 [28] SINGH H,MAO Y,SREERANGANATHAN A,et al. Application of digital image processing for implementation of complex realistic particle shapes/morphologies in computer simulated heterogeneous microstructures[J]. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering,2006,14(3): 351-363. doi: 10.1088/0965-0393/14/3/002 [29] SU Yishi,OUYANG Qiubao,ZHANG Wenlong,et al. Composite structure modeling and mechanical behavior of particle reinforced metal matrix composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2014,597: 359-369. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.01.024 [30] DALE O K. MatWeb metal material data sheets(MDS)[EB/OL]. (2011-01-26)[2021-12-01]. http://app.knovel.com/hotlink/toc/id:kpMMDS0002/metal-material-data-sheets/metal-material-data-sheets. [31] ZHANG J F,ZHANG X X,WANG Q Z,et al. Simulations of deformation and damage processes of SiCp/Al composites during tension[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2018,34(4): 627-634. [32] SHAO J C,XIAO B L,WANG Q Z,et al. An enhanced FEM model for particle size dependent flow strengthening and interface damage in particle reinforced metal matrix composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2011,71(1): 39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2010.09.014 [33] NAN C W,CLARKE D R. The influence of particle size and particle fracture on the elastic/plastic deformation of metal matrix composites[J]. Acta Materialia,1996,44(9): 3801-3811. doi: 10.1016/1359-6454(96)00008-0 [34] HILLERBORG A,MODÉER M,PETERSSON P E. Analysis of crack formation and crack growth in concrete by means of fracture mechanics and finite elements[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,1976,6(6): 773-781. doi: 10.1016/0008-8846(76)90007-7 [35] ZHANG Jie,OUYANG Qiubao,GUO Qiang,et al. 3D Microstructure-based finite element modeling of deformation and fracture of SiCp/Al composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2016,123: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2015.11.014 [36] LAGACÉ H,LLOYD D J. Microstructural analysis of Al-SiC composites[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly,1989,28(2): 145-152. doi: 10.1179/cmq.1989.28.2.145 [37] LEE J C,SUBRAMANIAN K N. Failure behaviour of particulate-reinforced aluminium alloy composites under uniaxial tension[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1992,27(20): 5453-5462. doi: 10.1007/BF00541606 -







 下载:
下载: