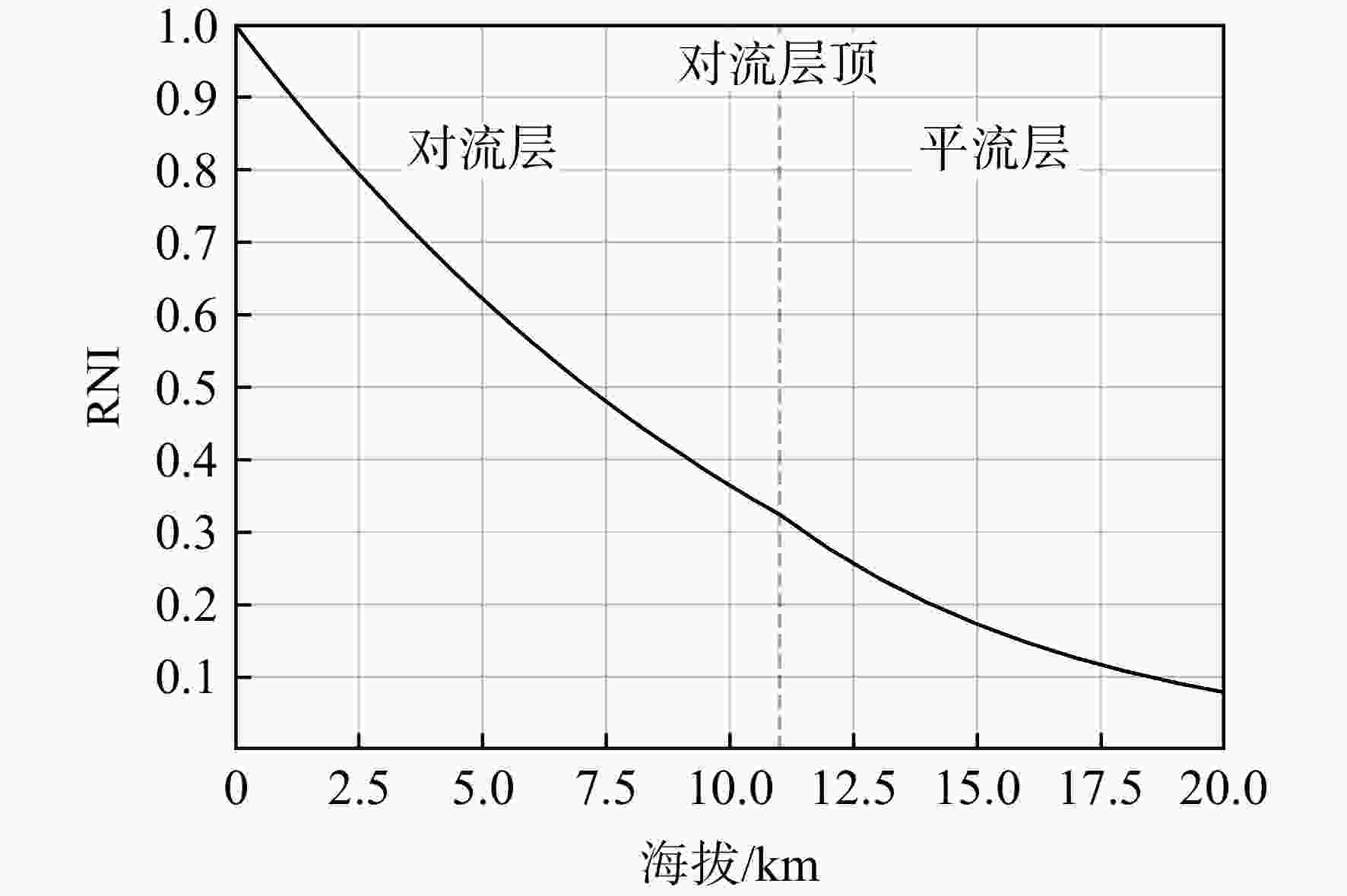
Analysis and application of relationship between Reynolds number index and Reynolds number ratio
-
摘要:
雷诺数指数(RNI)与雷诺数比(RNR)作为常用的雷诺数相关问题重要无量纲数广泛地用于航空发动机研发过程中,然而前者多用于工程研制阶段,后者多用于研究初期阶段,两者长期处于应用层级割裂状态。为了厘清RNI与RNR之间的关系,首先用
Π 定理和无量纲数代数推导两种方法推导出了RNI,结果揭示了RNI的物理含义为考虑马赫数修正的RNR,代表了雷诺数强相似性原理;RNR仅基于表速相似,代表了雷诺数弱相似性原理。其次,比较了雷诺数指数与雷诺数比之间的关系,在两者的相对差仅为温度的函数,在工况温度比处于0.94~1.06的范围时,RNI与RNR两者相差±3%以内,认为两者可以互换;因为工况间温度比差距过大目前以RNR为自变量的雷诺数修正公式在实际使用中误差过大的原因之一。最后,给出了一种基于RNI为1.0、保证雷诺数强相似性的冷热态工作点模化方法,作为RNI的应用范例,并给出了两组冷热态换算结果,计算得到冷热态工况的Π 函数是一致的,因此可以认为冷热态模化满足相似性原理。分析并解释了RNI与RNR的关系,可作为航空发动机研制各阶段中雷诺数相关问题无量纲参数选取的依据。Abstract:The Reynolds number index (RNI) and Reynolds number ratio (RNR) are commonly used as important dimensionless numbers for Reynolds number related problems in the development of aero-engine. However, the former is mostly used in the engineering development stage and the latter mostly used in the early stage of research, and the two have long been in a fragmented state at the application level. In order to clarify the relationship between RNI and RNR, RNI was firstly derived from two perspectives:
$ \varPi $ theorem and algebraic derivation of dimensionless numbers, whose physical meaning was RNR considering Mach number correction, which represented the Reynolds number strong similarity principle. Secondly, the relationship between RNI and RNR was compared, in which the relative difference between these two was only a function of temperature; and when the difference between RNI and RNR was within the working temperature ratio range of 0.94—1.06, the difference between RNI and RNR was within ±3% and these two were considered interchangeable; given the temperature ratio gap between working conditions was too large, this was one of the reasons why the current Reynolds number correction formula with RNR as the independent variable had too much errors in practice. Finally, the operation point at cold and hot states based on RNI of 1.0 was given as one of the applications of RNI, which guaranteed the strong Reynolds number similarity; and the results of two sets of cold and hot state conversions were given, and the$ \varPi $ functions of cold and hot state conditions were calculated to be consistent, and the cold and hot state modelling was considered to satisfy the similarity principle. The relationship between RNI and RNR explained and analyzed herein can be used as a basis for selection of dimensionless parameters for Reynolds number related problems in all stages of aero-engine development. -
表 1 [M−L−T]系统下叶轮机械表征参数
Table 1. Characterization parameters of turbomachinery under [M−L−T] system
特性类型 参数 符号 量纲 机械特征 特征直径/尺寸 $ D $ $ [L] $ 转速 $ N $ $ [{T^{ - 1}}] $ 工质物性 等熵指数 $ \kappa $ $ [1] $ 气体常数 $ R $ $ [1] $ 动力黏度 $ \,\mu $ $ [M{L^{ - 1}}{T^{ - 1}}] $ 流动状态 进口总压 $ p_1^* $ $ [M{L^{ - 1}}{T^{ - 2}}] $ 进口总温 $ T_1^* $ $ [{L^2}{T^{ - 2}}] $ 出口总压 $ p_2^* $ $ [M{L^{ - 1}}{T^{ - 2}}] $ 质量流量 $ \dot m $ $ [M{T^{ - 1}}] $ 特性参数 比焓升/降 $ \Delta h $ $ [{L^2}{T^{ - 2}}] $ 效率 $ \eta $ $ [1] $ 表 2 某低压涡轮冷热态模化结果
Table 2. Results of simularity under hot and cold conditions for a certain low pressure turbine
项目 热态[24] 冷态 给定转速 给定温度 进口质量流量/(kg/s) 4.200 2.333 2.558 进口总压/MPa 0.300 0.0926 0.111 进口总温/K 1078.000 332.716 400.000 膨胀比$ \pi ( {{\varPi _{p_2^*}}} ) $ 2.764 2.764 2.764 转子转速/(r/min) 21600.000 12000.000 13157.530 $ \,\mu $/10−5 (Pa·s) 5.110 2.840 3.112 $ {\varPi _N} $ 657.876 657.876 657.876 $ {\varPi _{\dot m}} $ 459.661 459.661 459.661 $ {\varPi _{\mu} } $ 178.824 178.824 178.824 -
[1] 甘晓华,薛洪涛,雷友锋. 航空发动机工程通论[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社,2021. [2] 李瑶. 航空发动机技术成熟度评价方法研究[J]. 燃气涡轮试验与研究,2010,23(2): 47-51. LI Yao. Aero-engine technology readiness assessment[J]. Gas Turbine Experiment and Research,2010,23(2): 47-51. (in Chinese doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2620.2010.02.012LI Yao. Aero-engine technology readiness assessment[J]. Gas Turbine Experiment and Research, 2010, 23(2): 47-51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2620.2010.02.012 [3] BALJE O E. A study on Reynolds number effects in turbomachines[J]. Journal of Engineering for Power,1964,86(3): 227-235. doi: 10.1115/1.3677584 [4] ROBERTS W B. The effect of Reynolds number and laminar separation on axial cascade performance[J]. Journal of Engineering for Power,1975,97(2): 261-273. doi: 10.1115/1.3445978 [5] WASSELL A B. Reynolds number effects in axial compressors[J]. Journal of Engineering for Power,1968,90(2): 149-156. doi: 10.1115/1.3609154 [6] BALL C L,HEIDELBERG L J,WEIGEL C. Effect of Reynolds number on overall performance of a 6-inch radial bladed centrifugal compressor[R]. NASA TN D-5761,1970. [7] HEIDELBERG L J,BALL C L. Effect of Reynolds number on overall performance of a 3.7-inch-diameter six-stage axial-flow compressor[R]. NASA TN D-6628,1972. [8] 国家国防科技工业局. 航空燃气涡轮发动机轴流涡轮气动性能试验方法: HB 7081-2012[S]. 北京: 中国航空综合技术研究所,2012. [9] 李特维诺夫 Ю А,ЛИТВИНОВ Ю А,鲍罗维克 В О,等. 航空涡轮喷气发动机的特性和使用性能[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社,1986. [10] GIEL P W,BOYLE R J,BUNKER R S. Measurements and predictions of heat transfer on rotor blades in a transonic turbine cascade[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2004,126(1): 110-121. doi: 10.1115/1.1643383 [11] 魏巍,任思源,马护生,等. 亚声速压气机平面叶栅雷诺数影响试验[J]. 航空动力学报,2022,37(5): 1020-1029. WEI Wei,REN Siyuan,MA Husheng,et al. Experiment of Reynolds number effects on subsonic compressor plane cascade[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2022,37(5): 1020-1029. (in ChineseWEI Wei, REN Siyuan, MA Husheng, et al. Experiment of Reynolds number effects on subsonic compressor plane cascade[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2022, 37(5): 1020-1029. (in Chinese) [12] BRACHMANSKI R E,NIEHUIS R,BOSCO A. Investigation of a separated boundary layer and its influence on secondary flow of a transonic turbine profile[R]. Düsseldorf,Germany: ASME Turbo Expo 2014: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition,2014. [13] MOSS J E,BRAITHWAITE W. Effect of slotted casing treatment with change in Reynolds number index on performance of a jet engine[R]. NASA TP 1058,1977. [14] BOBULA G,LOTTIG R A. Inlet Reynolds number and temperature effects on the steady-state performance of a TFE731-2 turbofan engine[R]. NASA TM X-3537,1977. [15] JOHNSEN R,CULLOM R. Altitude test of several afterburner configurations on a turbofan engine with a hydrogen heater to simulate an elevated turbine discharge temperature[R]. NASA TP 1068 E-9207,1977. [16] 侯敏杰. 高空模拟试验技术[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社,2014. [17] 朱俊强,徐纲,卢新根. 航空发动机高空性能分析与试验[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社,2022. [18] 邹滋祥. 相似理论在叶轮机械模型研究中的应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1984. [19] 赵凯华. 定性与半定量物理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社,1991. [20] 许国顺. 刘敏. 温度的本质及其量纲的讨论[J]. 内蒙古科技与经济,2003(2): 125-126. XU Guoshun,LIU Min. Discussion on the essence and dimension of temperature[J]. Inner Mongolia Science Technology and Economy,2003(2): 125-126. (in Chinese doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6921.2003.02.065XU Guoshun, LIU Min. Discussion on the essence and dimension of temperature[J]. Inner Mongolia Science Technology and Economy, 2003(2): 125-126. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6921.2003.02.065 [21] BRIDGMAN P W. Dimensional analysis[M]. New Haven: Yale University Press,1931. [22] 桂幸民,滕金芳,刘宝杰. 航空压气机气动热力学理论与应用[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社,2014. [23] 国家国防科技工业局. 航空燃气涡轮发动机涡轮叶片综合冷却效果试验方法: HB 20086-2012[S]. 北京: 中国航空综合技术研究所,2012. [24] 吴小芳,刘长青,熊清勇. 雷诺数对低压涡轮性能试验冷热态性能差异影响研究[J]. 航空科学技术,2020,31(8): 36-41. WU Xiaofang,LIU Changqing,XIONG Qingyong. Study on the influence of Reynolds number on the difference of cold and hot state of low pressure turbine performance test[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology,2020,31(8): 36-41. (in ChineseWU Xiaofang, LIU Changqing, XIONG Qingyong. Study on the influence of Reynolds number on the difference of cold and hot state of low pressure turbine performance test[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2020, 31(8): 36-41. (in Chinese) [25] 魏巍,马宏伟. 低速模拟技术在高压涡轮级中的应用[J]. 航空动力学报,2013,28(2): 418-425. WEI Wei,MA Hongwei. Applying low-speed modeling method to high pressure turbine stage[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2013,28(2): 418-425. (in ChineseWEI Wei, MA Hongwei. Applying low-speed modeling method to high pressure turbine stage[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2013, 28(2): 418-425. (in Chinese) -








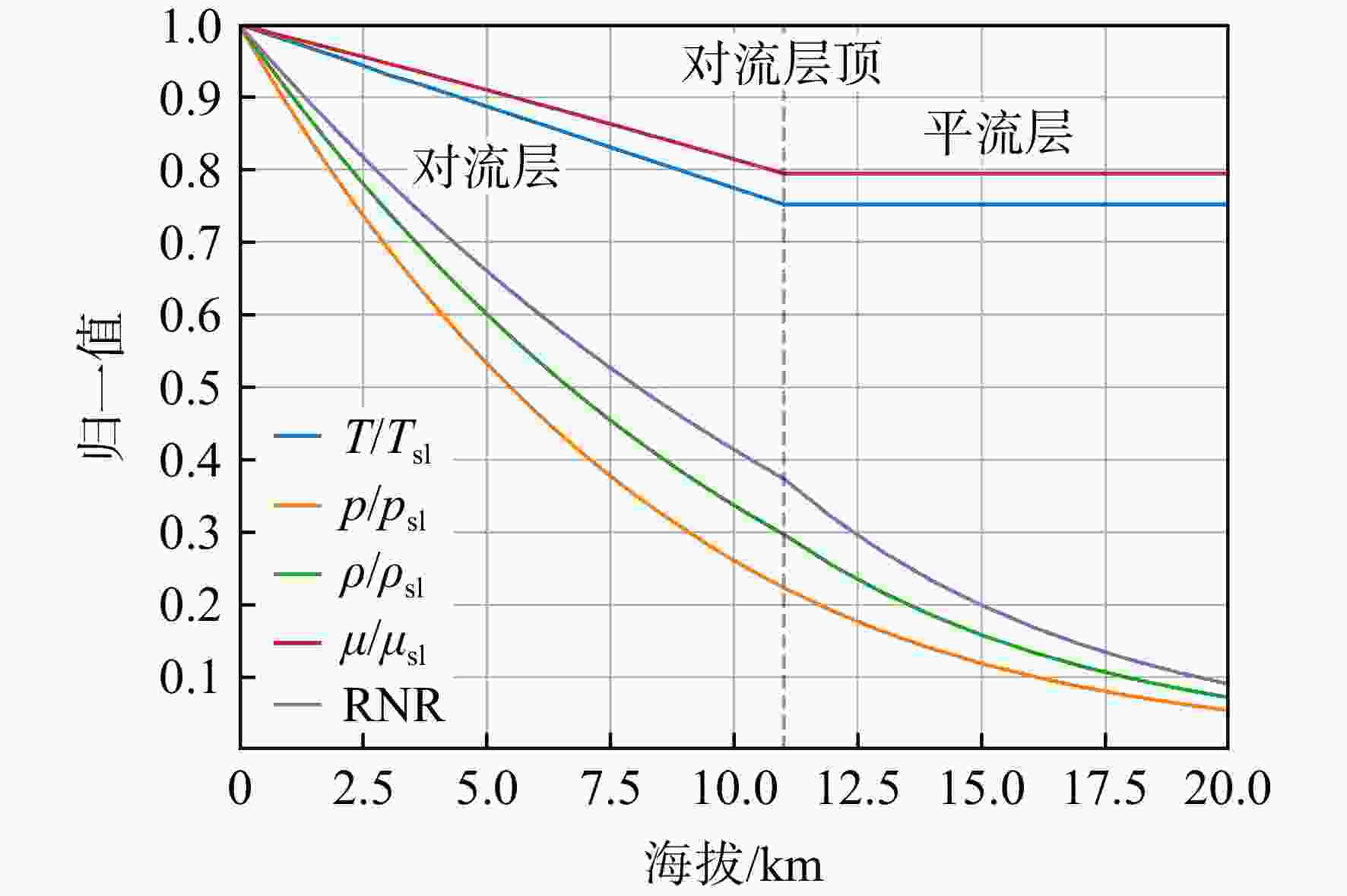
 下载:
下载: