Influence of circumferential position of intake struts on rotor blade excitation and vibration
-
摘要:
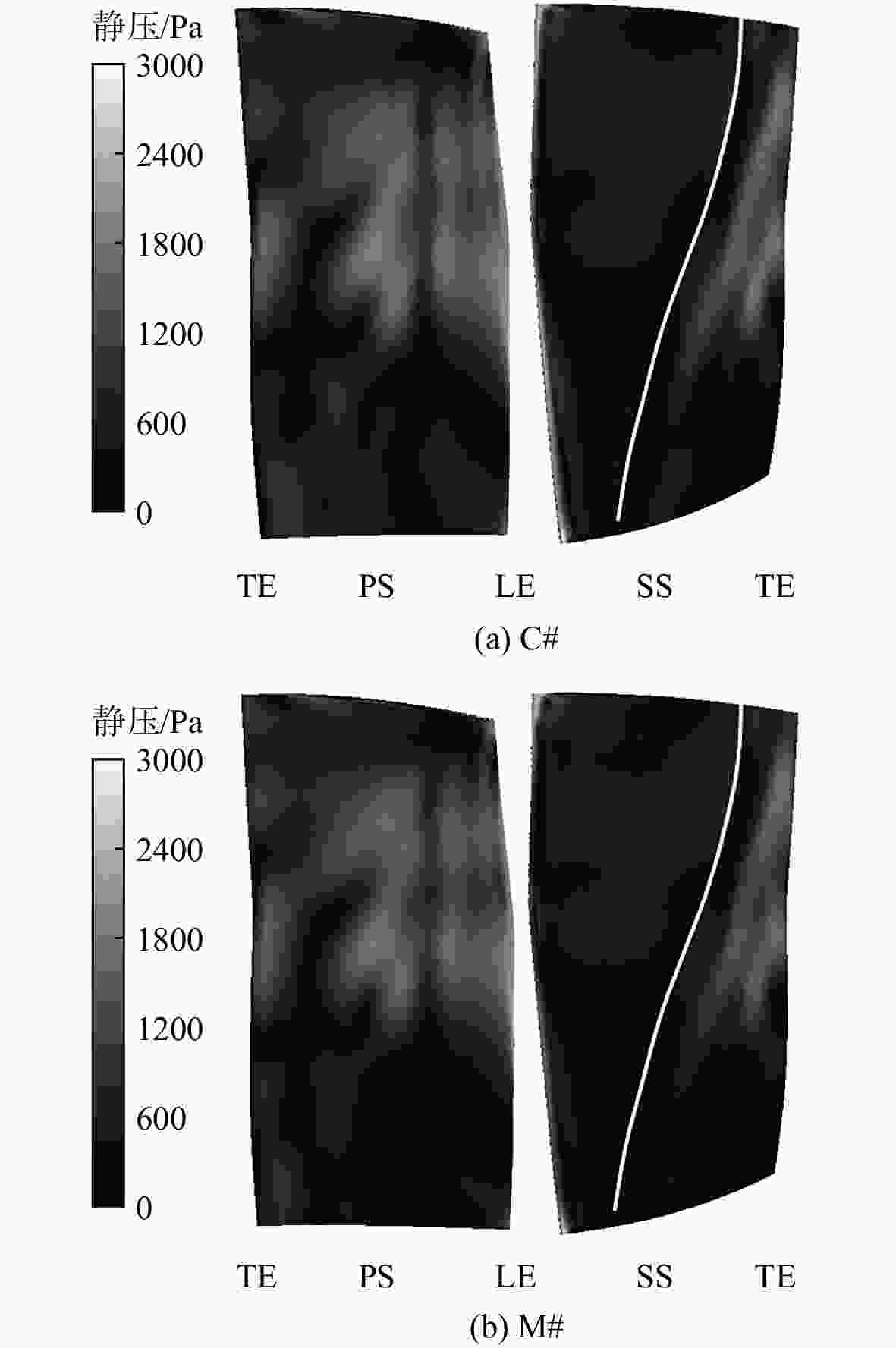
为探究进气支板与下游叶片相对周向位置对压气机动叶所受激励和振动的影响规律和机理,模拟了一个带进气支板的重型燃气轮机压气机前1.5级。通过对动叶片的流场和振动的分析发现:进气支板周向位置对总压比和总温比影响很小,但会明显改变动叶受到的激励和振动水平。当进气支板尾迹与导叶尾迹重合时,两种尾迹叠加加强,导致动叶的激励和振动整体增强。支板位置会明显改变支板尾迹和下游静叶势流对动叶的叠加影响,这对弦长中部非定常载荷和整体振动的影响较明显,对前尾缘附近影响很小。研究结果为支板的安装提供了参考和指导。
Abstract:In order to investigate the influence law and mechanism of the relative circumferential position of the intake struts and downstream blades on the excitation and vibration of the rotor blade, the first 1.5 stage of a heavy-duty gas turbine compressor with intake struts was numerically simulated. Through analysis of the flow field and vibration of the rotor blade, it was found that the circumferential position of the intake struts had little effect on the total pressure ratio and total temperature ratio, but it could obviously change the excitation and vibration level of the rotor blade. When intake strut wakes and guide vane wakes coincided, the two wakes were superimposed and strengthened, resulting in the overall enhancement of excitation and vibration on the rotor blade. The circumferential position of struts obviously changed the combined effect of strut wake and downstream static blade potential flow on rotor blades, which had obvious influence on the unsteady load and global vibration in the middle chord length, but had little influence on the unsteady load near the leading edge and trailing edge. The research results can provide a reference and guidance for the installation of struts.
-
Key words:
- intake struts /
- excitation /
- vibration /
- rotor-stator interaction /
- compressor
-
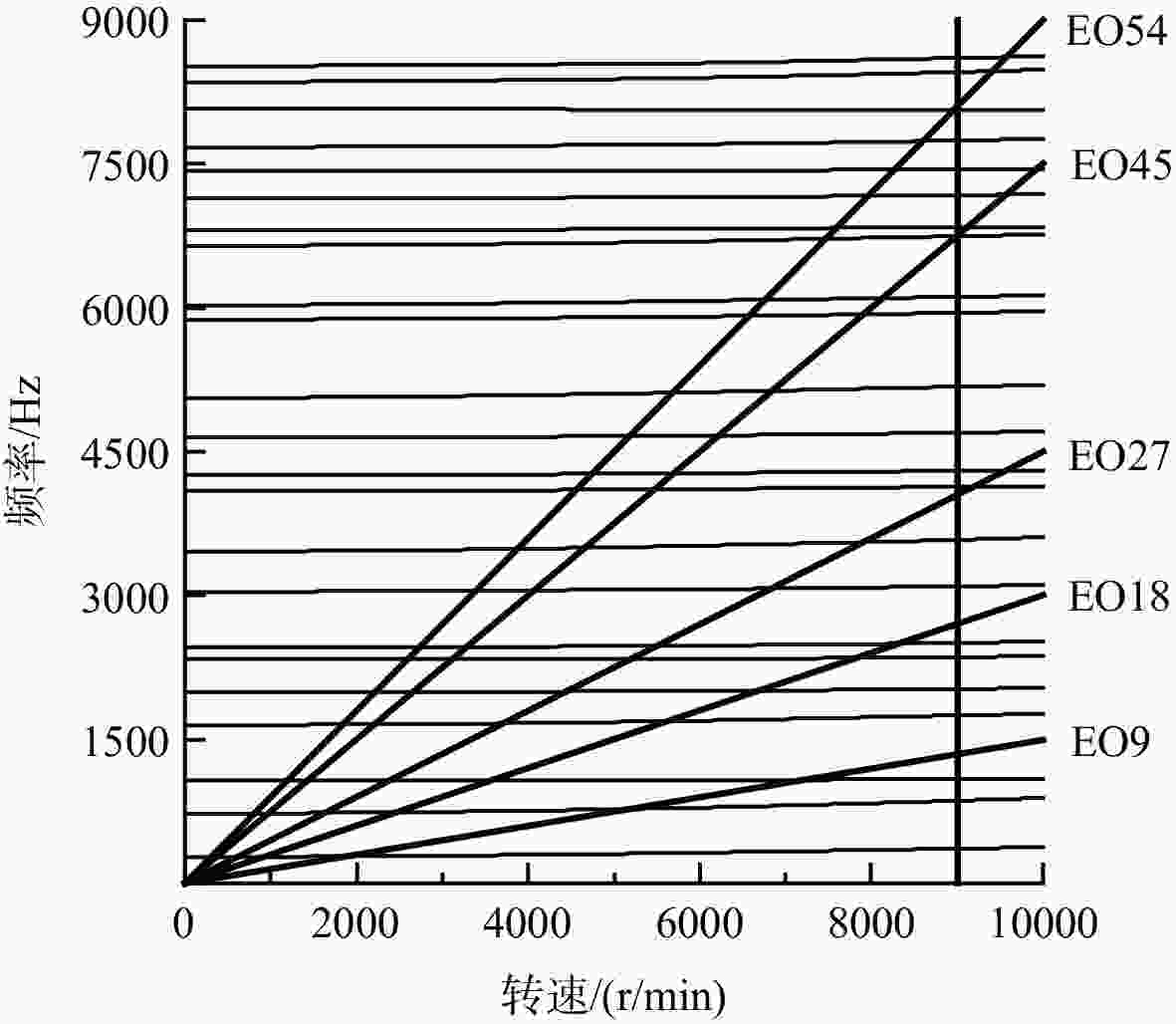
表 1 R1动叶受力的主要频率与叶片数关系
Table 1. Relationship between main frequencies of R1 rotor blade force and number of blades
频率/Hz 激励阶次EO 频率倍数 Strut IGV S1 1350 9 1 2700 18 2 4050 27 3 6750 45 5 1 8100 54 6 1 表 2 R1轴向力主要频率分量
Table 2. Main frequency component of R1 axial force
频率/Hz 轴向力/N 轴向力
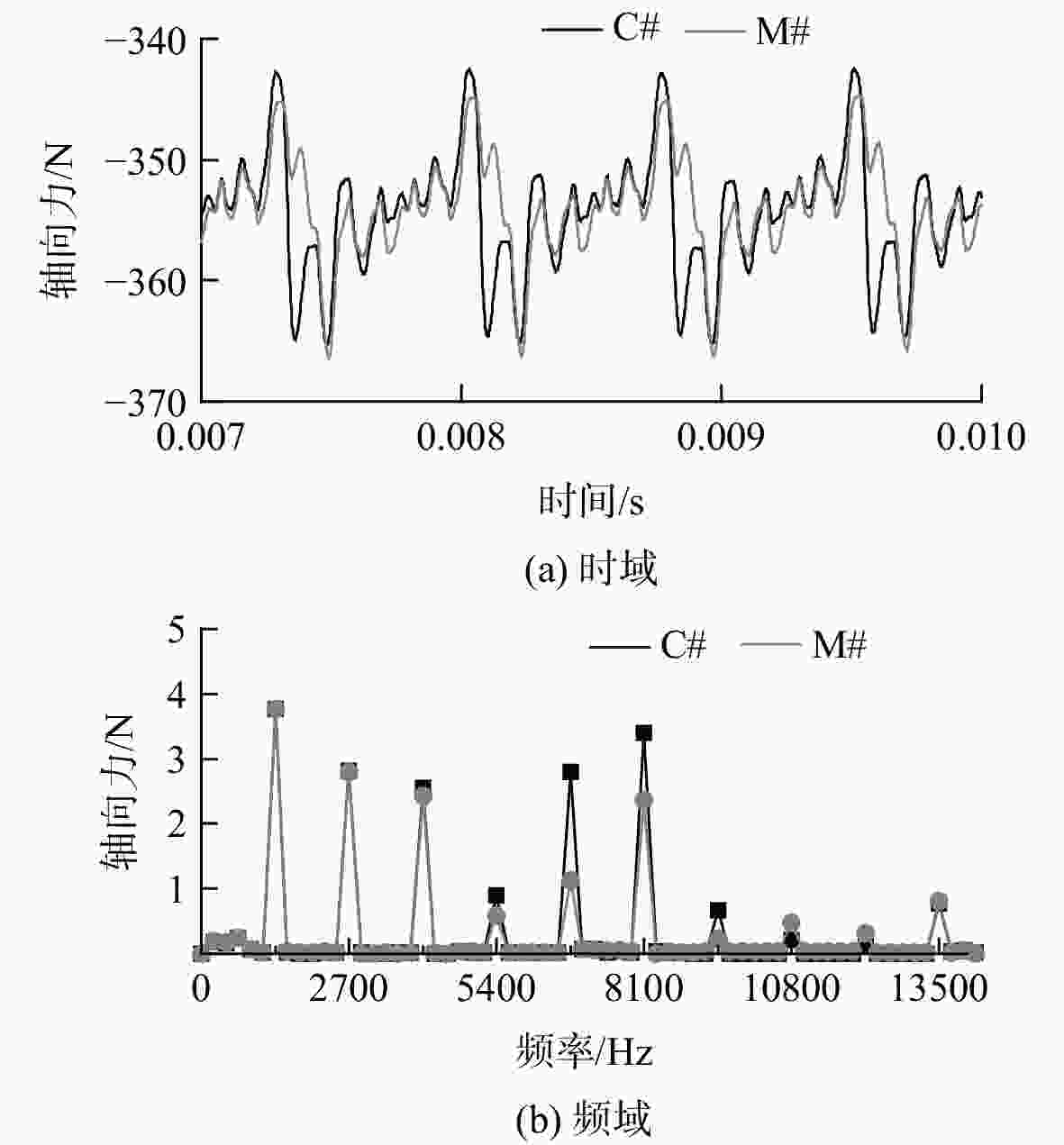
相对差值/%C# M# 1350 3.77 3.77 0.11 2700 2.81 2.81 −0.20 4050 2.55 2.43 −4.77 6750 2.79 1.13 −59.55 8100 3.40 2.36 −30.64 表 3 R1动叶最大振幅
Table 3. Maximum amplitude of R1 rotor blade
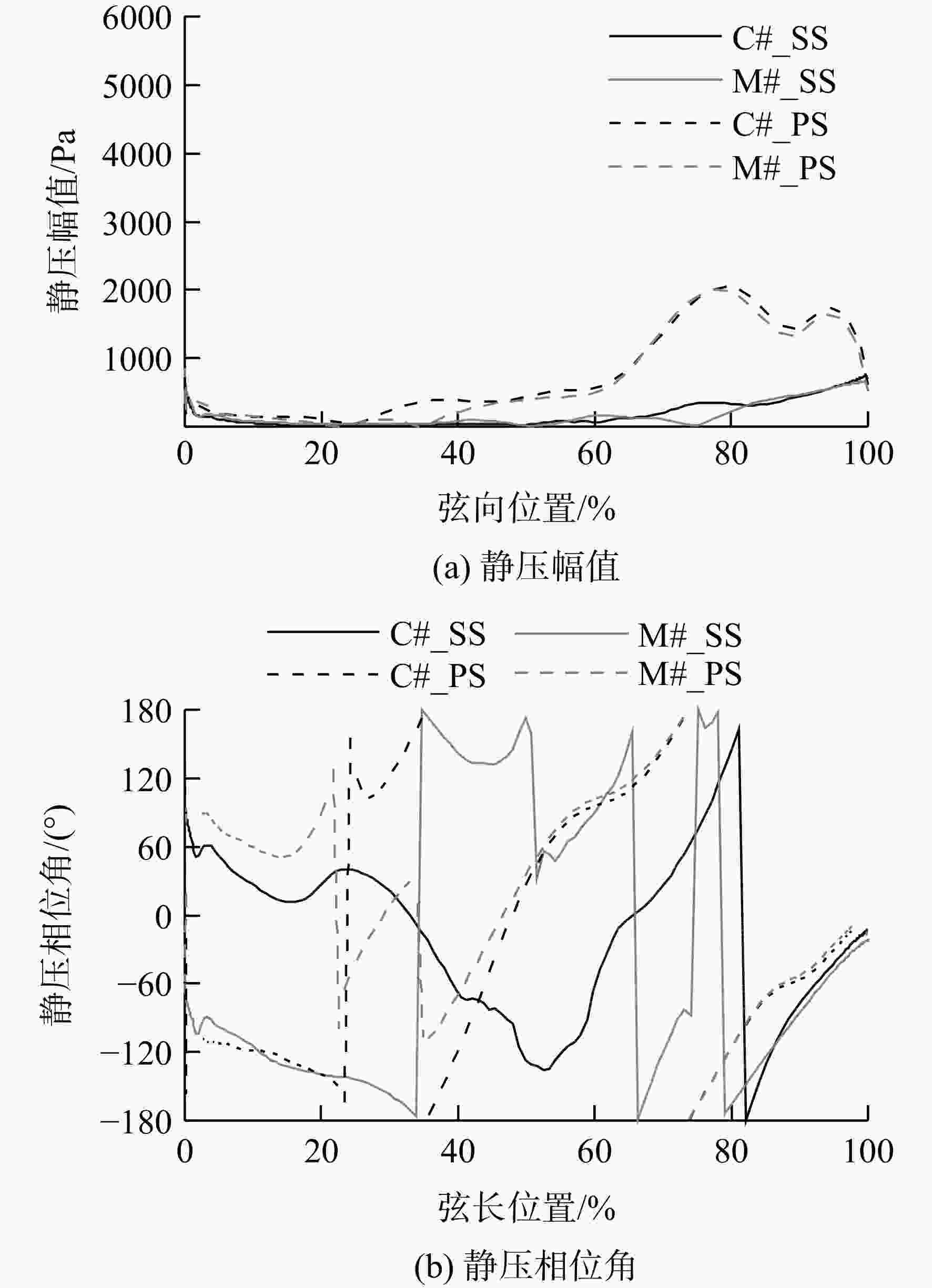
频率/Hz 振幅/μm 相对差值/% C# M# 1350 3.02 3.10 2.65 2700 0.98 1.03 5.10 4050 0.78 0.80 2.56 6750 5.63 4.20 −25.40 8100 0.63 0.52 −17.46 表 4 IGV/R1交界面处总压EO54分量
Table 4. EO54 component of total pressure at IGV/R1 interface
尾迹来源 总压谐波
分量/Pa总压幅值/
Pa相位角/
(°)进气支板+
进口导叶(C#)1079.9+566.88i 1219.6 27.70 进气支板+
进口导叶(M#)660.32+335.82i 740.81 26.96 单独进口导叶 865.93+447.35i 974.66 27.32 单独进气支板(C#) 213.95+119.53i 245.08 29.19 单独进气支板(M#) −205.60−111.54i 233.91 −151.52 -
[1] SRINIVASAN A V. Flutter and resonant vibration characteristics of engine blades[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power,1997,119(4): 742-775. doi: 10.1115/1.2817053 [2] 李茂义,袁巍,陆亚钧,等. 进气畸变对跨声速轴流压气机气动影响的机理研究[J]. 航空动力学报,2014,29(2): 374-383.LI Maoyi,YUAN Wei,LU Yajun,et al. Mechanism investigation of aerodynamic effect on the inlet flow distortion in a transonic axial-flow compressor[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2014,29(2): 374-383. (in Chinese) [3] WANG Ziwei,JIANG Xiong,CHEN Ti,et al. Numerical simulation of transonic compressor under circumferential inlet distortion and rotor/stator interference using harmonic balance method[J]. Modern Physics Letters B,2018,32(12/13): 1840021.1-1840021.6. [4] BARRECA P,PINELLI L,VANTI F,et al. Aeroelastic investigation of a transonic compressor rotor with multi-row effects[J]. Energy Procedia,2018,148: 58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2018.08.019 [5] SANDERS C,TERSTEGEN M,JESCHKE P,et al. Rotor-stator interactions in a 2.5-stage axial compressor: Part Ⅱ impact of aerodynamic modeling on forced response[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2019,141(10): 101008.1-101008.9. [6] HALAWA T,GADALA M S. Numerical investigation of compressor blades deformation during stall development into surge[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power,2017,33(5): 1074-1086. doi: 10.2514/1.B36076 [7] LIANG Feng,XIE Zhifeng,XIA Aiguo,et al. Aeroelastic simulation of the first 1.5-stage aeroengine fan at rotating stall[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2020,33(2): 529-549. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2019.05.004 [8] YANG Rongfei,WANG Guoliang,LIU Haixu,et al. Numerical study on the flow mechanism of compressor rotor blade vibration under different inlet probe configurations[J]. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering,2020,2020: 1-12. [9] HAN Le,WEI Dasheng,WANG Yanrong,et al. Analysis method of nonsynchronous vibration and influence of tip clearance flow instabilities on nonsynchronous vibration in an axial transonic compressor rotor[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2021,143(11): 111014.1-111014.15. [10] 李其汉,王延荣,王建军. 航空发动机叶片高循环疲劳失效研究[J]. 航空发动机,2003,29(4): 16-18, 41.LI Qihan,WANG Yanrong,WANG Jianjun. Investigation of high cycle fatigue failures for the aero engine blades[J]. Aeroengine,2003,29(4): 16-18, 41. (in Chinese) [11] MANWARING S R,WISLER D C. Unsteady aerodynamics and gust response in compressors and turbines[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,1993,115(4): 724-740. doi: 10.1115/1.2929308 [12] ARMSTRONG E K. Recent blade vibration techniques[J]. Journal of Engineering for Power,1967,89(3): 437-444. doi: 10.1115/1.3616710 [13] MAILACH R,VOGELER K. Rotor-stator interactions in a four-stage low-speed axial compressor: Part Ⅰ unsteady profile pressures and the effect of clocking[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2004,126(4): 507-518. doi: 10.1115/1.1791641 [14] VAHDATI M,SAYMA A I,IMREGUN M. An integrated nonlinear approach for turbomachinery forced response prediction: Part Ⅱ case studies[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures,2000,14(1): 103-125. doi: 10.1006/jfls.1999.0254 [15] BAUER H J,SCHULZ A,SCHWITZKE M. Aerodynamic excitation of blade vibrations in radial turbines[J]. MTZ Worldwide,2013,74(6): 48-54. doi: 10.1007/s38313-013-0065-9 [16] CHIANG H W D,TURNER M G. Compressor blade forced response due to downstream vane-strut potential interaction[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,1996,118(1): 134-142. doi: 10.1115/1.2836594 [17] JONES M G, BARTON M T, O’BRIEN W F. The use of circumferentially nonuniform stators to attenuate LP compressor rotor-stator-strut aerodynamic and mechanical interactions[C]//Proceedings of ASME International Gas Turbine and Aeroengine Congress and Exhibition. Chicago, US: ASME, 2015: 1-8 [18] WALKER A D, MARIAH I, HALL C. An experimental, aerodynamic evaluation of design choices for a low-pressure compressor transition duct[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition. Chicago, US: ASME, 2021: 091004.1-091004.14 [19] CIZMAS P G A,DORNEY D J. The influence of clocking on unsteady forces of compressor and turbine blades[J]. International Journal of Turbo and Jet Engines,2000,17(2): 133-142. [20] LI H D,HE L. Blade count and clocking effects on three-bladerow interaction in a transonic turbine[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2003,125(4): 632-640. doi: 10.1115/1.1622711 [21] LEE Yutai,FENG Jinzhang. Potential and viscous interactions for a multi-blade-row compressor[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2004,126(4): 464-472. doi: 10.1115/1.1740778 [22] KEY N L, LAWLESS P B, FLEETER S. An investigation of the flow physics of vane clocking using unsteady flow measurements[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air. Berlin, Germany: ASME, 2009: 2003-2014. [23] SALONTAY J R,KEY N L,FULAYTER R D. Investigation of flow physics of vane clocking effects on rotor resonant response[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power,2011,27(5): 1001-1007. doi: 10.2514/1.B34081 [24] SAYMA A I,VAHDATI M,IMREGUN M. An integrated nonlinear approach for turbomachinery forced response prediction: Part Ⅰ formulation[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures,2000,14(1): 87-101. doi: 10.1006/jfls.1999.0253 [25] CHAHINE C,VERSTRAETE T,HE L. A comparative study of coupled and decoupled fan flutter prediction methods under variation of mass ratio and blade stiffness[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures,2019,85: 110-125. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2018.12.009 [26] MOFFATT S,HE L. On decoupled and fully-coupled methods for blade forced response prediction[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures,2005,20(2): 217-234. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2004.10.012 [27] SUN Hai’ou,REN Aoyu,WANG Yanhua,et al. Deformation and vibration analysis of compressor rotor blades based on fluid-structure coupling[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis,2021,122: 105216.1-105216.18. [28] RAUBENHEIMER G. Vibration excitation of axial compressor rotor blades[D]. Cape Town, South Africa: University of Stellenbosch, 2011. -








 下载:
下载: