High-temperature fatigue life prediction model of GH4169 electron beam welding joint
-
摘要:
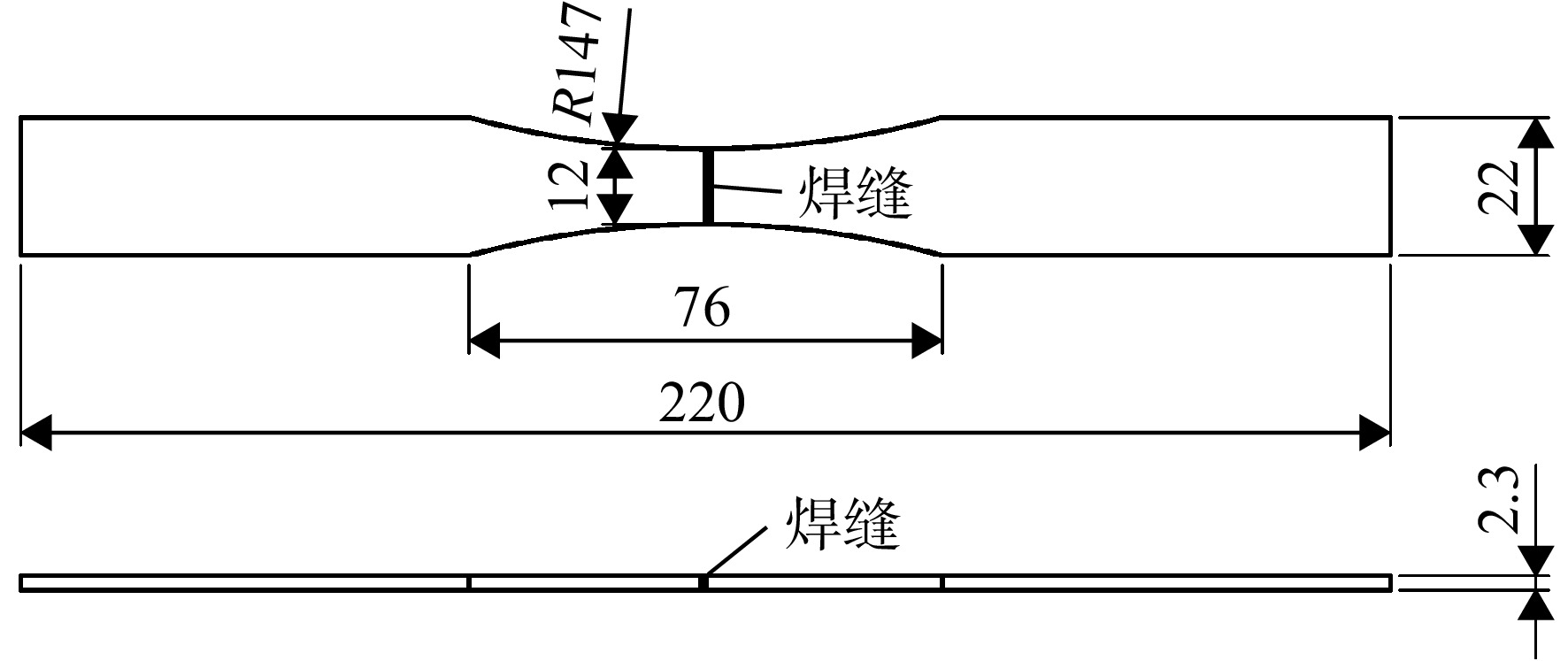
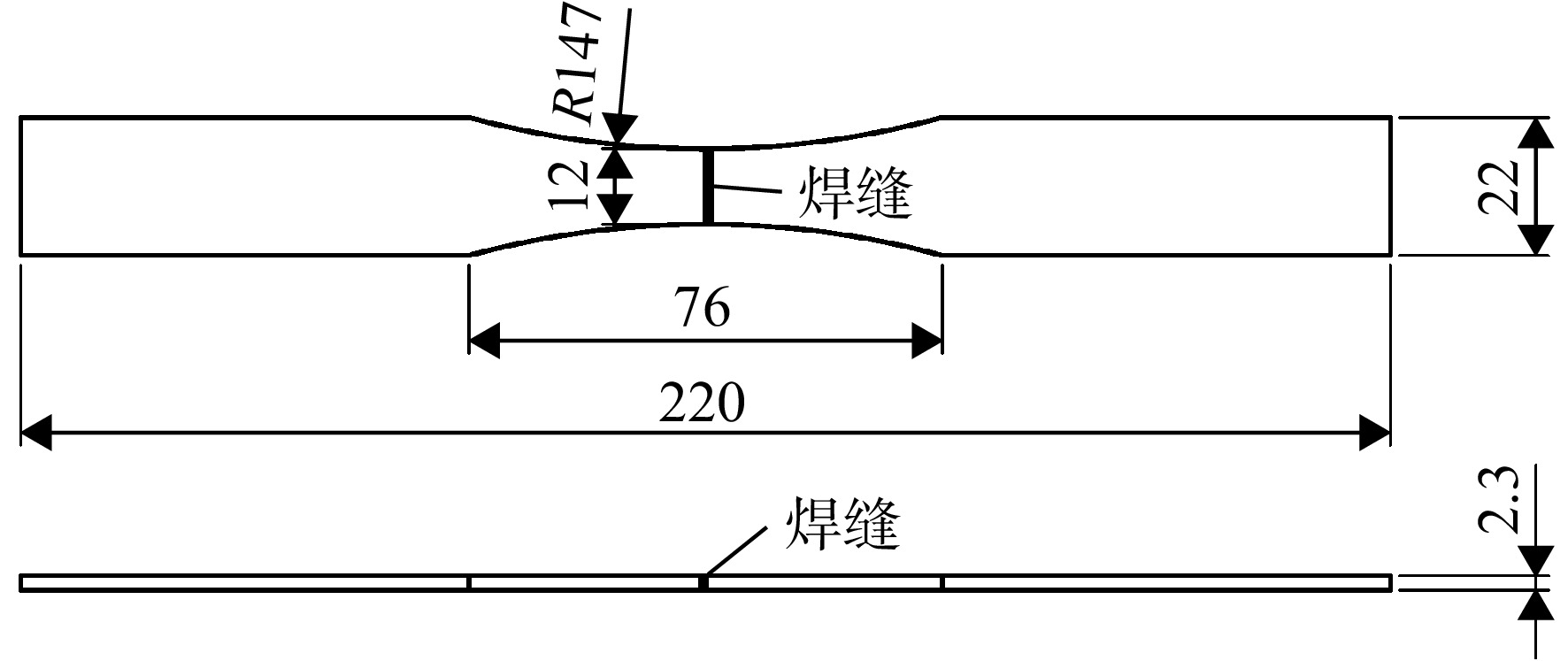
为建立GH4169电子束焊接头的高温疲劳寿命预测模型,开展了电子束焊接头多个温度下的疲劳试验,获得其不同温度下的应力-寿命(
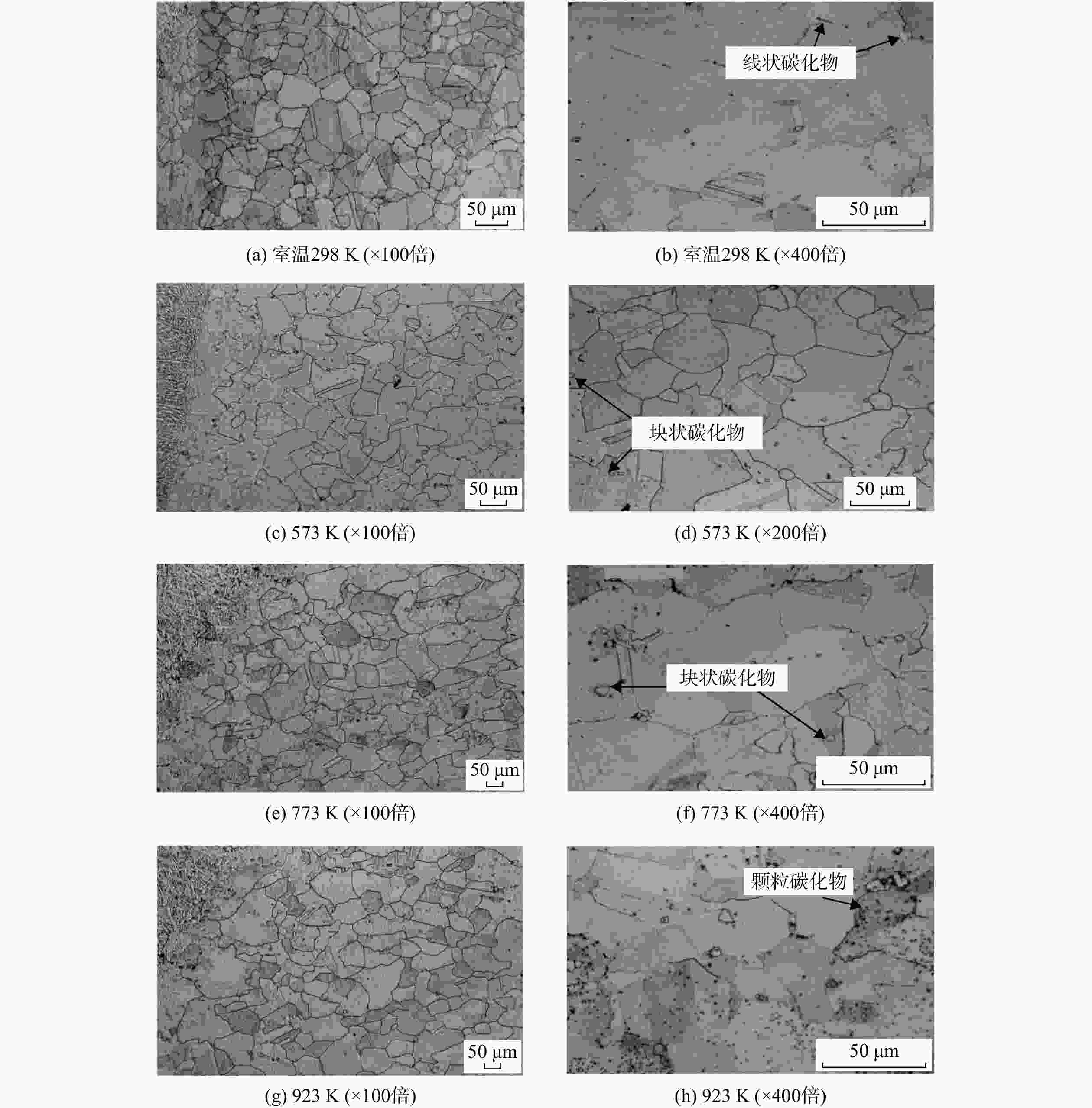
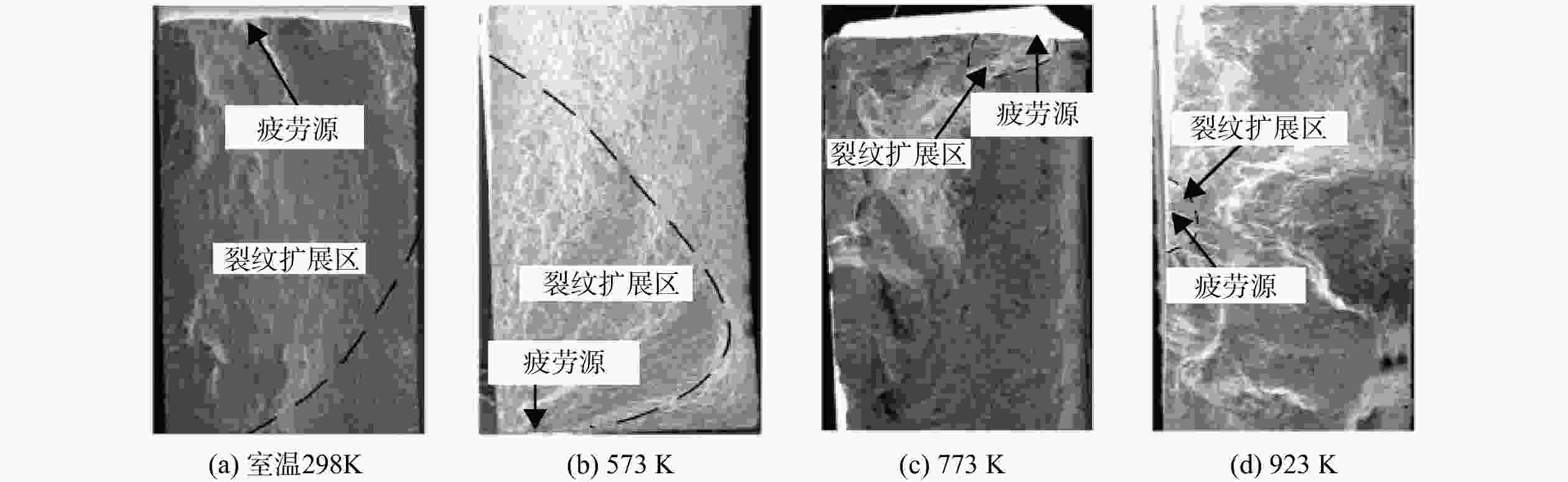
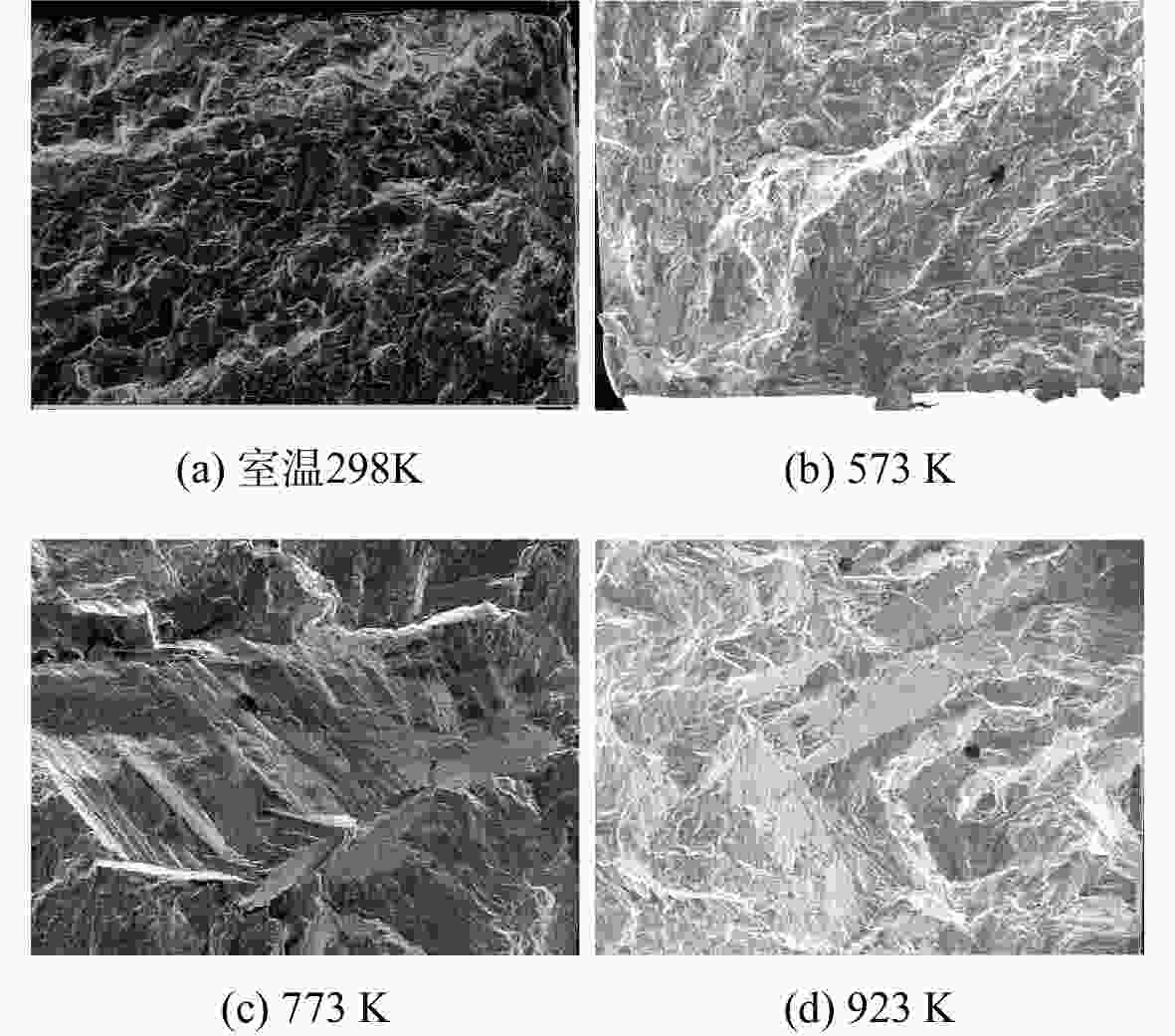
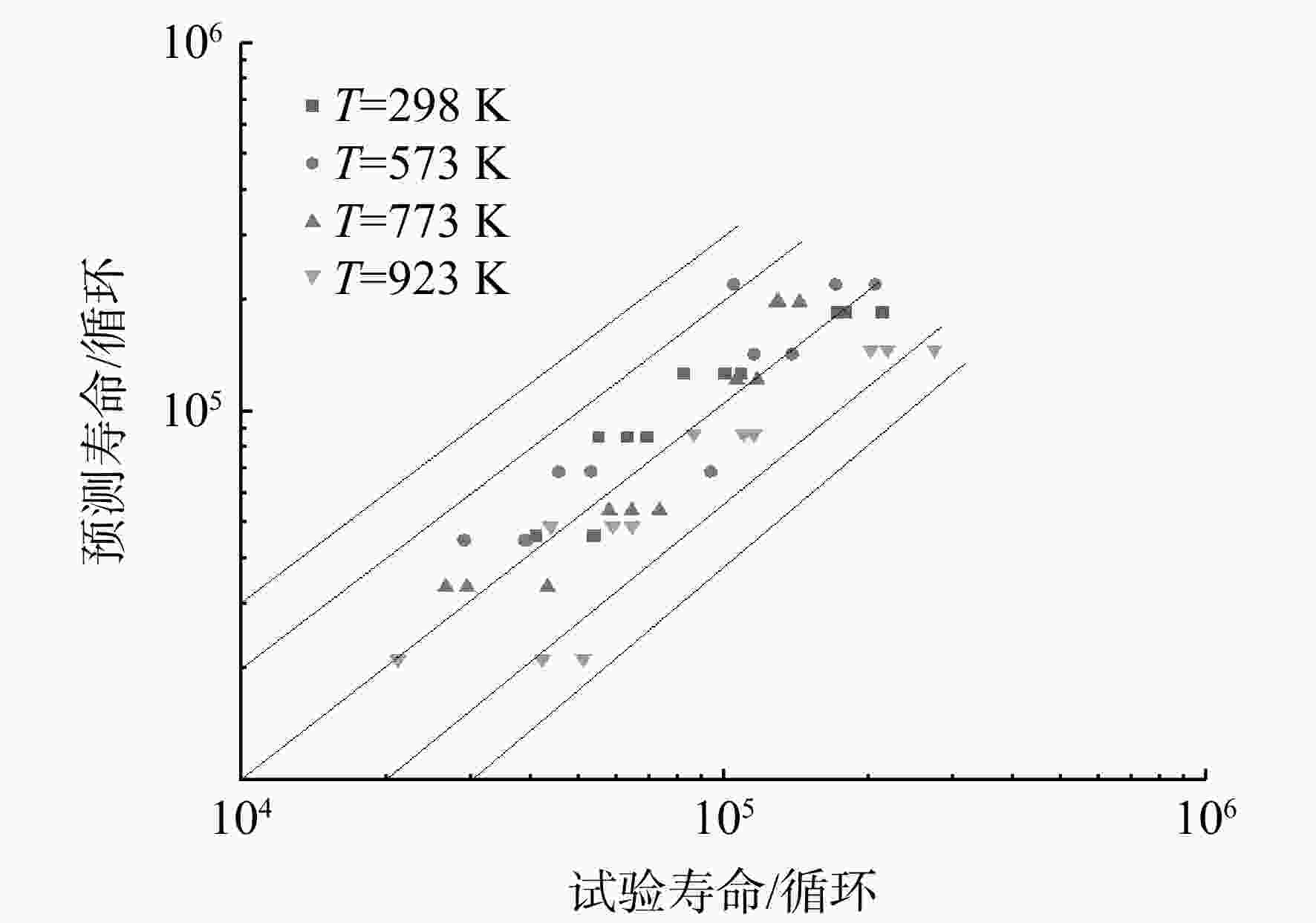
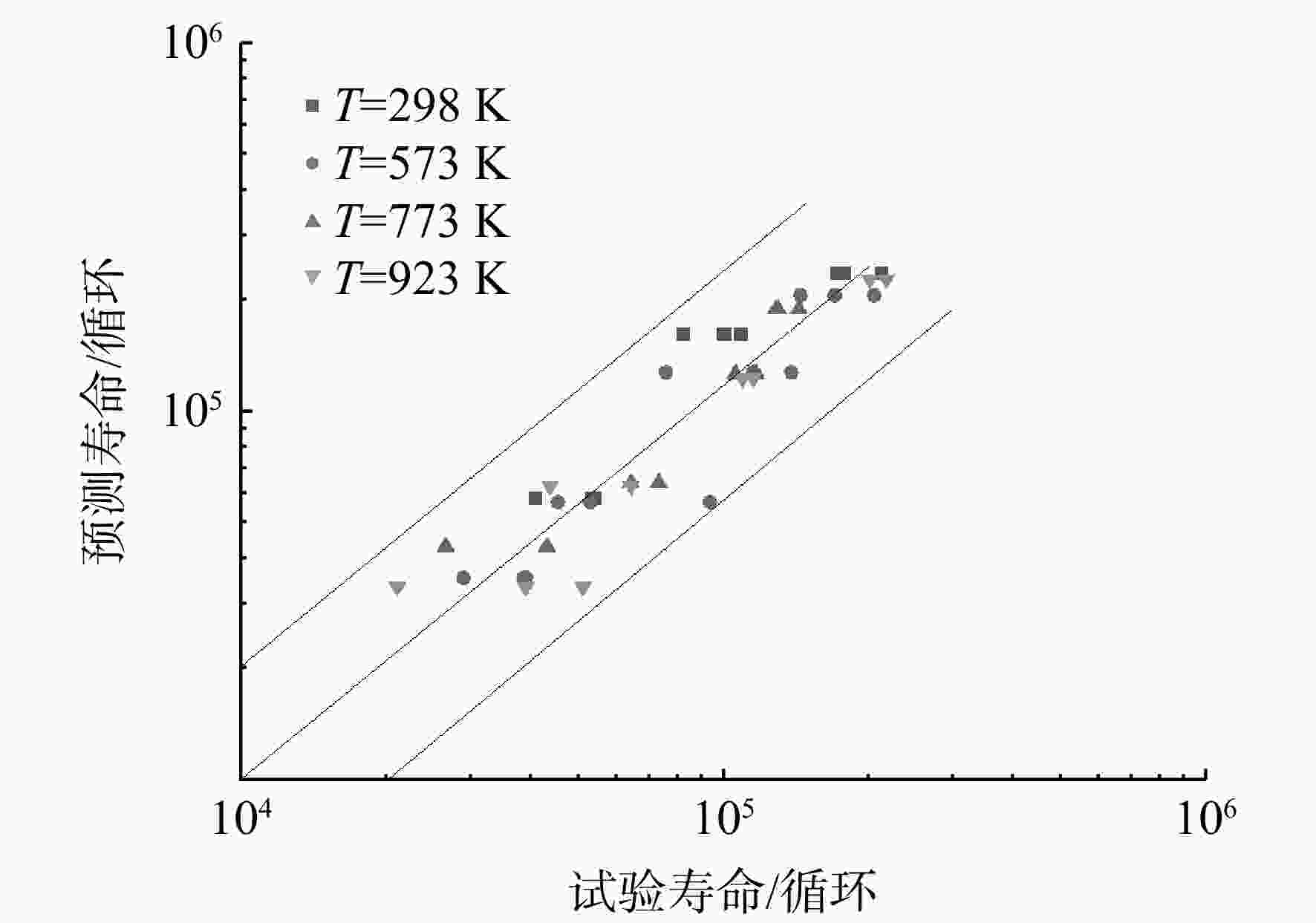
S -N )曲线,分析了温度对接头疲劳性能的影响规律。对疲劳断口进行金相分析和扫描电镜(SEM)观测,研究其高温疲劳损伤机理。结果表明,温度对接头疲劳性能的影响与载荷水平有关,当应力水平大于980 MPa时,随温度升高,接头的疲劳性能呈现明显的下降趋势;此外,接头室温下为穿晶脆性断裂,而高温下呈现出解理断裂特征。在上述分析基础上,考虑屈服强度及晶粒尺寸随温度的变化,结合疲劳试验数据对Basquin模型中材料参数进行修正,建立电子束焊接头高温疲劳寿命预测模型。结果表明:当仅考虑屈服强度因素对参数进行拟合,模型的预测精度较低,而综合考虑屈服强度及晶粒尺寸的影响,修正后的模型预测精度较高,其误差在±2倍分散带以内。Abstract:In order to establish the high-temperature fatigue life prediction model of GH4169 electron beam welded joints, fatigue tests at different temperatures were carried out to obtain the stress-life (
S -N ) curves respectively. The influence of temperature on the fatigue performance of joints was analyzed. The fatigue damage mechanism was studied by metallographic analysis and scanning electron microscope (SEM) test. The results showed that the effect of temperature on the fatigue performance of the joint was related to the load level. Under the load above 980 MPa, the fatigue performance showed an obviously downward trend with the increase of temperature. In addition, the fracture mechanism of joints presented transgranular brittle fracture at room temperature and cleavage fracture at high-temperature. On the basis of the above analysis, considering the changes of yield strength and grain size with temperature, the parameters in Basquin model were modified in combination with fatigue test data, and the high-temperature fatigue life prediction model of welded joints was established. The results showed that the prediction accuracy of the modified model was high when the yield strength and grain size were considered comprehensively, while the accuracy of the model was within 2 times of the dispersion band. -
表 1 电子束焊工艺参数
Table 1. Parameters of electron beam welding process
设备型号 真空度/
10−2 Pa电压/
kV工作距离/
mm扫描频率/
HzZComple X3 5 60 245 400 表 2 热处理工艺参数
Table 2. Parameters of heat treatment process
工艺 加热温度/K 保温时间/h 冷却方式 固溶处理 687 1 空冷 时效处理 447 8 空冷 表 3 不同温度下的静强度参数
Table 3. Static strength parameters at different temperatures
参数 数值 T/K 298 573 773 923 $ {\sigma _{\text{b}}} $/MPa 1391 1352 1255 1221 $ {\sigma _{\text{s}}} $/MPa 1274 1253 1172 1091 表 4 不同温度对应的系数a(T)和b(T)
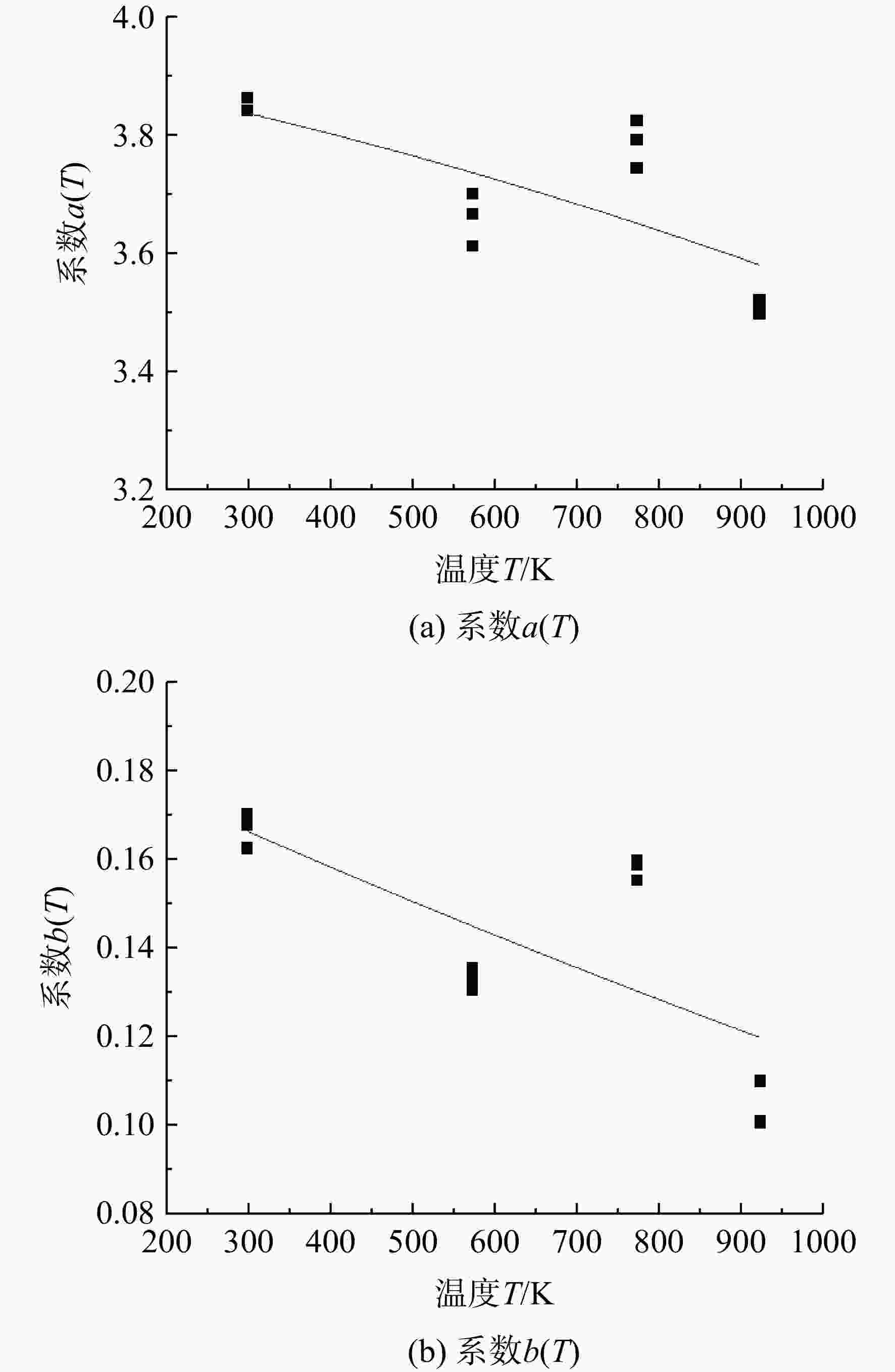
Table 4. Coefficients a(T) and b(T) corresponding to different temperatures
T/K 系数a(T) 系数b(T) 298 3.8412 0.1637 3.8541 0.1692 3.8419 0.1625 573 3.6669 0.1328 3.7013 0.1305 3.6121 0.1355 773 3.7931 0.1597 3.7251 0.1552 3.7453 0.1588 923 3.4994 0.0910 3.5214 0.1005 3.5126 0.1099 -
[1] 杨晓光,黄佳,王井科,等. 定向凝固镍基高温合金缺口低循环疲劳性能及寿命预测[J]. 航空学报,2013,34(7): 1596-1604. YANG Xiaoguang,HUANG Jia,WANG Jingke,et al. Properties and life prediction of low cycle fatigue behavior on notched DS Ni-based superalloy[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2013,34(7): 1596-1604. (in Chinese YANG Xiaoguang, HUANG Jia, WANG Jingke, et al . Properties and life prediction of low cycle fatigue behavior on notched DS Ni-based superalloy[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2013 ,34 (7 ):1596 -1604 . (in Chinese)[2] TAHERI M,KASHANI-BOZORG S F,ALIZADEH A,et al. Analysis of liquation and solidification cracks in the electron beam welding of GTD-111 nickel-base superalloy joint[J]. Materials Research Express,2021,8(7): 076507. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ac1007 [3] LI Ming,ZHU Zheng. Features and application of electron beam welding technology[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2015,1120/1121: 1308-1312. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1120-1121.1308 [4] 康文军,梁养民. 电子束焊接在航空发动机制造中的应用[J]. 航空制造技术,2008,51(21): 54-56. KANG Wenjun,LIANG Yangmin. Application of electron beam welding in aeroengine manufacturing[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2008,51(21): 54-56. (in Chinese doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2008.21.012 KANG Wenjun, LIANG Yangmin . Application of electron beam welding in aeroengine manufacturing[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2008 ,51 (21 ):54 -56 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2008.21.012[5] SONAR T,BALASUBRAMANIAN V,MALARVIZHI S,et al. An overview on welding of Inconel 718 alloy-Effect of welding processes on microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of joints[J]. Materials Characterization,2021,174: 110997. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2021.110997 [6] 肖阳,秦海勤,徐可君,等. 基于改进SWT模型的FGH96合金低周疲劳寿命预测[J]. 航空学报,2021,42(5): 524360. XIAO Yang,QIN Haiqin,XU Kejun,et al. Low cycle fatigue life prediction of FGH96 alloy based on modified SWT model[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2021,42(5): 524360. (in Chinese XIAO Yang, QIN Haiqin, XU Kejun, et al . Low cycle fatigue life prediction of FGH96 alloy based on modified SWT model[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2021 ,42 (5 ):524360 . (in Chinese)[7] KHAN R,KHAN Z,AL-SULAIMAN F,et al. Fatigue life estimates in woven carbon fabric/epoxy composites at non-ambient temperatures[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2002,36(22): 2517-2535. doi: 10.1177/002199802761405277 [8] KIM S,CHOI H,LEE J,et al. Room and elevated temperature fatigue crack propagation behavior of Inconel 718 alloy fabricated by laser powder bed fusion[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2020,140: 105802. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105802 [9] MADERBACHER H,OBERWINKLER B,GÄNSER H P,et al. The influence of microstructure and operating temperature on the fatigue endurance of hot forged Inconel® 718 components[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A,2013,585: 123-131. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.07.053 [10] WANG Runzi,ZHU Shunpeng,WANG Ji,et al. High temperature fatigue and creep-fatigue behaviors in a Ni-based superalloy: damage mechanisms and life assessment[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2019,118: 8-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.05.008 [11] SZUSTA J. Low cycle fatigue of metallic materials under uniaxialloading at elevated temperature[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2018,114: 272-281. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.05.025 [12] SZUSTA J,SEWERYN A. Damage accumulation modeling under uniaxial low cycle fatigue at elevated temperatures[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis,2015,56: 474-483. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2014.11.026 [13] 韩豫,王可胜,刘全坤. 基于Hull-Rimmer理论的应变强化奥氏体不锈钢高温疲劳寿命预测方法[J]. 机械工程学报,2015,51(12): 57-62. HAN Yu,WANG Kesheng,LIU Quankun. High temperature fatigue life prediction method of cold stretched austenitic stainless steel based on the hull-rimmer theory[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2015,51(12): 57-62. (in Chinese doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.12.057 HAN Yu, WANG Kesheng, LIU Quankun . High temperature fatigue life prediction method of cold stretched austenitic stainless steel based on the hull-rimmer theory[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2015 ,51 (12 ):57 -62 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.3901/JME.2015.12.057[14] KRUML T,OBRTLÍK K,PETRENEC M,et al. Cyclic response and fatigue life of TiAl alloys at high temperatures[J]. Key Engineering Materials,2009,417/418: 585-588. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.417-418.585 [15] REN Xudong,ZHANG Yongkang,ZHOU Jianzhou,et al. Effect of laser shock processing on residual stress and fatigue behavior of 6061-T651 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2006,16(3): 1305-1308. [16] OTT E,GROH J,BANIK A,et al. Superalloy 718 and derivatives[J]. International Symposium on Superalloys,2010,10(7): 23-49. [17] ZHU Xumin,GONG Congyang,JIA Yunfei,et al. Influence of grain size on the small fatigue crack initiation and propagation behaviors of a nickel-based superalloy at 650 ℃[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2019,35(8): 1607-1617. [18] 徐文帅,王春旭,厉勇,等. 40CrNi2MoE钢奥氏体晶粒长大的数学模型[J]. 材料热处理学报,2014,35(8): 232-238. XU Wenshuai,WANG Chunxu,LI Yong,et al. Mathematical models of austenite grain growth in 40CrNi2MoE steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment,2014,35(8): 232-238. (in Chinese doi: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2014.08.040 XU Wenshuai, WANG Chunxu, LI Yong, et al . Mathematical models of austenite grain growth in 40CrNi2MoE steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment,2014 ,35 (8 ):232 -238 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2014.08.040[19] QUAN Guozheng,ZHANG Pu,MA Yaoyao,et al. Characterization of grain growth behaviors by BP-ANN and Sellars models for nickle-base superalloy and their comparisons[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2020,30(9): 2435-2448. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65390-0 [20] XU Yaowen,TANG Di,SONG Yong,et al. Prediction model for the austenite grain growth in a hot rolled dual phase steel[J]. Materials & Design (1980-2015),2012,36: 275-278. -







 下载:
下载: