Passive control strategy for flow quality of linear cascade wind tunnel
-
摘要:
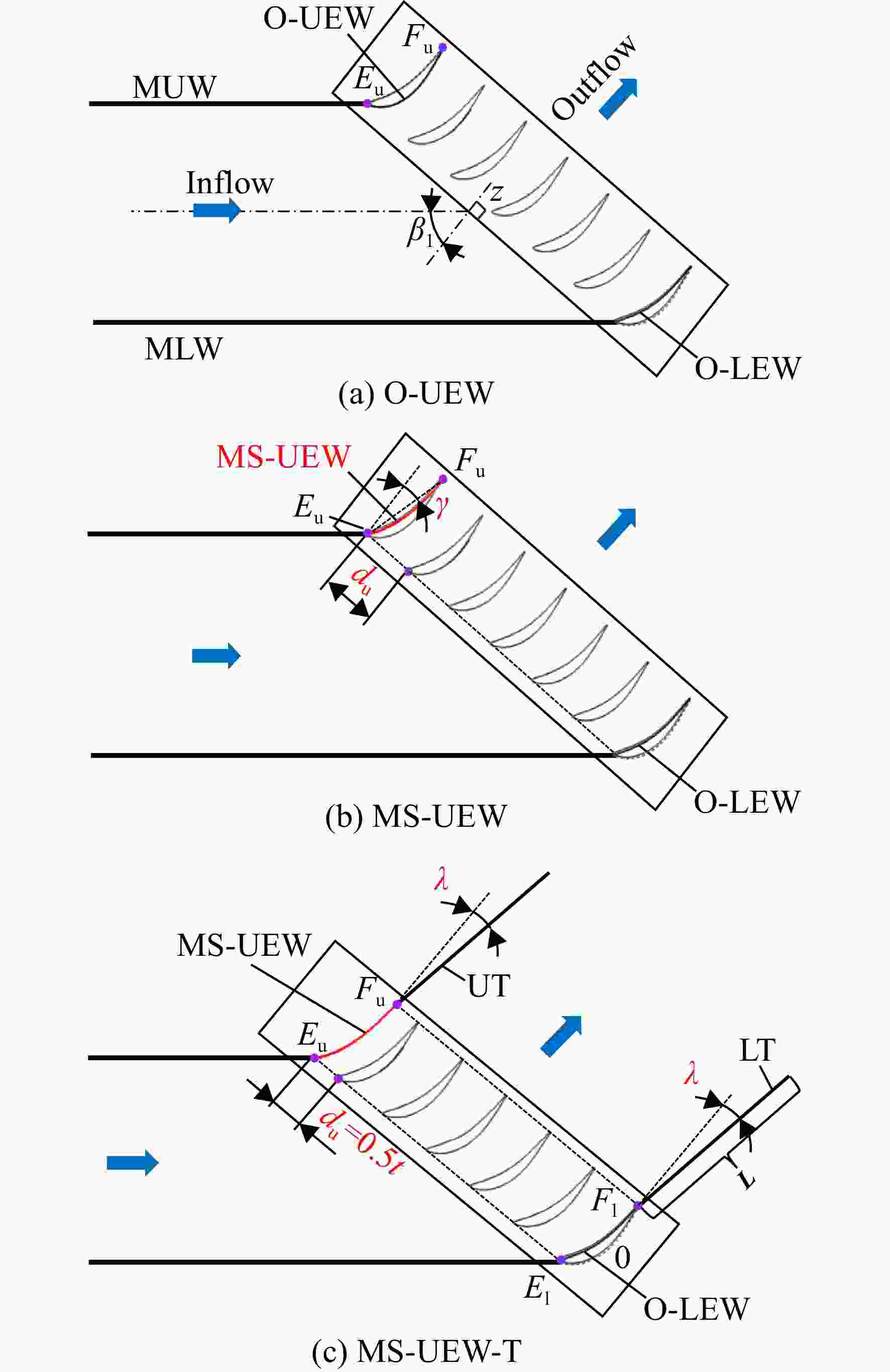
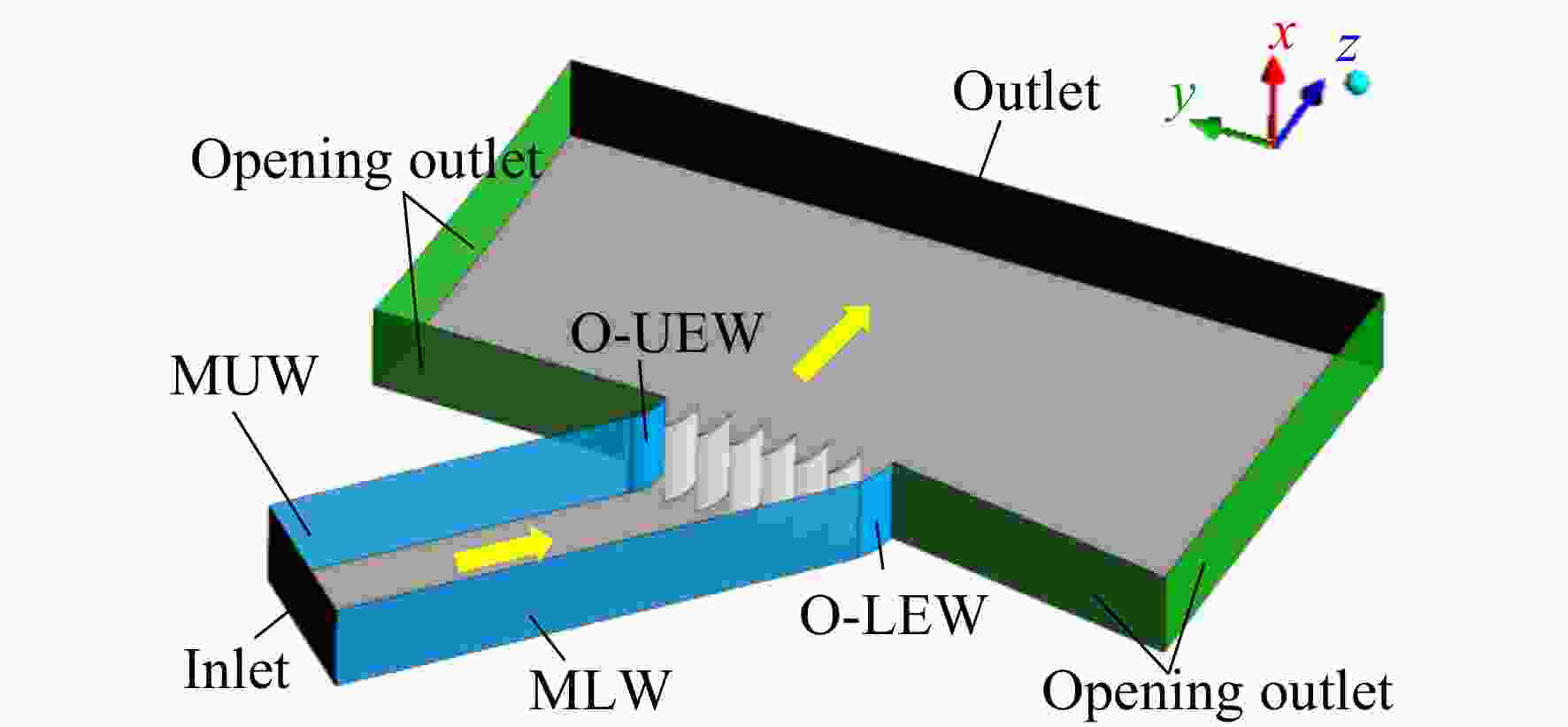
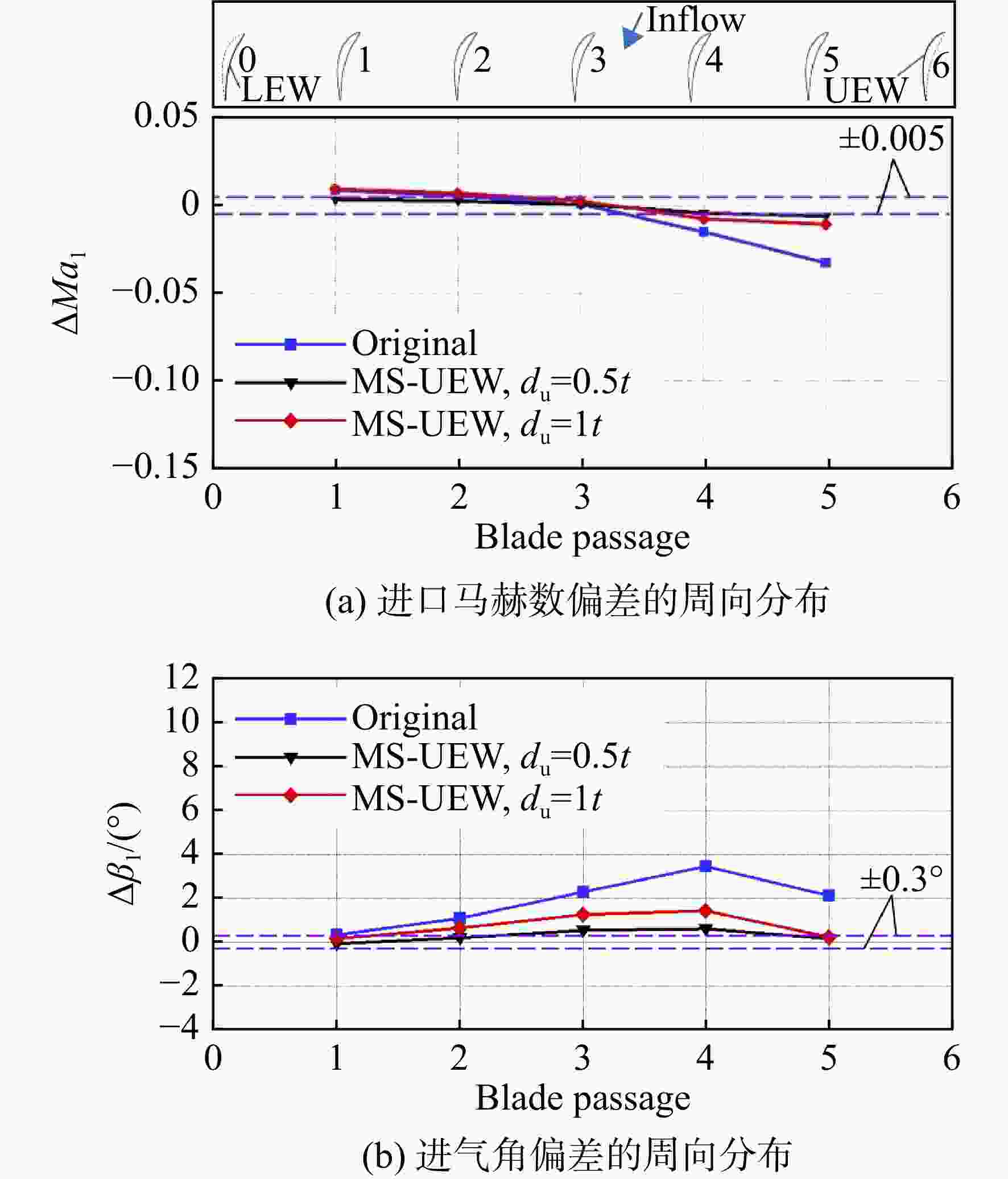
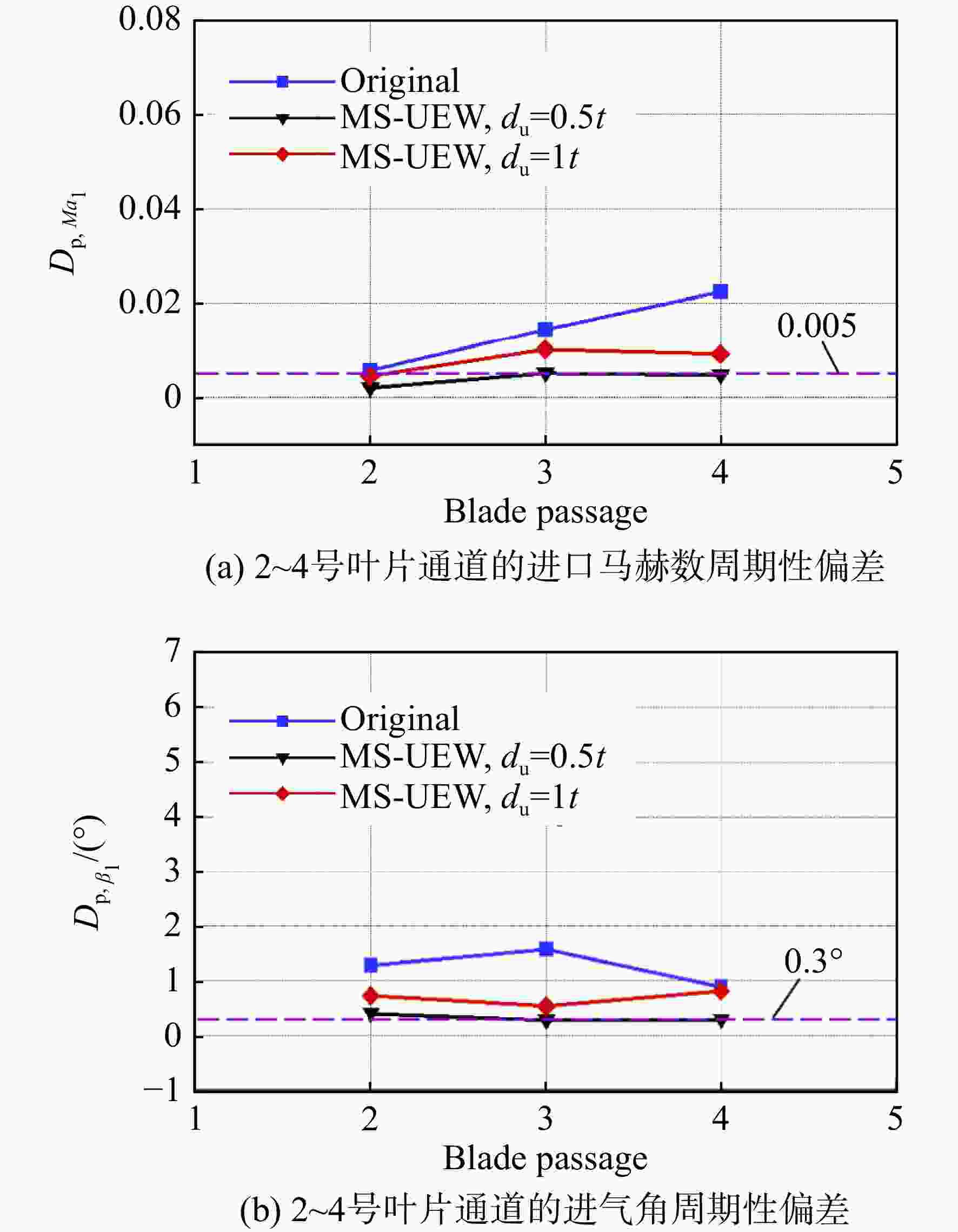
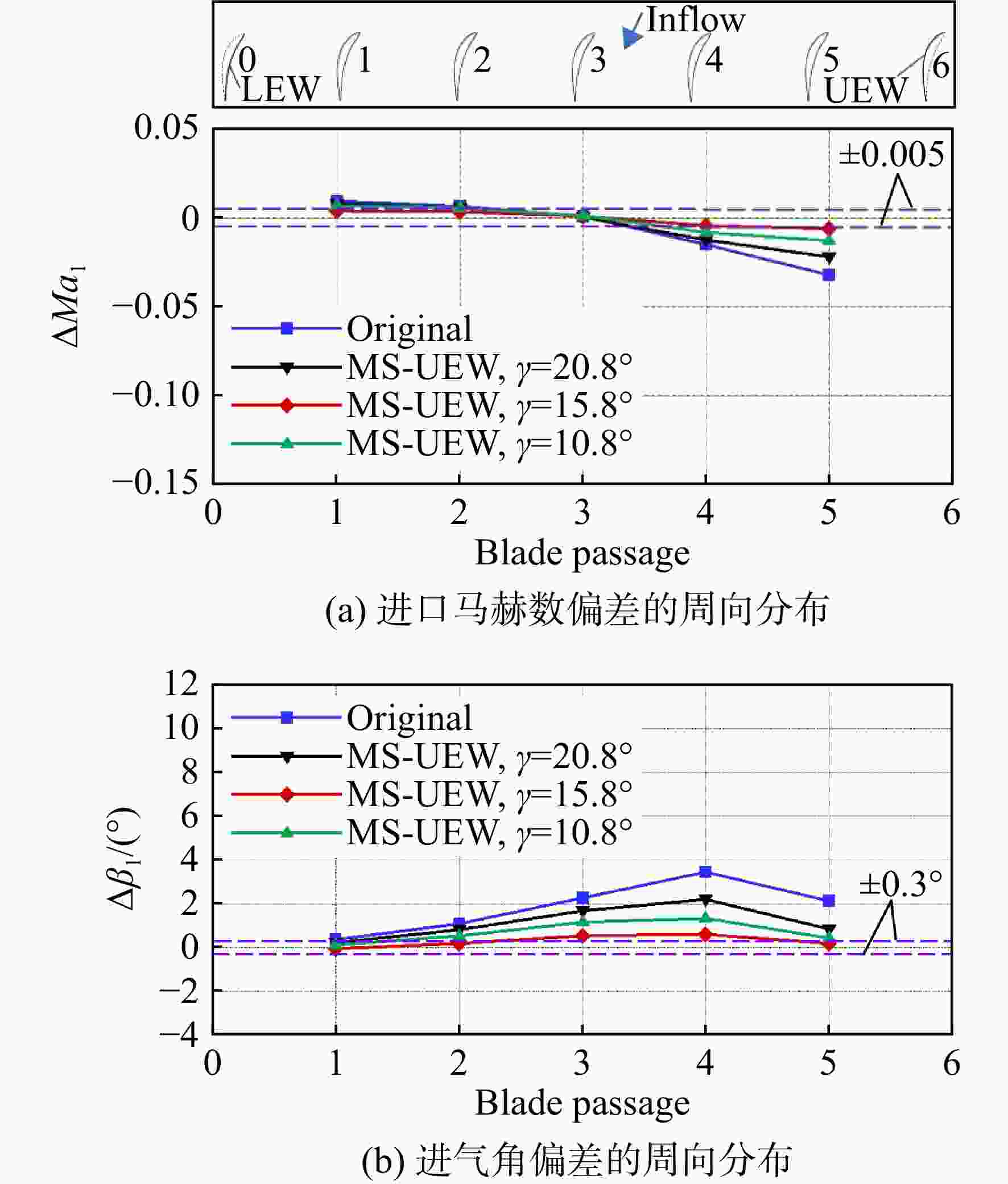
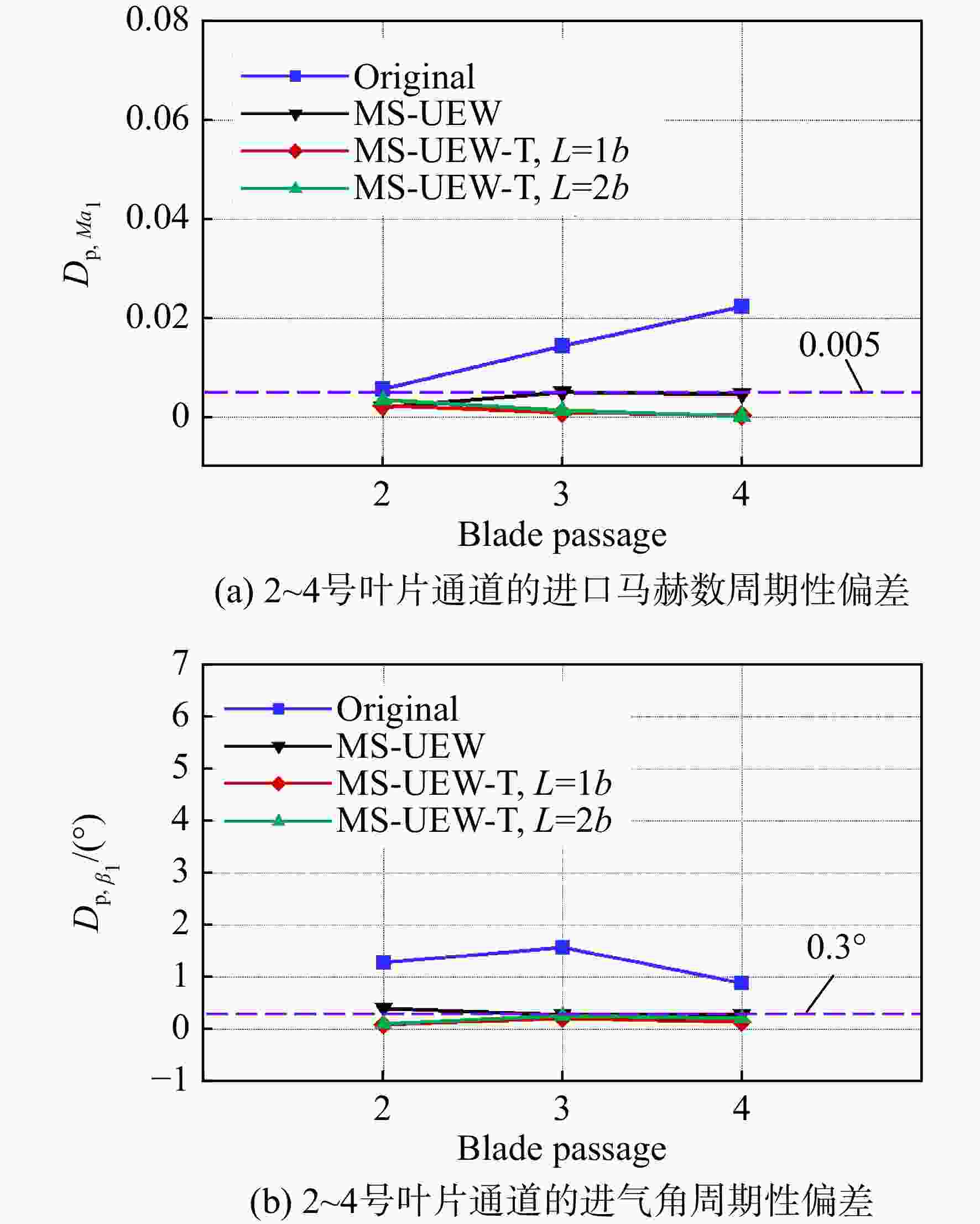
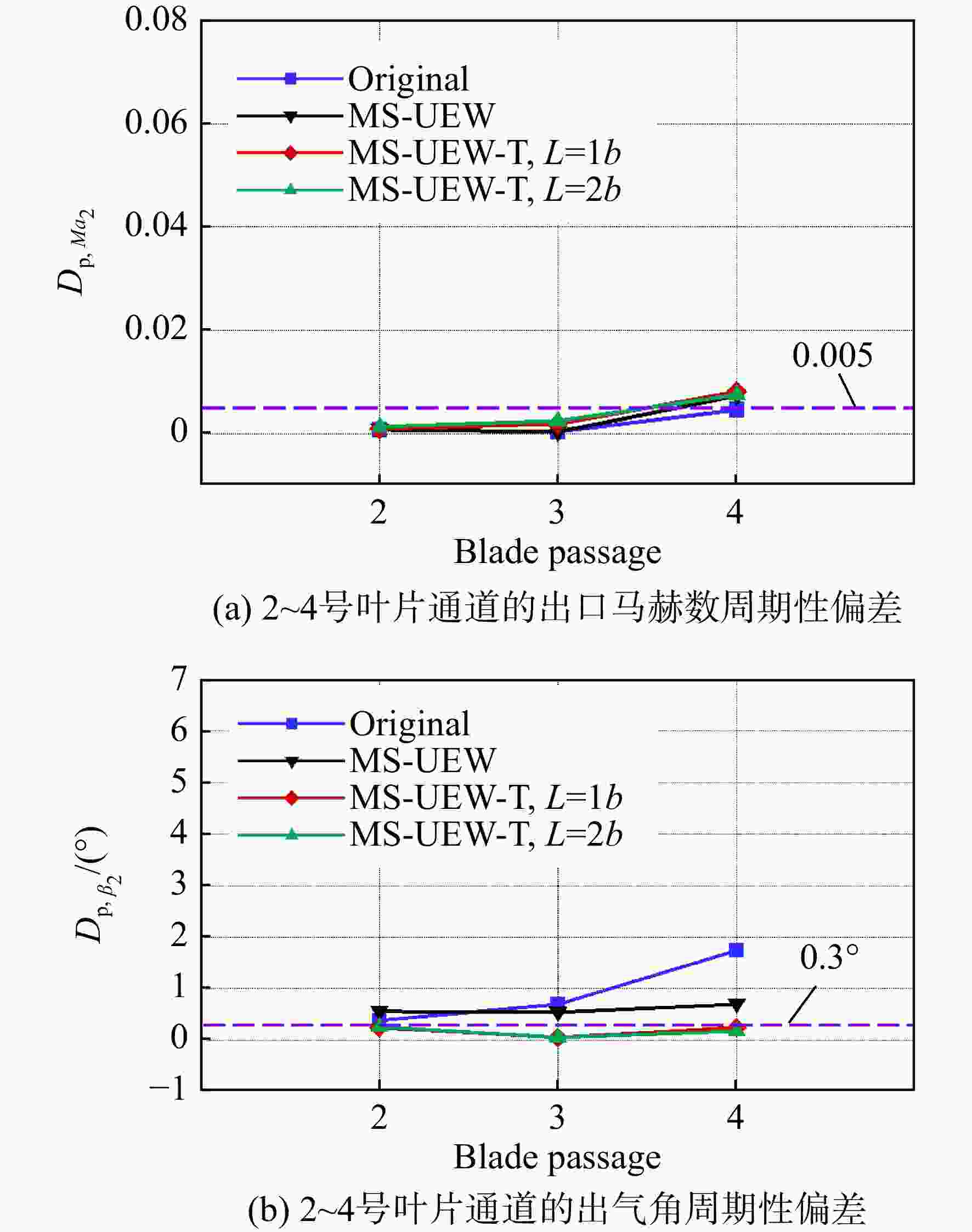
为了提升高负荷叶型的平面叶栅试验流场品质以保证试验数据的可靠性和准确性,建立了平面叶栅流场品质的评价参数,提出了中间流线型上端壁及其与出口可调尾板组合的两种被动调控方案。采用试验验证的数值模拟方法研究了以上两种方案对高负荷平面叶栅流场品质的调控策略。结果表明:两种调控方案均能够有效抑制上端壁区域的流场恶化,进而提升平面叶栅的来流准确性、流场周期性以及二维性。采用与平面叶栅理想中间流线相匹配的上端壁安装角和周向距离,以及尾板安装角时,两种方案对流场品质的提升效果最好。中间流线型上端壁组合出口尾板方案优于中间流线型上端壁方案,使叶栅中间三个叶片通道的进口马赫数偏差不超过±0.005,来流攻角偏差不超过±0.3°;叶栅进口和出口马赫数的周期性偏差不超过0.005,气流角的周期性偏差不超过0.3°;设计攻角下叶栅轴向速度密度比(AVDR)达到1.1,叶栅二维性较好。两种调控方案对叶栅大攻角工况的流场品质调节具有很好的适用性。
Abstract:To improve the flow quality of linear cascade tests with high-loading blade sections and ensure the reliability and accuracy of test data, the evaluation parameters of flow quality of linear cascade were established, and two passive control schemes of intermediate streamlined upper end-wall and its coupling with outlet adjustable tailboards were proposed. The control strategies of the above two schemes on the flow quality of high-loading linear cascade were studied by numerical simulation method verified by experiments. The results showed that both schemes can effectively suppress the deterioration of flow field near the upper end-wall area, thus improving the inflow accuracy, flow periodicity and two-dimensionality of cascade. When the set angle and gap of the upper end-wall and the tailboard angle matched the ideal intermediate streamline of cascade, the two schemes presented the best improvement on the flow quality. The scheme of intermediate streamlined end-wall combined outlet tailboards was superior to the intermediate streamlined end-wall scheme, such that the inlet Mach number deviation of the central three blade passages was less than ±0.005, and the incidence angle was less than ±0.3°. And the periodicity deviation of inlet and outlet Mach numbers shall not exceed 0.005, and the periodicity deviation of inlet and outlet flow angles shall not exceed 0.3°. The axial velocity density ratio (AVDR) of cascade was 1.1 at the incidence angle of 0°. The two control schemes showed good applicability to the flow quality adjustment of cascade at high incidence angle.
-
Key words:
- linear cascade test /
- end-wall modification /
- tailboards /
- flow quality /
- accuracy /
- periodicity
-
表 1 MS-UEW方案的调控工况
Table 1. Control conditions of MS-UEW
攻角$\alpha $/(°) 上端壁安装角γ/(°) 周向距离du/mm 0 15.8 0.5t, 1t 10.8, 15.8, 20.8 0.5t 6 17.8 0.5t 表 2 MS-UEW-T方案的调控工况
Table 2. Control conditions of MS-UEW-T
攻角$\alpha $/(°) 尾板长度L/mm 尾板安装角$\lambda $/(°) 0 1b, 2b 2.3 2b −1.7,2.3,6.3 6 2b 3.7 -
[1] OATES G C. 航空发动机部件气动热力学[M]. 金东海,高军辉,金捷,等,译. 北京: 航空工业出版社,2016. [2] GOSTELOW J P. Cascade aerodynamics[M]. New York: Pergamon Press,1984. [3] HERRIG L,EMERY J,ERWIN J. Systematic two-dimensional cascade tests of NACA 65-series compressor blades at low speeds[R]. NACA TN 3916,1957. [4] POLLARD D,GOSTELOW J P. Some experiments at low speed on compressor cascades[J]. Journal of Engineering for Power,1967,89(3): 427-436. doi: 10.1115/1.3616709 [5] LIEBLEIN S,SCHWENK F C,BRODERICK R. Diffusion factor for estimating losses and limiting blade loadings in axial-flow-compressor blade elements[R]. NACA RM E53D01,1953. [6] LIEBLEIN S,ROUDEBUSH W H. Theoretical loss relations for low-speed two-dimensional-cascade flow[R]. NACA TN 3662,1956. [7] 凌代军,代秋林,朱榕川,等. 叶栅试验技术综述[J]. 实验流体力学,2021,35(3): 30-38. LING Daijun,DAI Qiulin,ZHU Rongchuan,et al. Review of the cascade experimental technology[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics,2021,35(3): 30-38. (in Chinese LING Daijun, DAI Qiulin, ZHU Rongchuan, et al . Review of the cascade experimental technology[J]. Journal of Experiments in Fluid Mechanics,2021 ,35 (3 ):30 -38 . (in Chinese)[8] 恽起麟,孙邵鹏,徐明方,等. 高速风洞和低速风洞流场品质规范: GJB 1179-91[S]. 北京:国防科学技术工业委员会,1991: 1-15. [9] 姜正礼,凌代军,于宏军,等. 超跨音速平面叶栅试验方法: HB 20145-2014[S]. 北京: 国防科技工业局,2015: 1-14. [10] ERWIN J,SAVAGE M,EMERY J. Two-dimensional low-speed cascade investigation of NACA compressor blade sections having a systematic variation in mean-line loading[R]. NACA RM 153I30b,1953. [11] ERWIN J,EMERY J. Effect of tunnel configuration and testing technique on cascade performance[R]. NASA Report 1016,1951. [12] DUNAVANT J C,EMERY J,WALCH H,et al. High-speed cascade tests of the NACA 65-(12A10)10 and NACA 65-(12A2I8b)10 compressor blade sections[R]. NASA RM-L55I08,1955. [13] EMERY J,DUNAVANT J C. Two-dimensional cascade tests of NACA 65-(CloA10)10 blade sections at typical compressor hub conditions for speeds up to choking[R]. NACA RM L57H05,1957. [14] PIANKO M. Modern methods of testing rotating components of turbomachines[R]. AGARD-AG-167,1972. [15] HERGT A,MEYER R,ENGEL K. Experimental investigation of flow control in compressor cascades[R]. ASME Paper GT 2006-90415,2006. [16] KIESNER M,KING R. Multivariable closed-loop active flow control of a compressor stator cascade[J]. AIAA Journal,2017,55(10): 3371-3380. doi: 10.2514/1.J055728 [17] SONG Bo,GUI Xingmin,LI Shiming,et al. Flow periodicity improvement in a high speed compressor cascade with a large turning-angle[R]. AIAA 2002-3539,2002. [18] 杨泳,徐开俊,李珊珊,等. 平面叶栅周期性特性数值研究[J]. 液压与气动,2018(9): 92-97. YANG Yong,XU Kaijun,LI Shanshan,et al. Numerical simulation on flow periodic characteristics of linear cascade[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics,2018(9): 92-97. (in Chinese doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2018.09.016 YANG Yong, XU Kaijun, LI Shanshan, et al . Numerical simulation on flow periodic characteristics of linear cascade[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics,2018 (9 ):92 -97 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2018.09.016[19] 蔡明,高丽敏,刘哲,等. 基于抽吸的亚声速平面叶栅风洞流场品质控制研究[J]. 推进技术,2021,42(9): 1985-1992. CAI Ming,GAO Limin,LIU Zhe,et al. Flow field quality control of subsonic linear cascade wind tunnel based on suction[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2021,42(9): 1985-1992. (in Chinese doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190873 CAI Ming, GAO Limin, LIU Zhe, et al . Flow field quality control of subsonic linear cascade wind tunnel based on suction[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2021 ,42 (9 ):1985 -1992 . (in Chinese) doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.190873[20] TIAN Simeng,PETRIE-REPAR P,GLODIC N,et al. CFD-aided design of a transonic aeroelastic compressor rig[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery,2019,141(10): 101003. doi: 10.1115/1.4043884 -








 下载:
下载: