Mechanism analysis for aero-elastic stability improvement of intentional mistuned bladed disk
-
摘要:
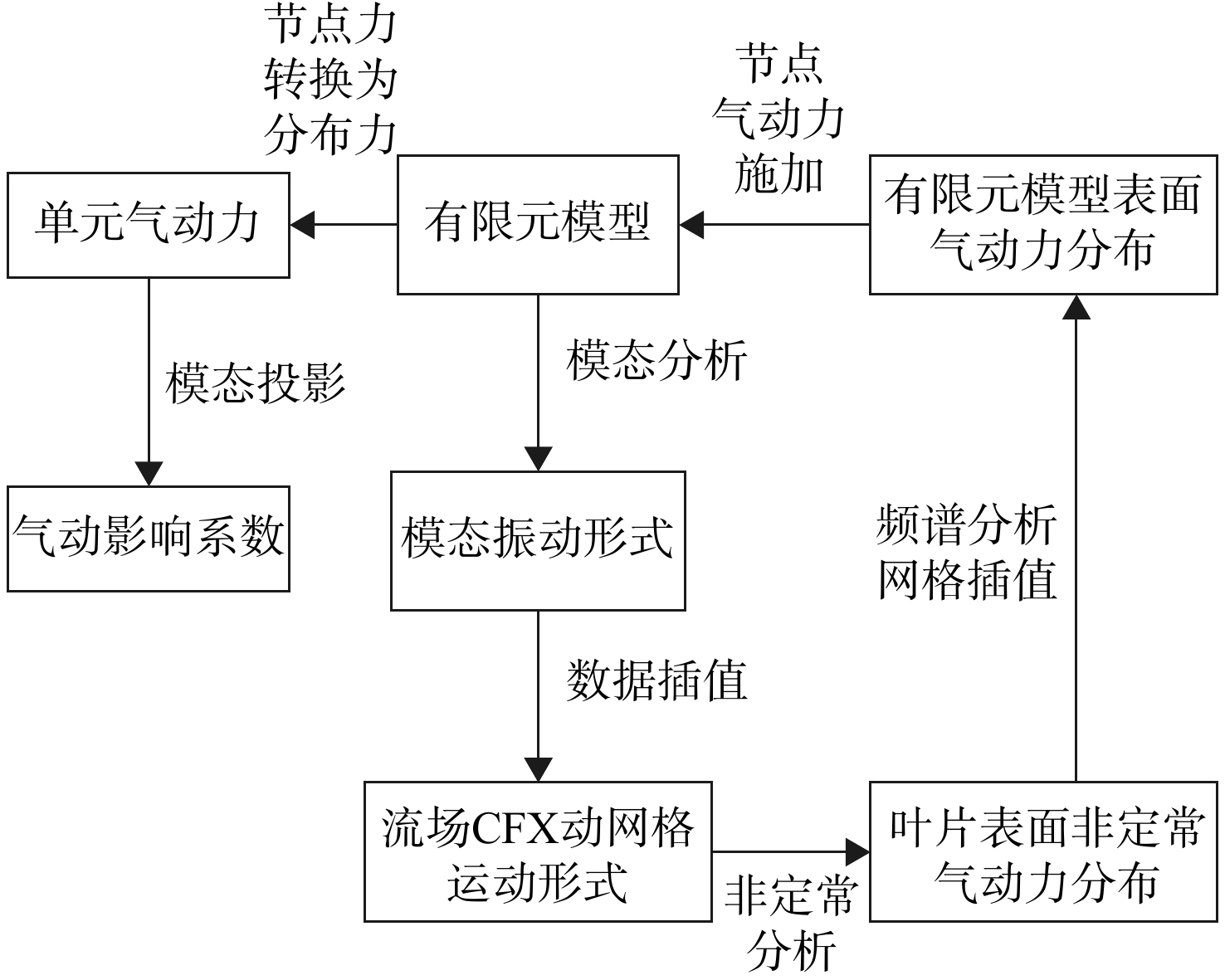
理解人为失谐提升叶盘气动弹性稳定性的机理,有助于提高航空发动机叶盘的结构设计水平。首先,通过将失谐叶盘的气弹耦合模态投影到谐调模态张成的线性空间中,获得了以谐调叶盘气动阻尼比线性叠加表示的失谐叶盘气动阻尼比的解析表达式。从理论上证明了:失谐气弹耦合模态振型中包含多个彼此独立的谐调叶盘模态振型的贡献;气动阻尼比水平较高的谐调叶盘模态的参与提高了失谐叶盘的气弹稳定性。接着,提出了失谐叶盘气弹稳定性的预测方法,在计算过程中先分别分析失谐和气弹耦合的模态特性,再相互结合预测失谐叶盘的气动阻尼比水平。该方法只需进行一次气弹耦合分析,一是在实际设计中可降低对失谐设计叶盘气弹稳定性实验测量需求,二是降低仿真过程中的计算量,加快失谐模式寻优过程。最后,采用具有NASA-Rotor37叶型的叶盘作为研究对象,在多种失谐模式和失谐强度下验证了上述理论的正确性。结果表明:解析表达式误差小于0.1%;预测方法对稳定边界有一定的高估且误差在5%以内,对于总体影响规律的预测与精确解一致。
Abstract:By projecting the aero-elastic modes of the mistuned bladed disk to the modal space spanned by the tuned modes, a closed-form expression of the mistuned aerodynamic damping ratio as a linear superposition of the tuned damping was obtained. It was theoretically demonstrated that: a mistuned aero-elastic mode was constructed by several tuned and independent modes; and the contribution of the tuned modes with high aeroelastic damping can increase the aeroelastic damping of the mistuned mode. A method to predict the aerodynamic damping ratio of the mistuned bladed disk was proposed. It started with respective analysis of aero-elastic coupling and mistuning, and the aerodynamic damping ratio of the mistuned modes can be predicted. A single-time aeroelastic analysis was required for two significant benefits. One is reducing the experimental measurements and the other is decreasing the calculation cost to accelerate the optimization process of mistuning pattern. The bladed disk with NASA-Rotor37 blade profile was considered, and several typical mistuning patterns were applied with different levels of mistuning strength. Results showed that the closed-form expression had an error lower than 0.1%. The prediction method would overrate the stability boundary with error lower than 5%, so it is capable to capture the overall trends of the accurate results.
-
-
[1] SRINIVASAN A V. Flutter and resonant vibration characteristics of engine blades[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,1997,119(4): 742-775. doi: 10.1115/1.2817053 [2] WHITEHEAD D S. Effect of mistuning on the vibration of turbo-machine blades induced by wakes[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science,1966,8(1): 15-21. doi: 10.1243/JMES_JOUR_1966_008_004_02 [3] BENDIKSEN O O. Flutter of mistuned turbomachinery rotors[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,1984,106(1): 25-33. [4] GROTH P,MARTENSSON H,ANDERSSON C. Design and experimental verification of mistuning of a supersonic turbine blisk[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2010,132(1): 011012.1-011012.9. [5] FIGASCHEWSKY F, KÜHHORN A, BEIROW B, et al. Design and analysis of an intentional mistuning experiment reducing flutter susceptibility and minimizing forced response of a jet engine fan[R]. Charlotte, US: Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, 2017 [6] BIAGIOTTI S,PINELLI L,POLI F,et al. Numerical study of flutter stabilization in low pressure turbine rotor with intentional mistuning[J]. Energy Procedia,2018,148: 98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2018.08.035 [7] CORRAL R,KHEMIRI O,MARTEL C. Design of mistuning patterns to control the vibration amplitude of unstable rotor blades[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology,2018,80: 20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2018.06.034 [8] KAZA K R V,KIELB R E. Flutter and response of a mistuned cascade in incompressible flow[J]. AIAA Journal,1982,20(8): 1120-1127. doi: 10.2514/3.51172 [9] KIELB R E,KAZA K R V. Aeroelastic characteristics of a cascade of mistuned blades in subsonic and supersonic flows[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics,1983,105: 425-433. doi: 10.1115/1.3269124 [10] KIELB R E,KAZA K R V. Effects of structural coupling on mistuned cascade flutter and response[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,1984,106(1): 17-24. doi: 10.1115/1.3239532 [11] SHAPIRO B. Symmetry approach to extension of flutter boundaries via mistuning[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power,1998,14(3): 354-366. doi: 10.2514/2.5288 [12] CRAWLEY E F,HALL K C. Optimization and mechanisms of mistuning in cascades[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,1985,107(2): 418-426. doi: 10.1115/1.3239742 [13] FANG M,WANG Y. Intentional mistuning effect on the blisk vibration with aerodynamic damping[J]. AIAA Journal,2022,60(6): 3884-3893. doi: 10.2514/1.J060797 [14] KIELB R E, HALL K C, HONG E, et al. Probabilistic flutter analysis of a mistuned bladed disks[R]. Barcelona, Spain: Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, 2006. [15] LI L, YU X, WANG P. Research on aerodynamic damping of bladed disk with random mistuning[R]. Charlotte, US: Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, 2017. [16] LIU X, LI L, FAN Y, et al. Improving the aero-elastic stability of bladed disks through parallel piezoelectric network[R]. Cincinnati, US: Joint Propulsion Conference, 2018. [17] ZHANG X,WANG Y. Mistuning effects on aero-elastic stability of contra-rotating turbine blades[J]. International Journal of Aeronautical and Space Sciences,2019,20(1): 100-113. doi: 10.1007/s42405-018-0108-1 [18] LIU X,FAN Y,LI L,et al. Improving aeroelastic stability of bladed disks with topologically optimized piezoelectric materials and intentionally mistuned shunt capacitance[J]. Materials,2022,15(4): 1309-1332. doi: 10.3390/ma15041309 [19] HANAMURA Y,TANAKA H,YAMAGUCHI K. A simplified method to measure unsteady forces acting on the vibrating blades in cascade[J]. Bulletin of Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers,1980,23(180): 880-887. doi: 10.1299/jsme1958.23.880 [20] MARTEL C, CORRAL R, LLORENS J M. Stability increase of aerodynamically unstable rotors using intentional mistuning[R]. Barcelona, Spain: Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, 2006 [21] BLEEG J M,YANG M T,ELEY J A. Aeroelastic analysis of rotors with flexible disks and alternate blade mistuning[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2009,131(1): 011011.1-011011.9. [22] MARTEL C, SÁNCHEZ J J. Intentional mistuning with predominant aerodynamic effects[R]. Oslo, Norway: Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air, 2018. [23] HSU K,HOYNIAK D. A fast influence coefficient method for aerodynamically mistuned disks aeroelasticity analysis[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2011,133(12): 122502-122511. doi: 10.1115/1.4004110 [24] PANOVSKY J,KIELB R E. A design method to prevent low pressure turbine blade flutter[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,2000,122(1): 89-98. doi: 10.1115/1.483180 [25] CAMPOBASSO M S, GILES M. Analysis of the effect of mistuning on turbomachinery aeroelasticity[R]. Lyon, France: 9th International Symposium on Unsteady Aerodynamics, Aeroacoustics and Aeroelasticity of Turbomachines, 2000. [26] FEINER D M,GRIFFIN J H. A fundamental model of mistuning for a single family of modes[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2002,124(4): 597-605. doi: 10.1115/1.1508384 [27] 李其汉, 王延荣. 航空发动机结构强度设计问题[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2014. [28] REID L, MOORE R D. Design and overall performance of four highly loaded, high speed inlet stages for an advanced high-pressure-ratio core compressor[R]. NASA-TP-1337, 1978. -








 下载:
下载: