Construction and validation of reduced reaction mechanism of natural gas
-
摘要:
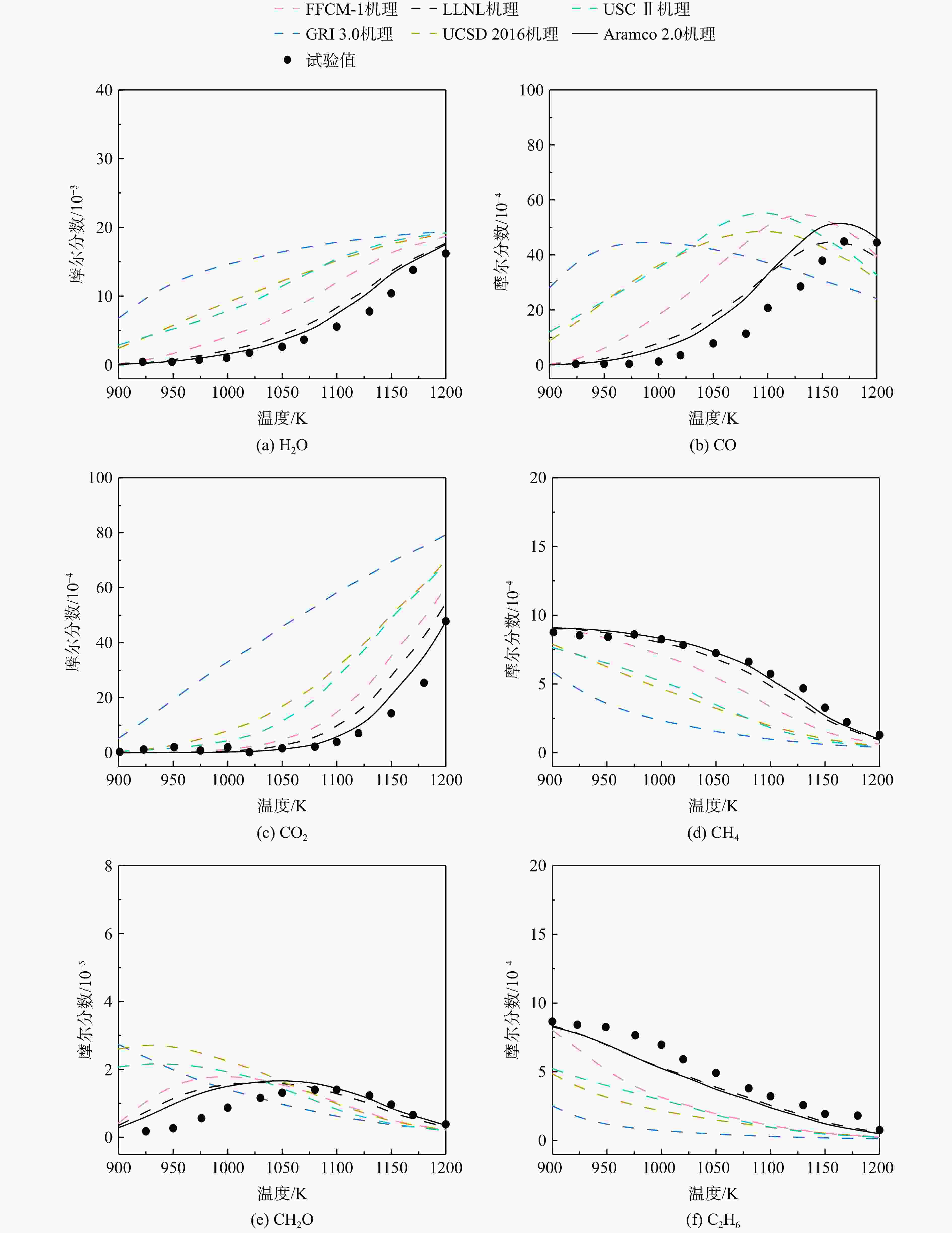
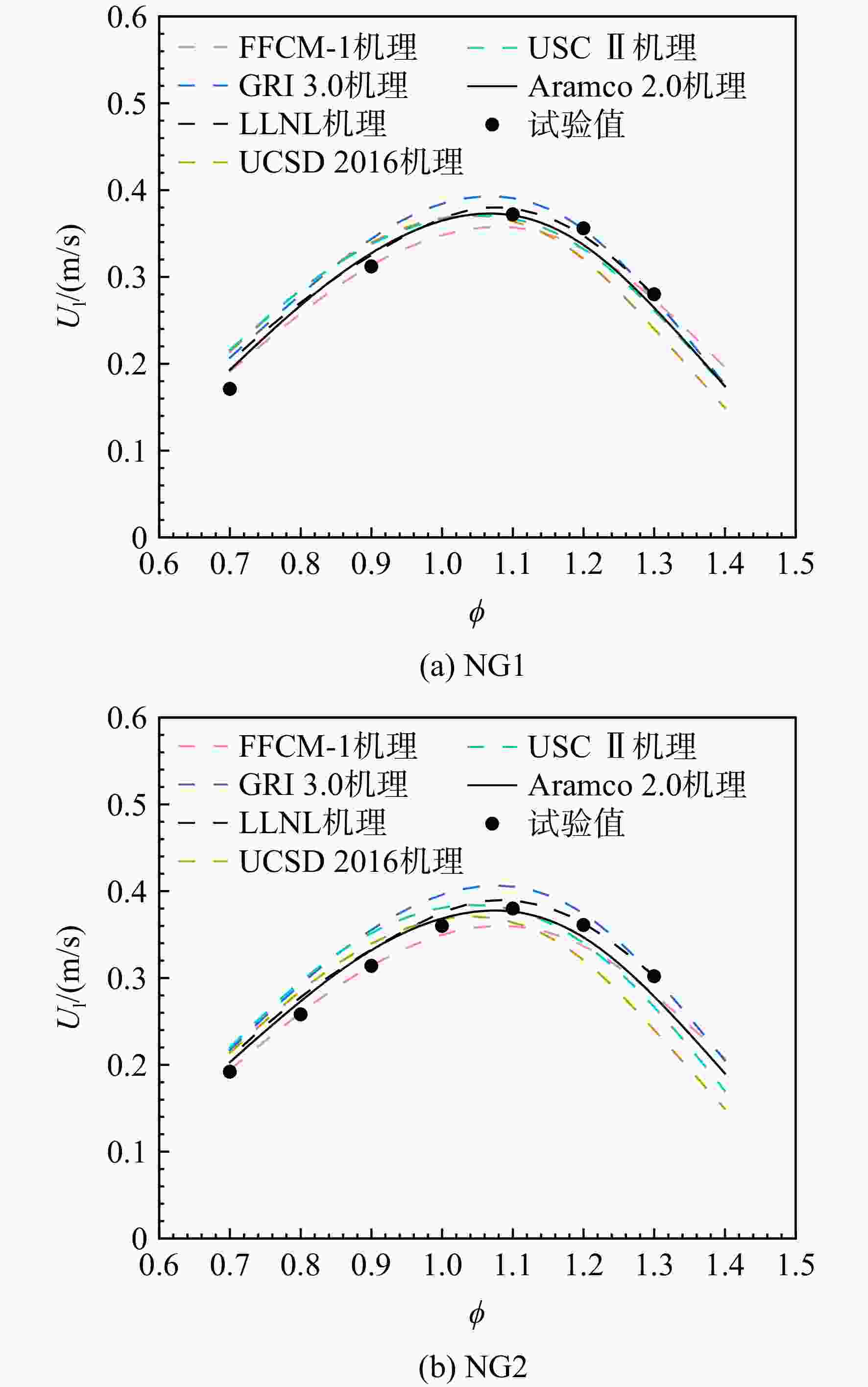
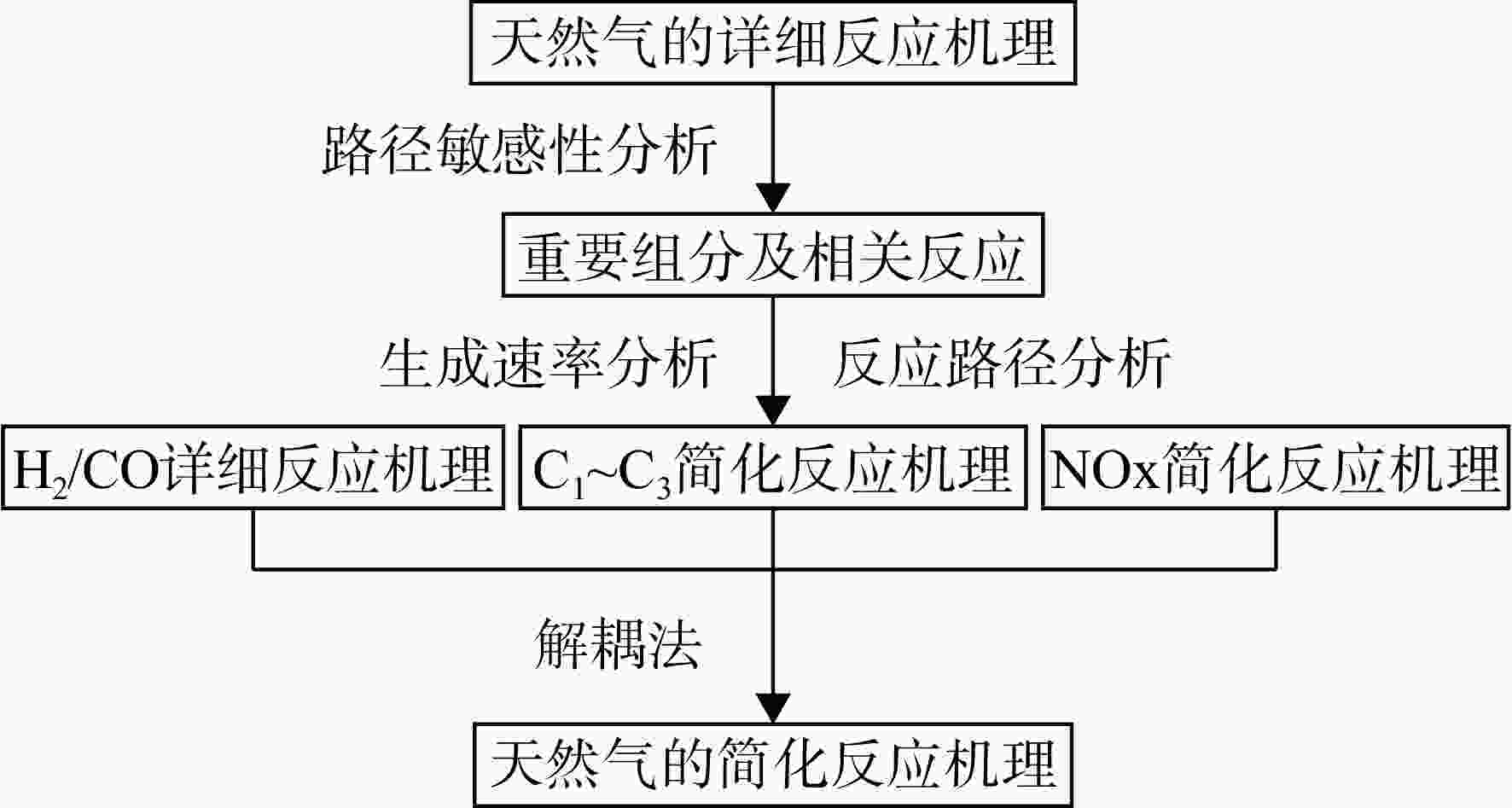
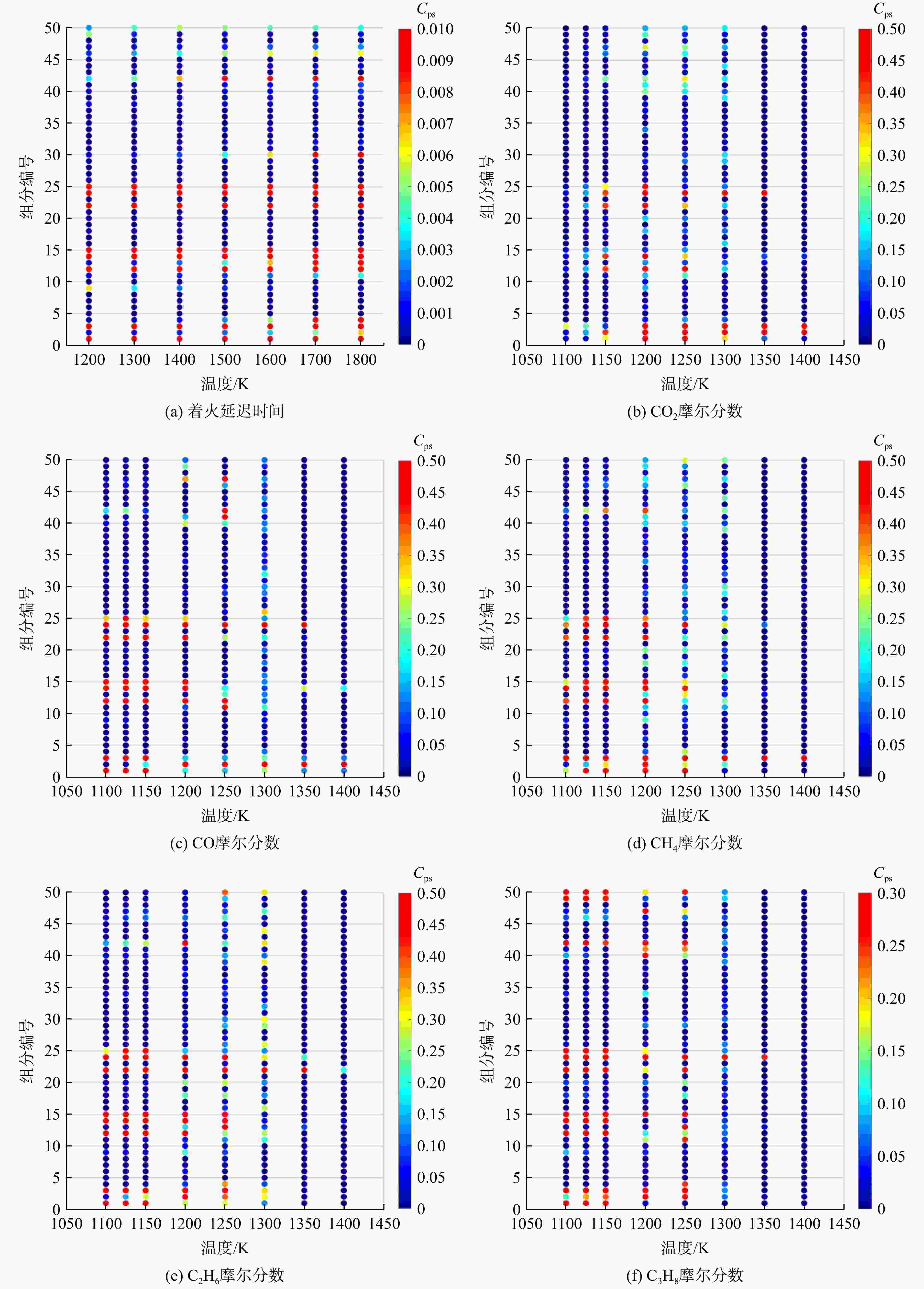
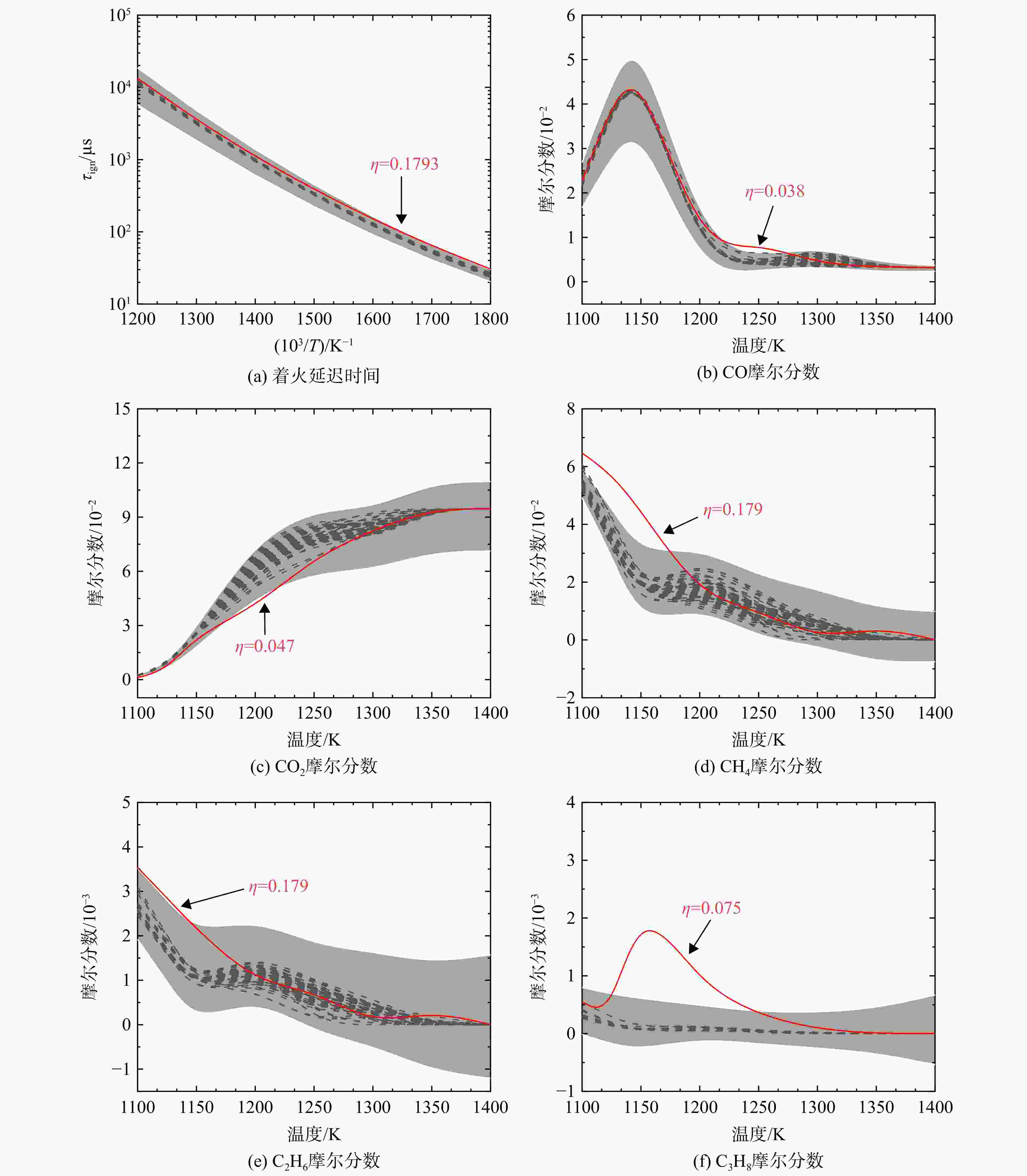
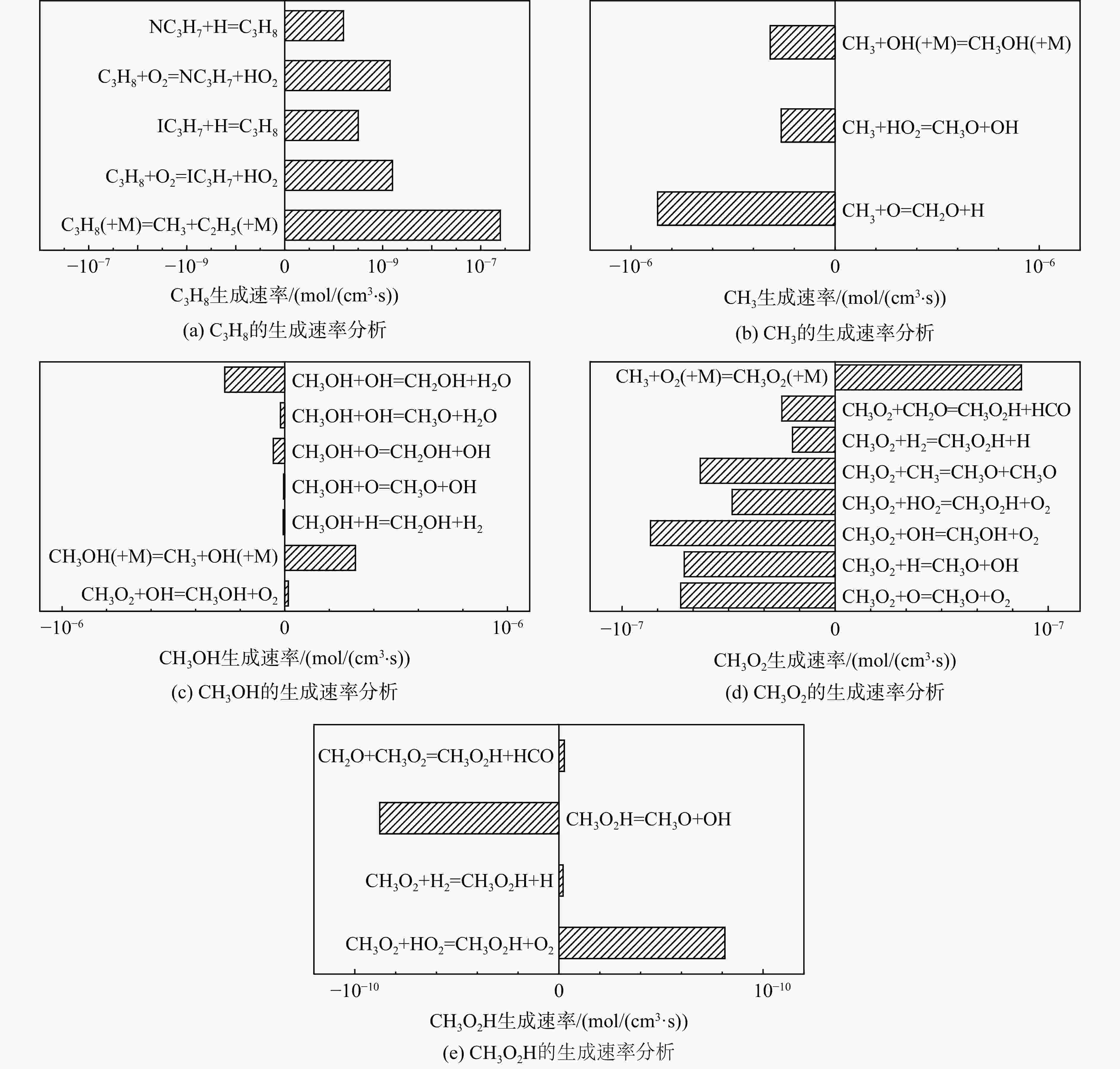
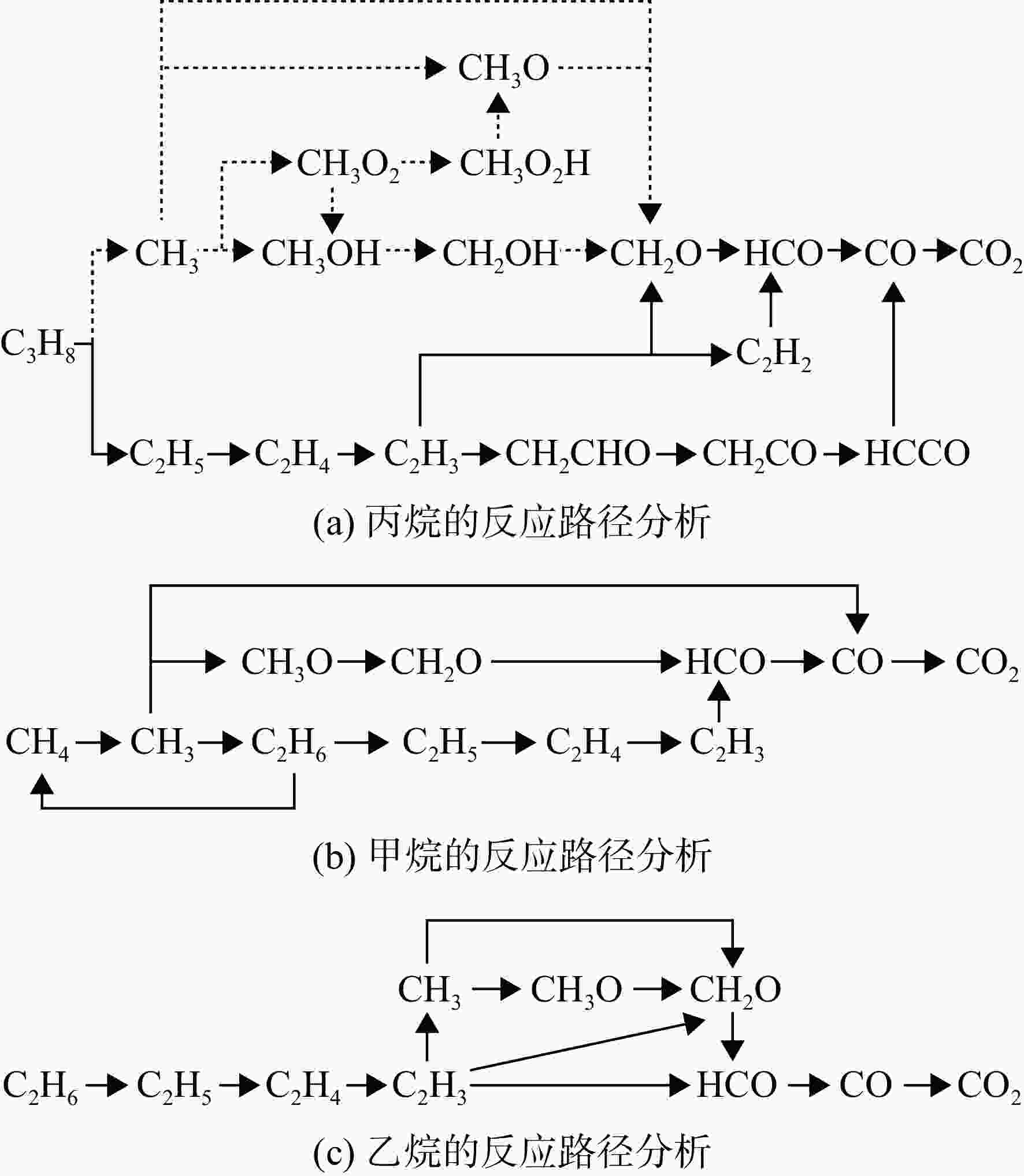
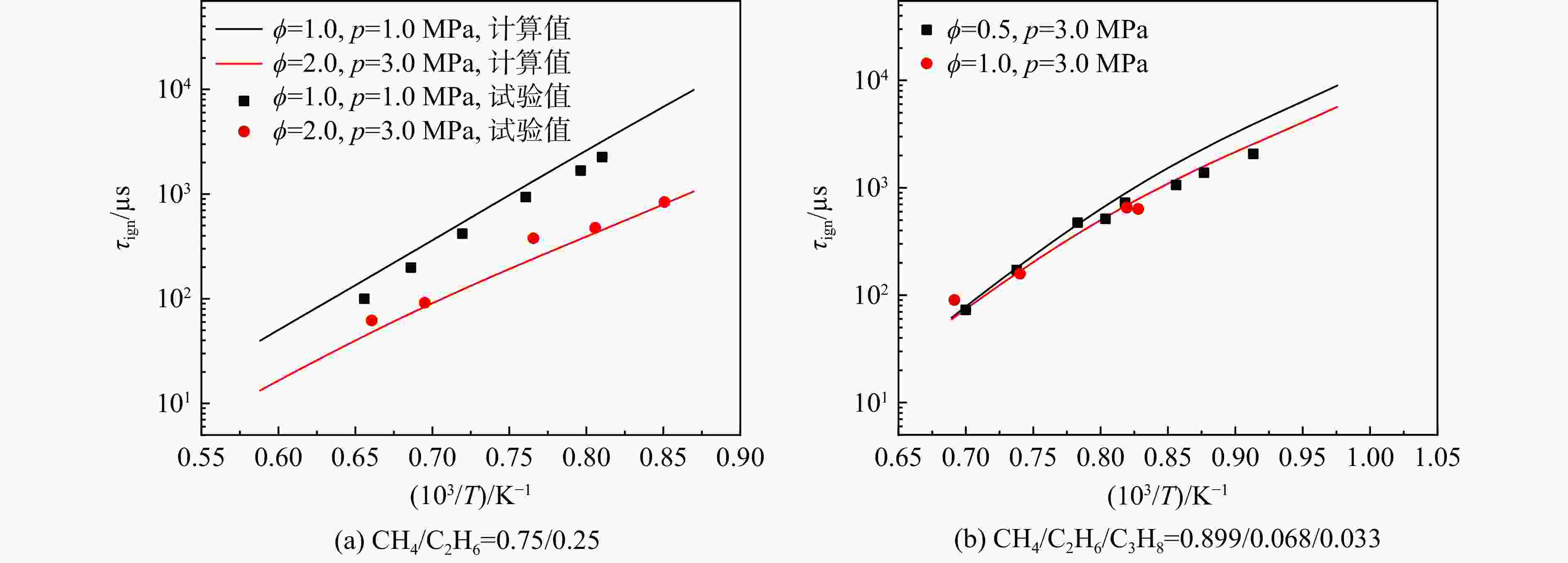
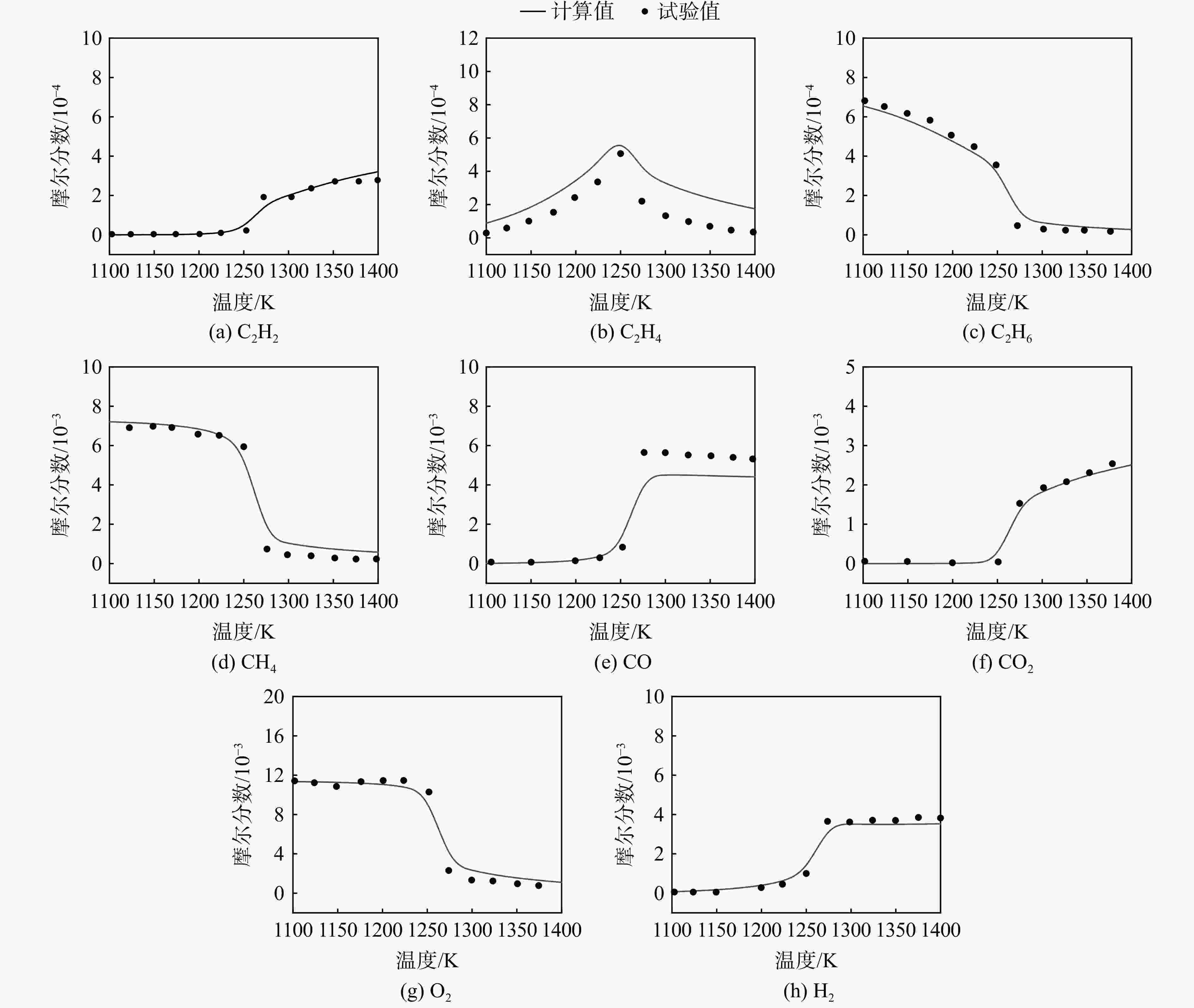
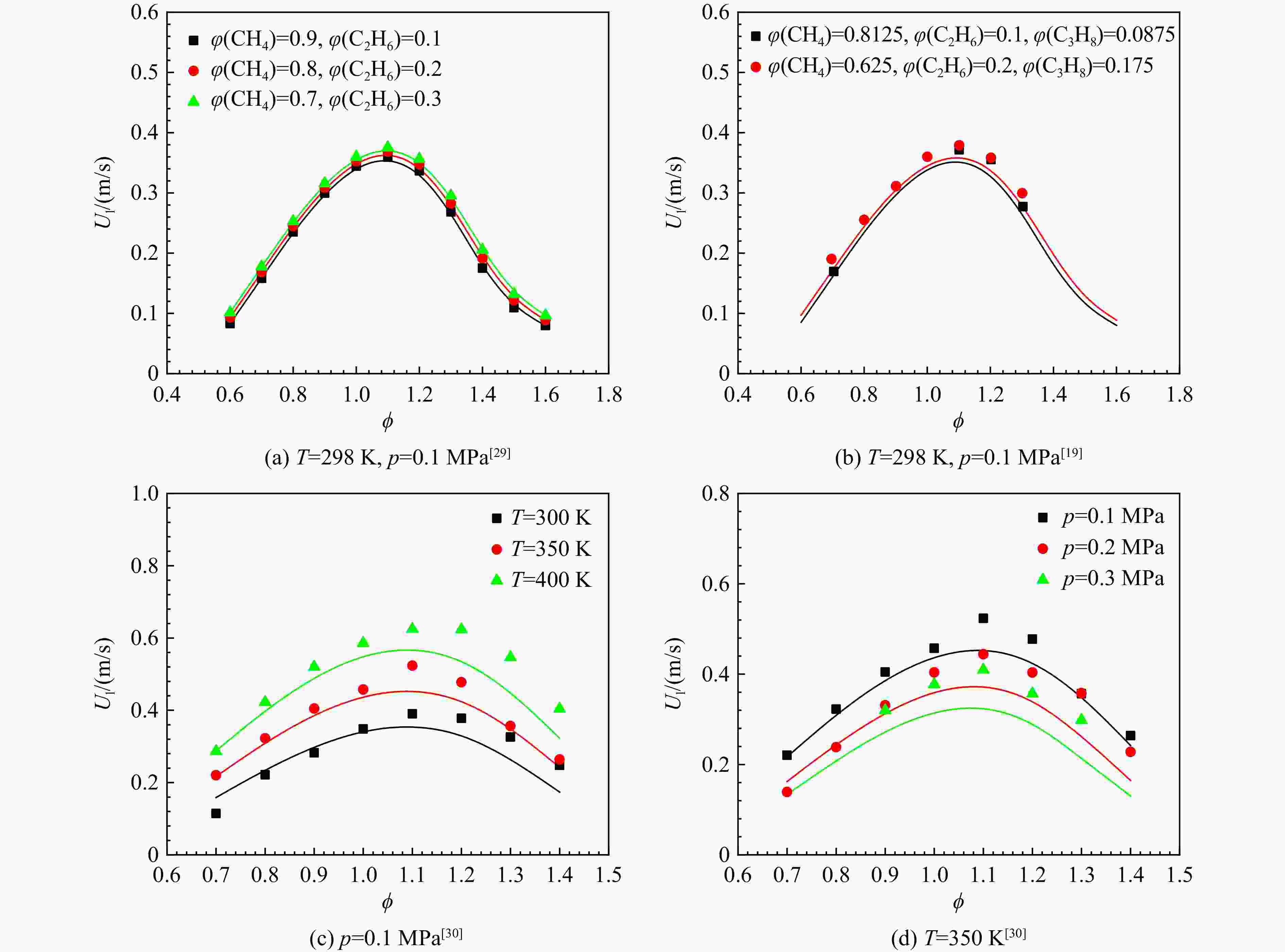
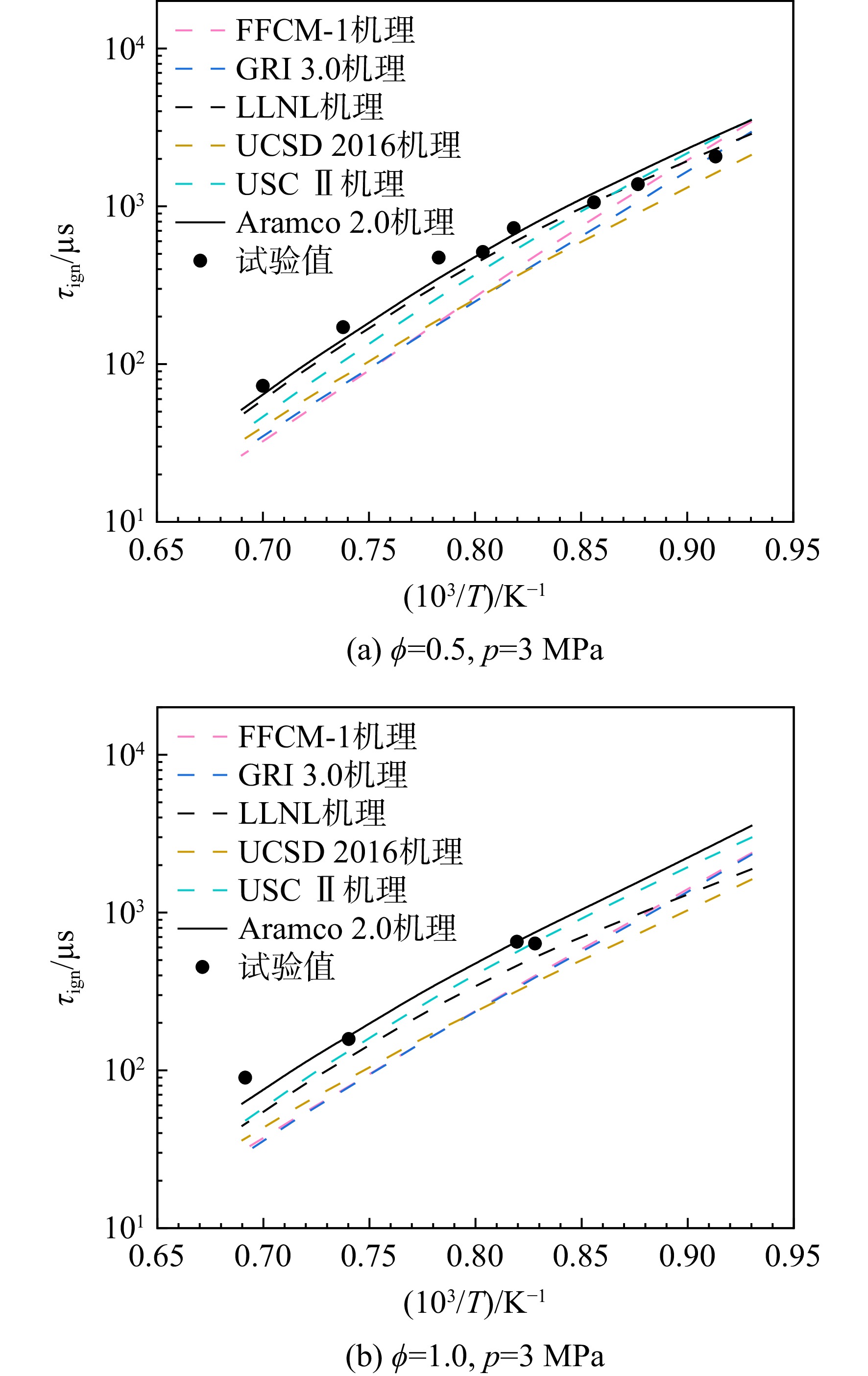
采用6种详细反应机理对多工况条件下天然气的着火延迟时间、层流燃烧速度以及氧化过程中主要组分摩尔分数进行了数值计算,并与相应试验数据进行了对比分析。结果表明:相比于其它五种详细反应机理,Aramco 2.0机理在天然气的着火延迟、层流燃烧以及氧化特性的预测上精度最高。基于Aramco 2.0机理,通过路径敏感性分析、生成速率分析与反应路径分析,形成了天然气(CH4/C2H6/C3H8)的初始简化机理(包含21种组分、150个反应);同时,基于解耦法,耦合初始简化反应机理中的C1~C3反应机理、H2/CO详细反应机理和NOx简化反应机理,构建了天然气的简化反应机理(包含40种组分、189个反应)。通过与相应试验数据的对比发现,该简化反应机理能很好的预测多工况条件下天然气的着火延迟、层流燃烧与氧化特性。
Abstract:The ignition delay time, the laminar combustion speed of natural gas and the main species concentrations in the natural gas oxidation process were simulated by six detailed reaction mechanisms, and also compared with corresponding experimental data. The results showed that, compared with the other five detailed reaction mechanisms, Aramco 2.0 mechanism had the highest accuracy in predicting the ignition delay, laminar combustion and oxidation characteristics of natural gas. Based on Aramco 2.0 mechanism, an initial reduced reaction mechanism (including 21 species and 150 reactions) of natural gas (including CH4, C2H6 and C3H8) was formed using the path sensitivity analysis, production rate analysis and reaction path analysis. At the same time, based on decoupling method, through combining the reaction mechanism of C1−C3 in the initial reduced reaction mechanism with the detailed reaction mechanism of H2/CO and the reduced reaction mechanism of NOx, the reduced reaction mechanism of natural gas was constructed (including 40 species and 189 reactions). Compared with the corresponding experimental data, it was found that the reduced reaction mechanism can well predict the ignition delay, laminar combustion and oxidation characteristics of natural gas under various conditions.
-
表 1 反应组分编号表
Table 1. Reaction component numbering table
组分编号 反应组分 组分编号 反应组分 1 CO 26 CHOCHO 2 CO2 27 C2H3OOH 3 CH3 28 C2H3OO 4 CH2 29 CHCHO 5 CH2(S) 30 C2H2 6 C 31 C2H 7 CH 32 H2CC 8 CHV 33 C2H5OH 9 CH3O2 34 C2H5O 10 CH2O2H 35 PC2H4OH 11 CH3OH 36 SC2H4OH 12 CH3O 37 C2H4O2H 13 CH2OH 38 C2H4O1-2 14 CH2O 39 C2H3O1-2 15 HCO 40 CH3CHO 16 HCOH 41 CH3CO 17 HO2CHO 42 CH2CHO 18 HOCH2O 43 HO2CH2CO 19 O2CHO 44 C2H3OH 20 HOCHO 45 C2H2OH 21 OCHO 46 CH2CO 22 C2H5 47 HCCO 23 C2H5O2 48 HCCOH 24 C2H4 49 IC3H7 25 C2H3 50 NC3H7 -
[1] 尉曙明,索建秦. 航空衍生工业燃气轮机双燃料贫燃预混低污染燃烧技术[J]. 航空动力学报,2015,30(9): 2049-2057.WEI Shuming,SUO Jianqin. Aero-derivative industrial gas turbine dual fuel lean premixed low emission combustion technology[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2015,30(9): 2049-2057. (in Chinese) [2] DE ALMEIDA D S,LACAVA P T. Analysis of pollutant emissions in double-stage swirl chamber for gas turbine application[J]. Energy Procedia,2015,66: 117-120. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2015.02.067 [3] BULAT G,JONES W P,MARQUIS A J. NO and CO formation in an industrial gas-turbine combustion chamber using LES with the Eulerian sub-grid PDF method[J]. Combustion and Flame,2014,161(7): 1804-1825. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2013.12.028 [4] LYRA S,CANT R S. Analysis of high pressure premixed flames using Equivalent Reactor Networks for predicting NOx emissions[J]. Fuel,2013,107: 261-268. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.12.066 [5] STARIK A M,KOZLOV V E,LEBEDEV A B,et al. Application of reactor net models for the simulation of gas-turbine combustor emissions[J]. International Journal of Sustainable Aviation,2014,1(1): 43-57. doi: 10.1504/IJSA.2014.062867 [6] ZENG Wen,PANG Liyao,ZHENG Weilin,et al. Study on combustion and emission characteristics of a heavy-duty gas turbine combustor fueled with natural gas[J]. Fuel,2020,275: 117988.1-117988.12. [7] 陈威昌. 天然气发动机燃烧及排放的CFD模拟研究[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2017.CHEN Weichang. CFD simulation for combustion and emission of a natural gas engine[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2017. (in Chinese) [8] 咸凯. 天然气发动机爆震特性研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018.XIAN Kai. Research on knock characteristic of natural gas engine[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2018. (in Chinese) [9] DROST S,AZNAR M S,SCHIEBL R,et al. Reduced reaction mechanism for natural gas combustion in novel power cycles[J]. Combustion and Flame,2021,223: 486-494. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2020.09.029 [10] POORGHASEMI K,SARAY R K,BAHLOULI K,et al. 3D CFD simulation of a natural gas fueled HCCI engine with employing a reduced mechanism[J]. Fuel,2016,182: 816-830. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.06.005 [11] SMITH G P, TAO Y, WANG H. Foundational fuel chemistry model version 1.0 (FFCM-1)[EB/OL]. [2022-04-20]. http://nanoenergy.stanford.edu/ffcm1, 2016. [12] SMITH G. An optimized detailed chemical reaction mechanism for methane combustion[EB/OL]. [2022-04-20]. http://www.me.berkeley.edu/gri_mech. [13] CURRAN H J,GAFFURI P,PITZ W J,et al. A comprehensive modeling study of n-heptane oxidation[J]. Combustion and Flame,1998,114(1/2): 149-177. [14] WILLIAMS F A. Chemical-kinetic mechanisms for combustion applications[EB/OL]. [2022-04-20]. http://web.eng.ucsd.edu/mae/groups/combustion/mechanism.html. [15] YOU X Q, AMEYA V, WANG H. USC mech version II. High-temperature combustion reaction model of H2/CO/C1-C4 Compounds[EB/OL]. [2022-04-20]. http://ignis.usc. edu/USC_Mech_II.htm. [16] METCALFE W K,BURKE S M,AHMED S S,et al. A hierarchical and comparative kinetic modeling study of C1-C2 hydrocarbon and oxygenated fuels[J]. International Journal of Chemical Kinetics,2013,45(10): 638-675. doi: 10.1002/kin.20802 [17] HEALY D,CURRAN H J,SIMMIE J M,et al. Methane/ethane/propane mixture oxidation at high pressures and at high, intermediate and low temperatures[J]. Combustion and Flame,2008,155(3): 441-448. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2008.07.003 [18] DAGAUT P,DAYMA G. Hydrogen-enriched natural gas blend oxidation under high-pressure conditions: experimental and detailed chemical kinetic modeling[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2006,31(4): 505-515. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2005.04.020 [19] BOURQUE G,HEALY D,CURRAN H,et al. Ignition and flame speed kinetics of two natural gas blends with high levels of heavier hydrocarbons[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2010,132(2): 021504.1-021504.11. [20] CHANG Yachao,JIA Ming,NIU Bo,et al. Reduction of large-scale chemical mechanisms using global sensitivity analysis on reaction class/sub-mechanism[J]. Combustion and Flame,2020,212: 355-366. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2019.11.019 [21] CHANG Yachao,JIA Ming,FAN Weiwei,et al. Decoupling methodology: an effective way for the development of reduced and skeletal mechanisms[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2016,32(9): 2209-2215. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201605262 [22] CHANG Yachao,JIA Ming,LIU Yaodong,et al. Development of a new skeletal mechanism for n-decane oxidation under engine-relevant conditions based on a decoupling methodology[J]. Combustion and Flame,2013,160(8): 1315-1332. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2013.02.017 [23] 蒋勇,邱榕. 复杂化学机理简化的关联水平法[J]. 化学学报,2010,68(5): 403-412.JIANG Yong,QIU Rong. A level of connection method for mechanism reduction of complex chemistry[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica,2010,68(5): 403-412. (in Chinese) [24] BURKE U,METCALFE W K,BURKE S M,et al. A detailed chemical kinetic modeling, ignition delay time and jet-stirred reactor study of methanol oxidation[J]. Combustion and Flame,2016,165: 125-136. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2015.11.004 [25] HUANG Haozhong,LÜ Delin,ZHU Jizhen,et al. Development of a new reduced diesel/natural gas mechanism for dual-fuel engine combustion and emission prediction[J]. Fuel,2019,236: 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.08.161 [26] SEERY D J,BOWMAN C T. An experimental and analytical study of methane oxidation behind shock waves[J]. Combustion and Flame,1970,14(1): 37-47. doi: 10.1016/S0010-2180(70)80008-6 [27] BAKALI A E,DAGAUT P,PILLIER L,et al. Experimental and modeling study of the oxidation of natural gas in a premixed flame, shock tube, and jet-stirred reactor[J]. Combustion and Flame,2004,137(1/2): 109-128. [28] 田雨师,曾文,陈潇潇,等. 天然气氧化特性的实验与数值计算[J]. 航空动力学报,2022,37(9): 1886-1895.TIAN Yushi,ZENG Wen,CHEN Xiaoxiao,et al. Experiment and simulation on oxidation characteristics of natural gas[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2022,37(9): 1886-1895. (in Chinese) [29] DIRRENBERGER P,LE GALL H,BOUNACEUR R,et al. Measurements of laminar flame velocity for components of natural gas[J]. Energy & Fuels,2011,25(9): 3875-3884. [30] 党嘉莹, 曾文, 陈潇潇, 等. 天然气层流燃烧特性的实验与数值计算[EB/OL]. [2021-12-27]. https: //doi.org/10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20210468 -








 下载:
下载: