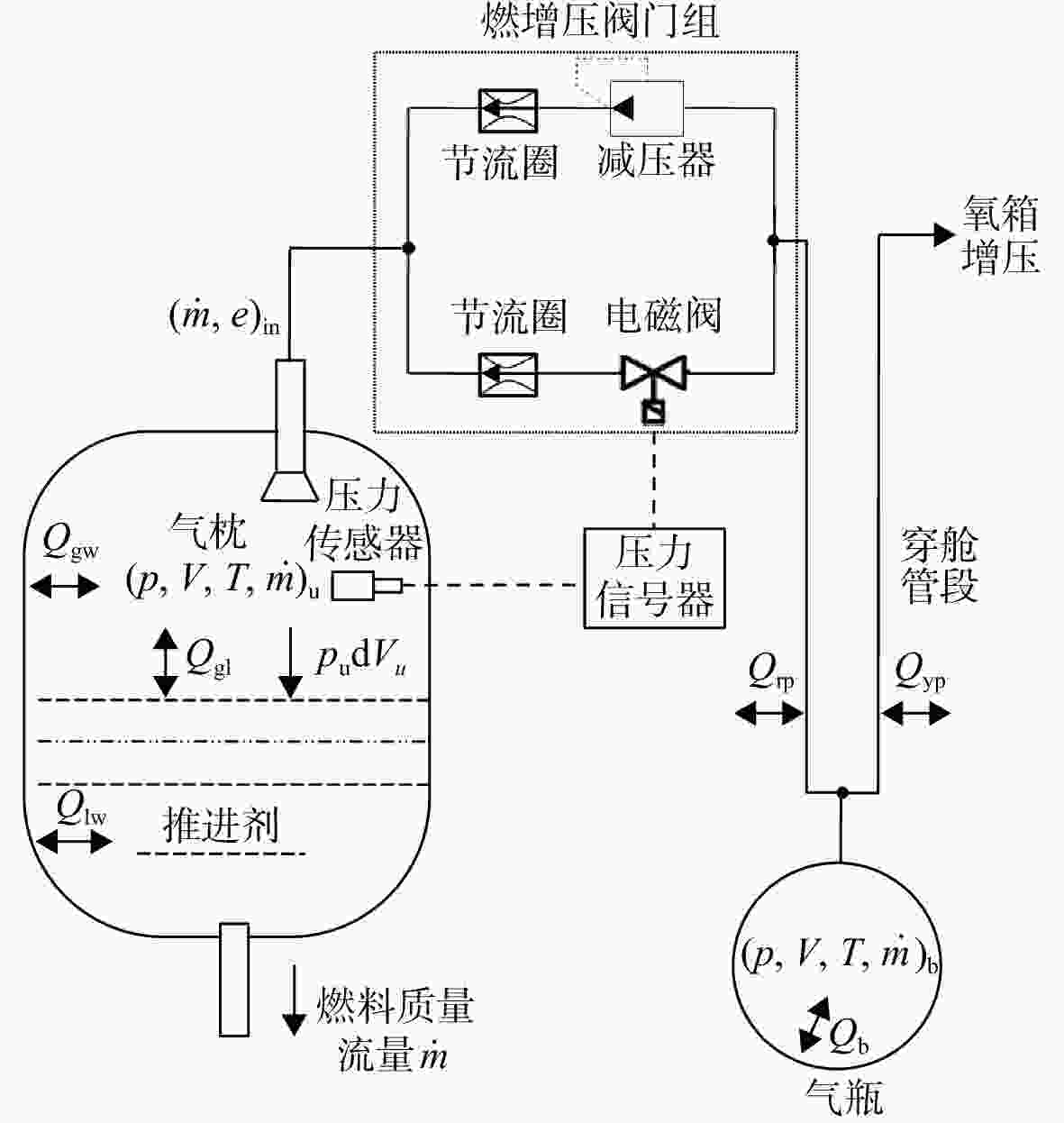
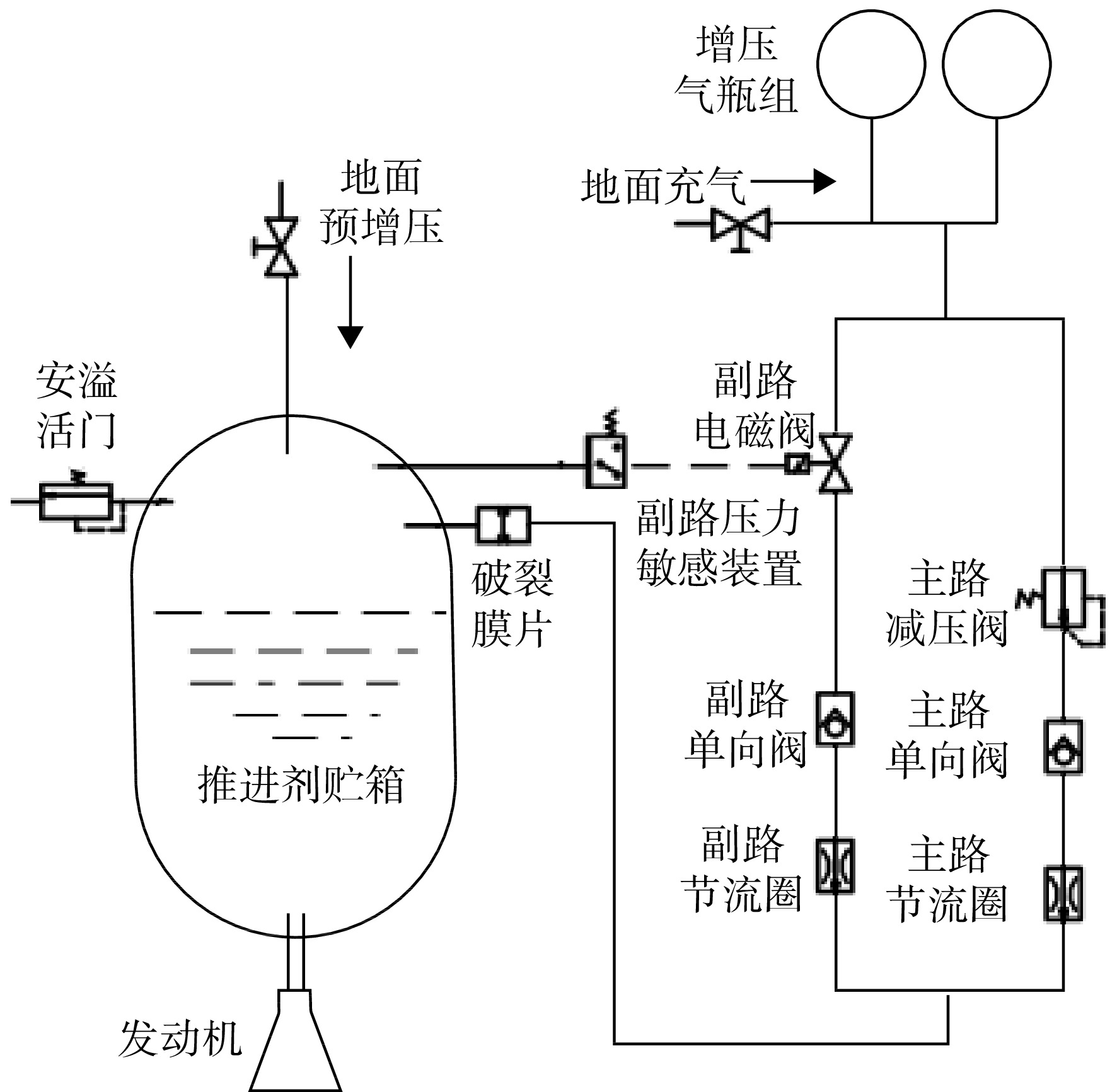
Identification of key transfer parameters of rocket engine pressurization system
-
摘要:
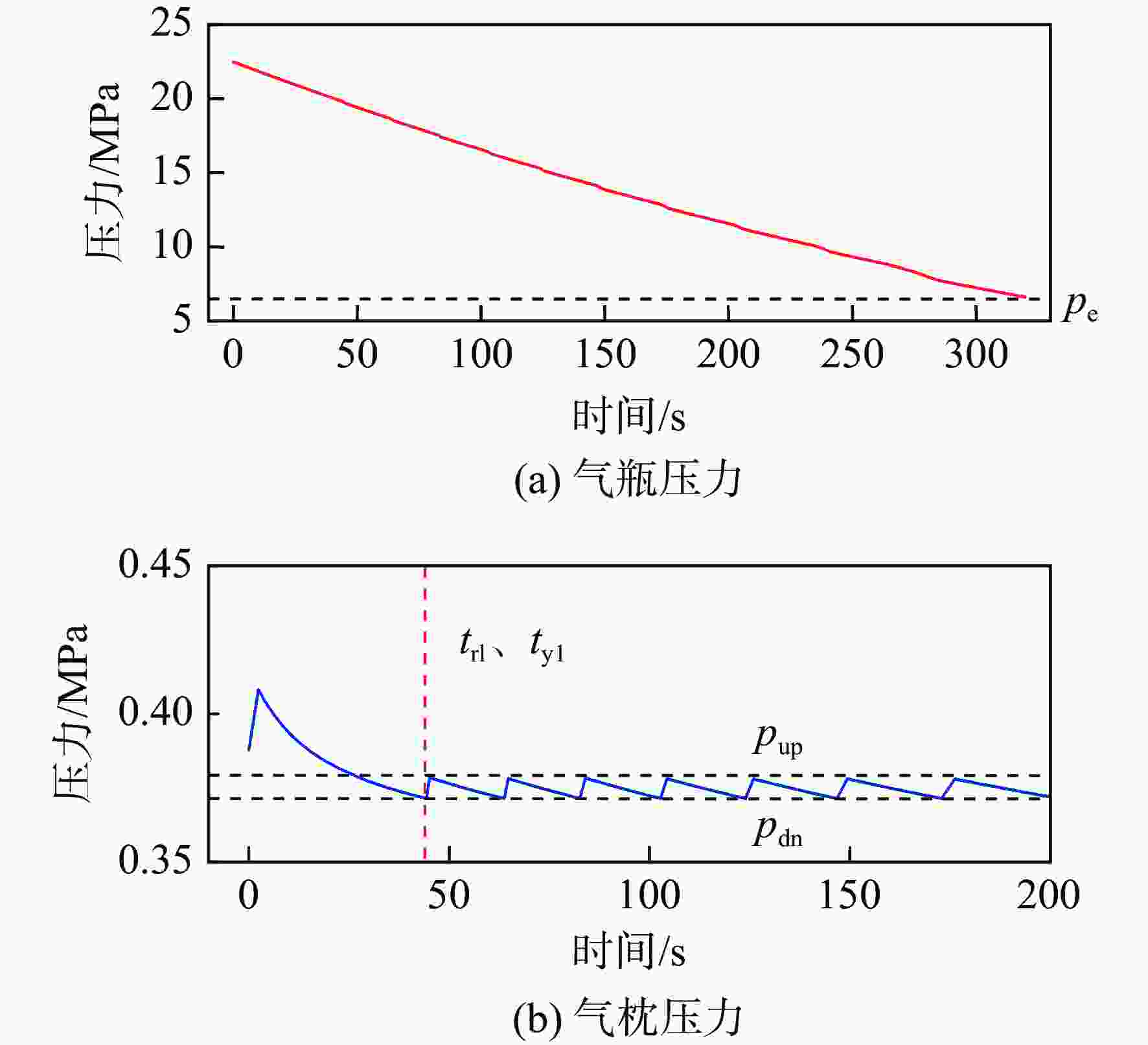
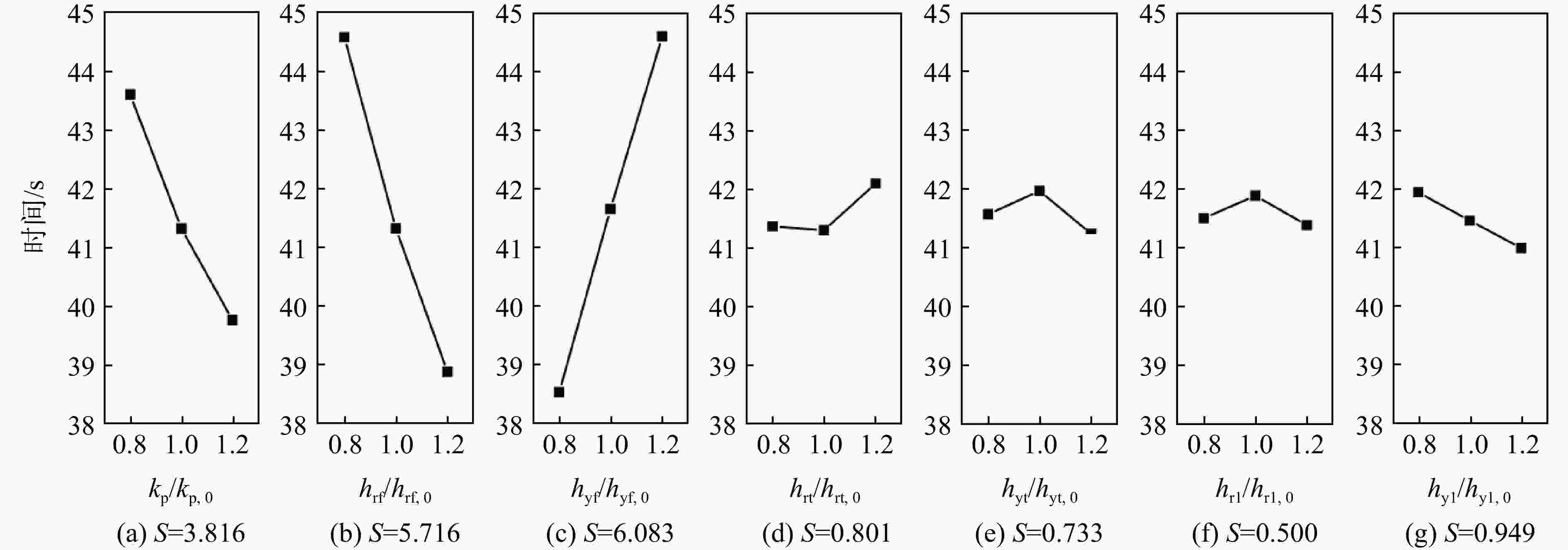
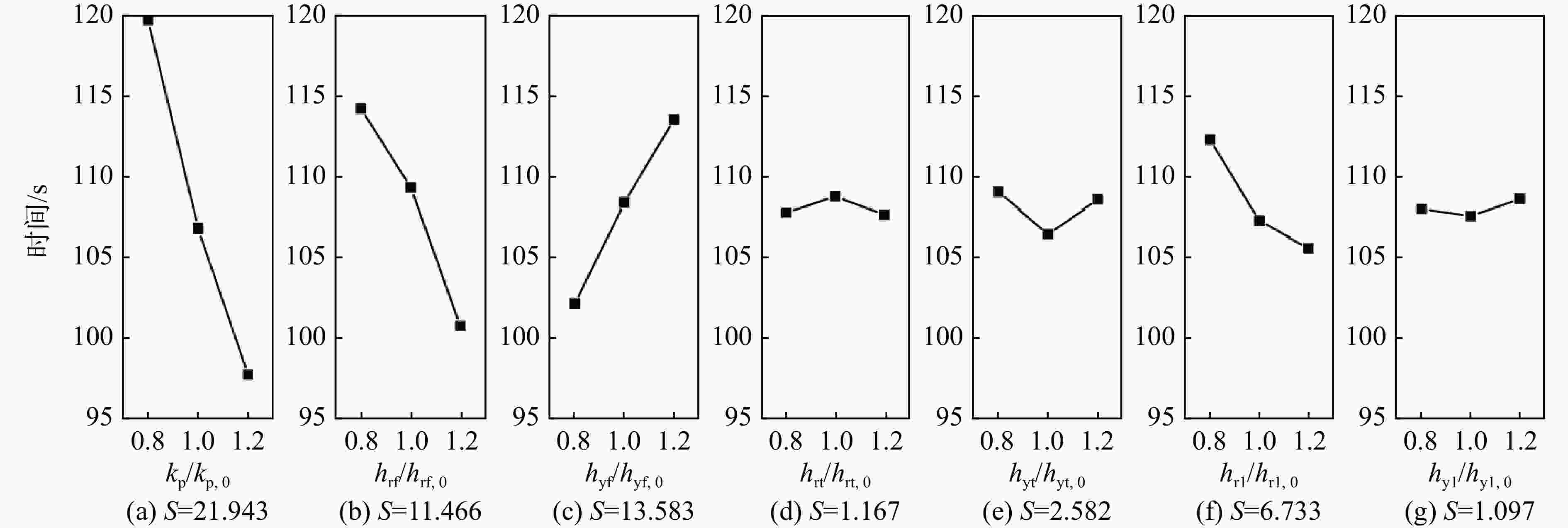
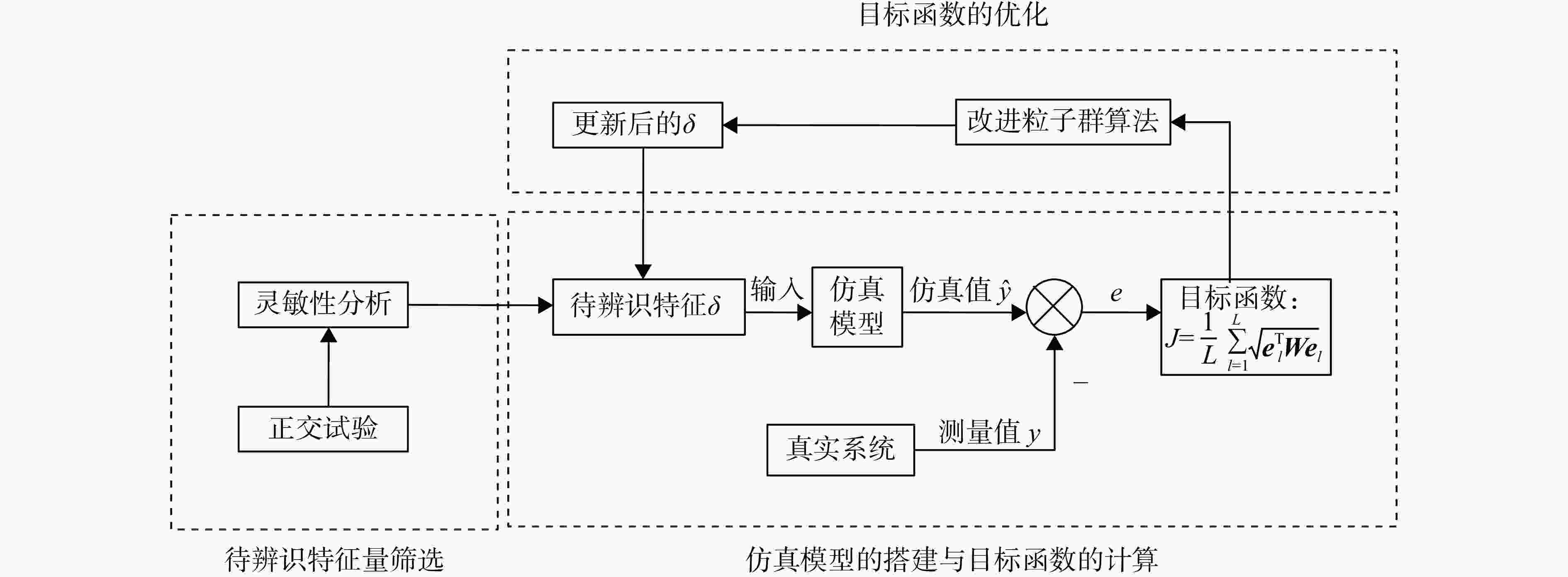
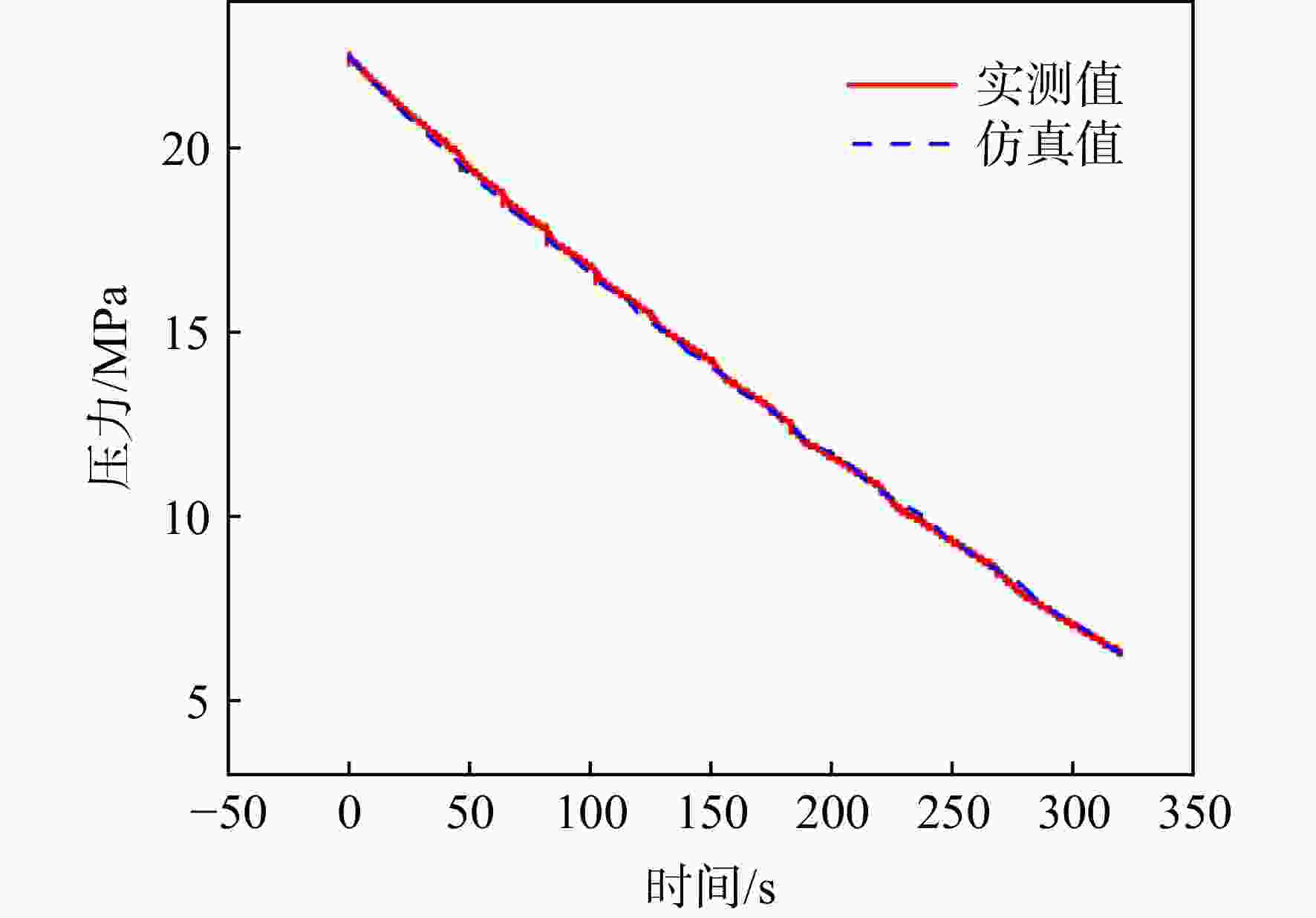
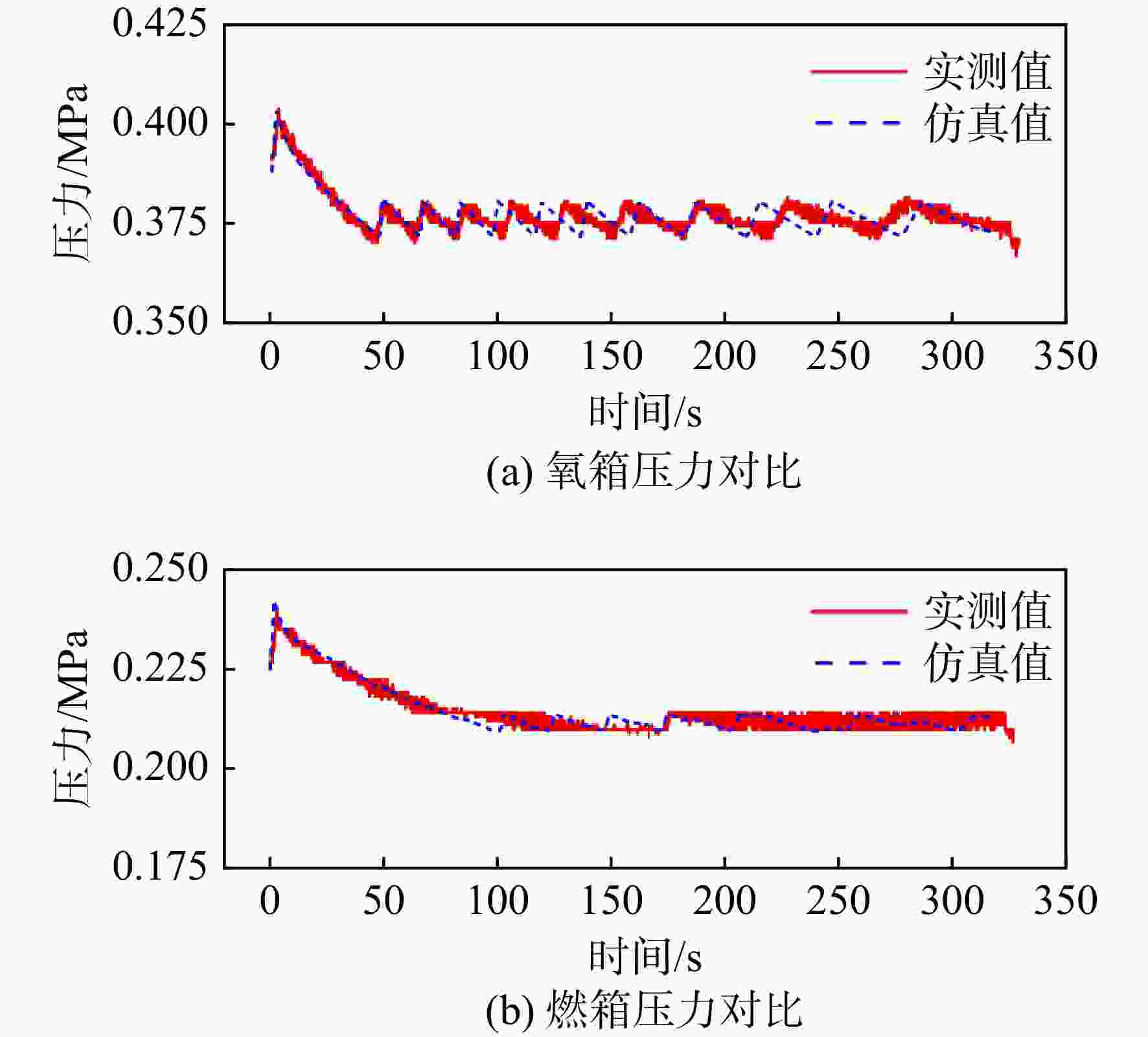
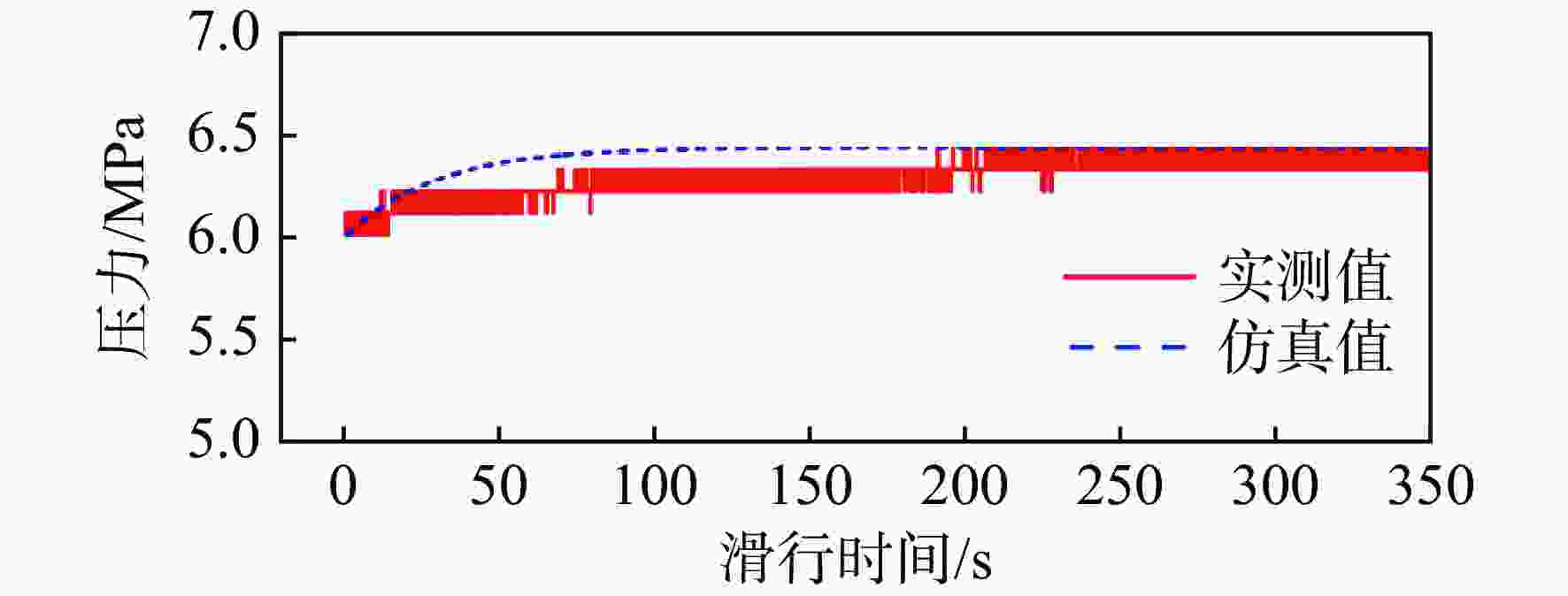
针对火箭增压系统设计过程中关键换热参数难以确定的问题,提出1种基于混沌自适应粒子群算法(ACPSO)的增压系统换热参数辨识方法。建立了考虑换热模型的液体火箭增压系统非线性数学模型,通过灵敏度分析筛选出待识别参数,采用含有早熟抑制和惯性权重自适应调节策略的粒子群方法对选定参量进行辨识,对引入了权重衰减机制的方均根目标函数进行优化。结果表明:辨识后的仿真曲线与实测曲线具有良好的一致性,氧箱增压电磁阀打开时间仿真值与实测值偏差低于3%,气瓶1次飞行结束温度仿真值与实测值仅相差2.4 K。将辨识结果应用于某相似的新研型号,气瓶设计容积和质量相比绝热假设的设计方案降低了32 L和11.6 kg,有效减少了由设计过度冗余造成的额外试验和设计迭代成本。
Abstract:In order to solve the difficulty of determining the key heat transfer parameters in the design of rocket pressurization system, a heat transfer parameter identification method based on adaptive chaotic particle swarm optimization (ACPSO) algorithm was proposed. The mathematical model of the pressurization system considering the heat transfer terms was established. The parameters to be identified were selected by sensitivity analysis, and then identified by particle swarm optimization method with local minimum prevention and adaptive weight strategy. The root mean square function with weight decay was optimized. The results showed that the identified simulation value was in good agreement with the measured value. The deviation between the simulation and the measured value of the opening time of the pressurization electric valve of the oxygen tank was less than 3%, and the deviation between the simulation value and the measured value of the temperature at the end of a flight of the gas bottle was only 2.4 K. If the identification results were applied to a similar newly developed pressurization system, the volume and weight of the gas bottle was reduced by 32 L and 11.6 kg compared with the design under the adiabatic assumption, which effectively saved cost caused by redundant design.
-
表 1 增压输送系统换热参数表
Table 1. Heat transfer parameters in the pressurization system
换热位置 换热项 待辨识参数 搜索范围 增压气瓶 气瓶综合传热系数$ {k_{\text{p}}} $ $ {k_{\text{p}}} $ 100~500 燃、氧路增压气体
与穿舱管壁燃、氧增压气体与管壁强制
表面传热系数$ {h}_{\text{rf}}、{h}_{\text{yf}} $$ {c_{\text{r}}} $、$ {c_{\text{y}}} $ 0.1~0.3 $ {n_{\text{r}}} $、$ {n_{\text{y}}} $ 0.6~0.9 燃、氧箱气枕
与贮箱壁燃、氧箱壁与气枕自然表面传热系数
$ {h}_{\text{rl}}、{h}_{\text{yl}} $ (平行于过载方向)$ {c_{\text{r}}} $、$ {c_{\text{y}}} $ 0.5~0.7 $ {n_{\text{r}}} $、$ {n_{\text{y}}} $ 0.15~0.35 燃、氧箱气枕
与推进剂液面燃、氧箱气枕与推进剂液面自然
表面传热系数$ {h}_{\text{rl}}、{h}_{\text{yl}} $ (垂直于过载方向)$ {c_{\text{r}}} $、$ {c_{\text{y}}} $ 0.5~0.7 $ {n_{\text{r}}} $、$ {n_{\text{y}}} $ 0.15~0.35 表 2 增压输送系统换热参数辨识结果
Table 2. Identification result of heat transfer parameters in the pressurization system
参数 数值 $ {k_{\text{p}}} $/(W/(m2·K)) 424.41 $ {c_{\text{r}}} $ 0.153 $ {n_{\text{r}}} $ 0.759 $ {c_{\text{y}}} $ 0.213 $ {n_{\text{y}}} $ 0.731 -
[1] 廖少英. 一种新的运载火箭上面级和航天器轻型增压系统[J]. 上海航天,2005,22(1): 6-10.LIAO Shaoying. The new light-duty pressurization system for upper stage of the launch vehicle and spacecraft[J]. Aerospace Shanghai,2005,22(1): 6-10. (in Chinese) [2] STOUT P, SNELL S. Multiple on-off solenoid valve control for a launch vehicle propellant tank pressurization system[R]. AIAA 99-4085, 1999. [3] 赵曦,何巍,李东,等. 基于NSGA-Ⅱ的低温贮箱地面增压系统多目标参数优化[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术,2015(6): 33-38.ZHAO Xi,HE Wei,LI Dong,et al. Multi-objective optimization of cryogenic tank ground pressurization system based on NSGA-Ⅱ algorithm[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles,2015(6): 33-38. (in Chinese) [4] 张浩,王帅,耑锐,等. 过冷度对飞行器贮箱热力学排气系统性能的影响[J]. 火箭推进,2020,46(4): 74-81.ZHANG Hao,WANG Shuai,ZHUAN Rui,et al. Effect of subcooled degree on performance of thermodynamic vent system in spacecraft tank[J]. Journal of Rocket Propulsion,2020,46(4): 74-81. (in Chinese) [5] 汪彬,王天祥,黄永华,等. 液氢贮箱热力学排气系统建模及控压特性[J]. 化工学报,2016,67(增刊2): 20-25.WANG Bin,WANG Tianxiang,HUANG Yonghua,et al. Modeling and pressure control characteristics of thermodynamic venting system in liquid hydrogen storage tank[J]. CIESC Journal,2016,67(Suppl.2): 20-25. (in Chinese) [6] CORPENING J, BROWN T. Analytic modeling of pressurization and cryogenic propellant conditions for liquid rocket based vehicle designs[R]. Colorado, US: 57th JANNAF Joint Propulsion Meeting, 2010 [7] 王文斌. 液体火箭增压输送系统动态特性仿真与分析[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2009.WANG Wenbin. Numerical simulation and analysis on dynamic characteristics for liquid rocket pressurization feed system[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2009. (in Chinese) [8] AKCAL U, YUKSEK B, URE N K. Modeling and simulation of aerobee-150A sounding rocket[R]. AIAA 2017-1557, 2017. [9] 李心瞳,张源俊,李萌,等. 火星环绕器推进系统建模与可视化研究[J]. 宇航学报,2022,43(2): 221-231.LI Xintong,ZHANG Yuanjun,LI Meng,et al. Research on modeling and visualization of Mars orbiter propulsion system[J]. Journal of Astronautics,2022,43(2): 221-231. (in Chinese) [10] 巩岩博,郑大勇,胡程炜. 低温火箭发动机稳态特性仿真模型与应用[J]. 火箭推进,2020,46(5): 48-56.GONG Yanbo,ZHENG Dayong,HU Chengwei. Model and application of steady-state characteristics simulation for cryogenic rocket engine[J]. Journal of Rocket Propulsion,2020,46(5): 48-56. (in Chinese) [11] 胡正根,湛利华,朱文俐,等. 短壳绝热面积对液氢贮箱绝热性能影响[J]. 航空动力学报,2020,35(8): 1786-1792.HU Zhenggen,ZHAN Lihua,ZHU Wenli,et al. Effect of short-shell insulated area on thermal insulation performance of liquid hydrogen tank[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2020,35(8): 1786-1792. (in Chinese) [12] KUMAR S P,PRASAD B V S S S,VENKATARATHNAM G,et al. Influence of surface evaporation on stratification in liquid hydrogen tanks of different aspect ratios[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2007,32(12): 1954-1960. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2006.08.052 [13] CHEN Liang,LIANG Guozhu. Simulation research of vaporization and pressure variation in a cryogenic propellant tank at the launch site[J]. Microgravity Science and Technology,2013,25(4): 203-211. doi: 10.1007/s12217-013-9340-2 [14] LUDWIG C,DREYER M E,HOPFINGER E J. Pressure variations in a cryogenic liquid storage tank subjected to periodic excitations[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2013,66: 223-234. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2013.06.072 [15] 王峰,周宜红,赵春菊,等. 基于混合粒子群算法的特高拱坝不同材料热学参数反演分析[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2021,61(7): 747-755.WANG Feng,ZHOU Yihong,ZHAO Chunju,et al. Thermal parameter inversion for various materials of super high arch dams based on the hybrid particle swarm optimization method[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology),2021,61(7): 747-755. (in Chinese) [16] 马驰,赵亮,梅雪松,等. 基于粒子群算法与BP网络的机床主轴热误差建模[J]. 上海交通大学学报,2016,50(5): 686-695.MA Chi,ZHAO Liang,MEI Xuesong,et al. Thermal error modeling of machine tool spindle based on particle swarm optimization and neural network[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University,2016,50(5): 686-695. (in Chinese) [17] 杜明杰,吕旭飞,魏锦洲,等. 基于粒子群算法的飞机燃油箱热参数反演[J]. 航空动力学报,2023,38(1): 250-256. doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20210360DU Mingjie,LÜ Xufei,WEI Jinzhou,et al. Inversion of thermal parameters of aircraft fuel tank based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2023,38(1): 250-256. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20210360 [18] 石宇,夏新林,陈学,等. 基于高温瞬态热响应的石英窗口传热系数反演[J]. 航空动力学报,2022,37(4): 755-764.SHI Yu,XIA Xinlin,CHEN Xue,et al. Inversion of thermal conductivity of quartz window based on transient thermal response at high temperature[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2022,37(4): 755-764. (in Chinese) [19] 聂万胜,陈新华,戴德海,等. 姿控推进系统发动机关机的管路瞬变特性[J]. 推进技术,2003,24(1): 6-8.NIE Wansheng,CHEN Xinhua,DAI Dehai,et al. Transient characteristics during shutdown operation of liquid feed line for attitude control propulsion subsystem[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2003,24(1): 6-8. (in Chinese) [20] 滕浩,石玉鹏,张亮,等. 基于AMESim减压阀动态特性仿真与试验研究[J]. 上海航天,2015,32(1): 48-53, 67.TENG Hao,SHI Yupeng,ZHANG Liang,et al. Simulative and experimental study of dynamic characteristics of pressure relief valve based on AMESim[J]. Aerospace Shanghai,2015,32(1): 48-53, 67. (in Chinese) [21] 李爱兵. 边坡稳定性影响因素敏感度的正交极差分析方法[J]. 勘察科学技术,1995(4): 28-31, 27.LI Aibing. Orthogonal polar difference analysis method of the sensitivity of the influencing factors for slope stability[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology,1995(4): 28-31, 27. (in Chinese) [22] KENNEDY J, EBERHART R. Particle swarm optimization[C]//Proceedings of ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway, US: IEEE, 2002: 1942-1948. [23] SHI Yuhui, EBERHART R C. Parameter selection in particle swarm optimization[M].Berlin: Springer, 1998: 591-600. [24] 管军,周家胜,易文俊,等. 基于自适应混沌变异粒子群优化算法的旋转弹丸气动参数辨识[J]. 兵工学报,2017,38(1): 73-80.GUAN Jun,ZHOU Jiasheng,YI Wenjun,et al. Identification of spinning projectile aerodynamic parameters using adaptive chaotic mutation particle swarm optimization[J]. Acta Armamentarii,2017,38(1): 73-80. (in Chinese) -







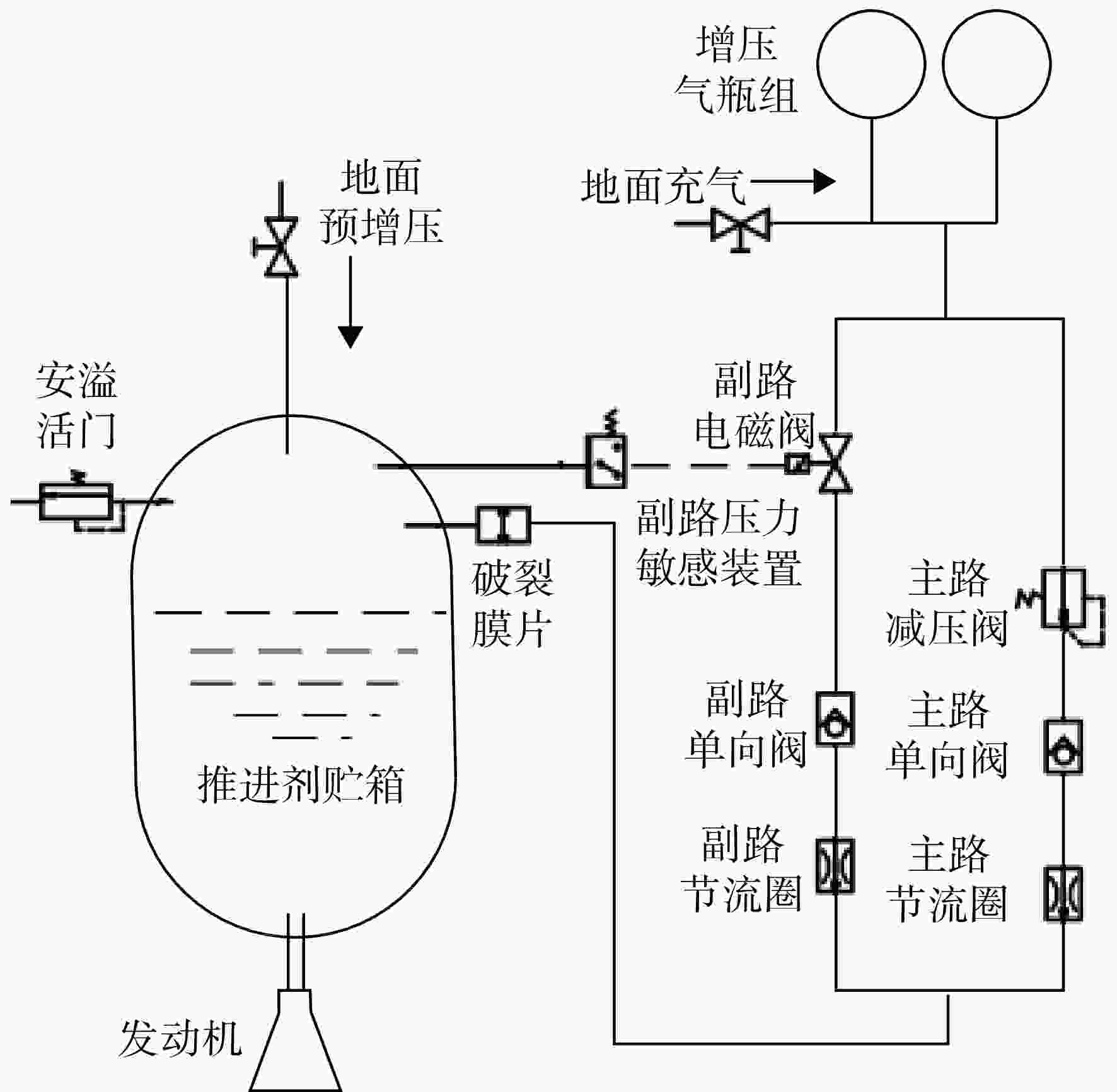
 下载:
下载: