Simulation analysis of staged startup of large thrust LOX/kerosene staged combustion rocket engine
-
摘要:
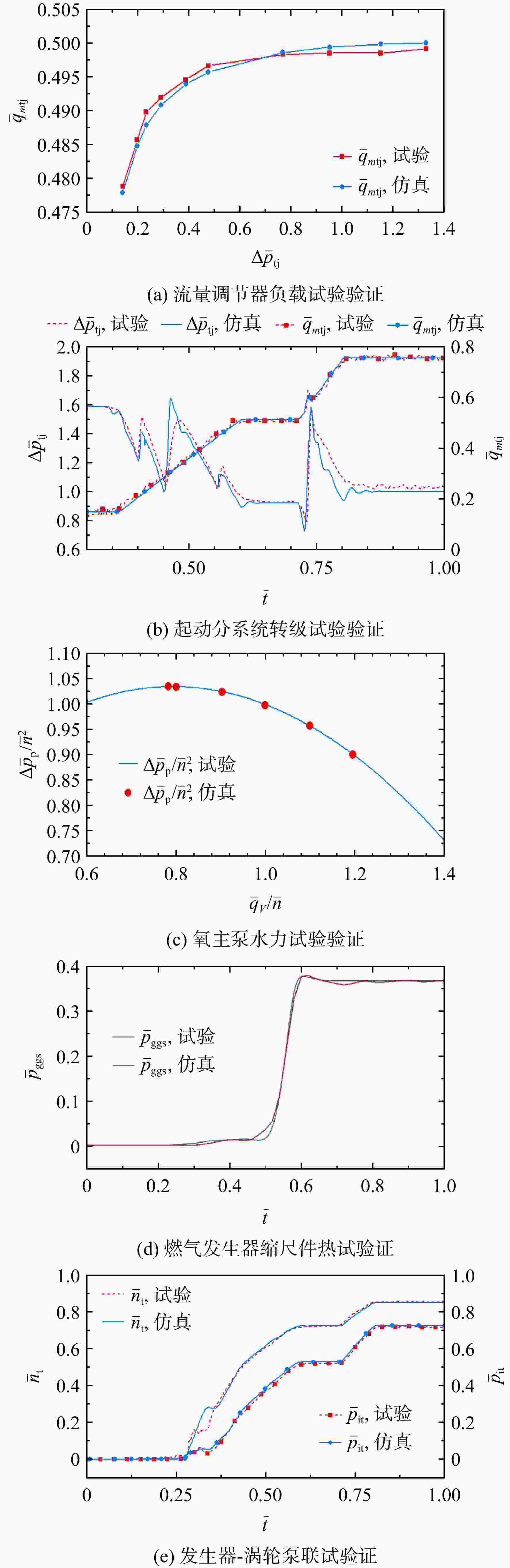
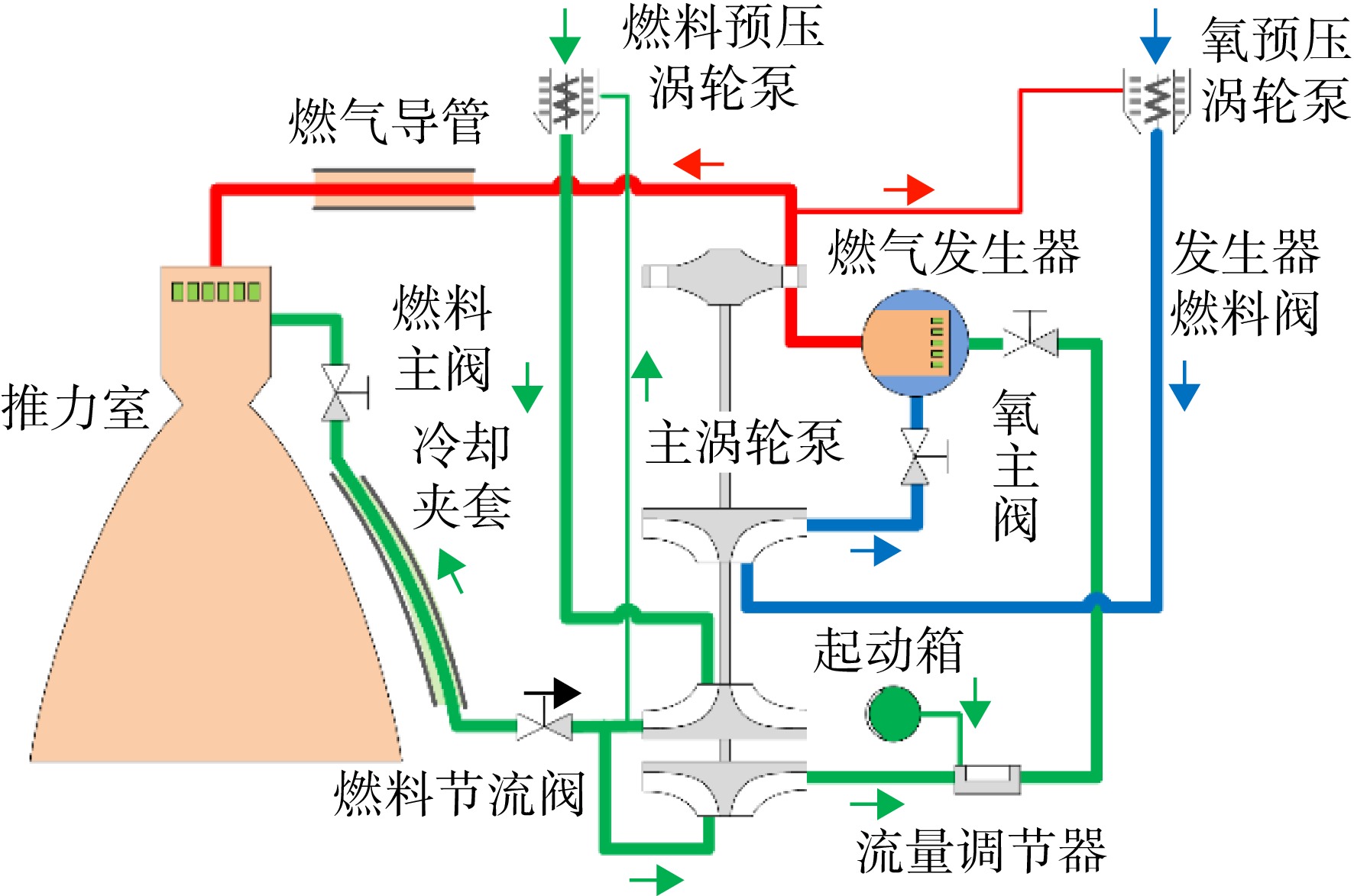
分级起动是提高大推力液氧煤油补燃发动机起动品质和发射可靠性的重要措施。通过系统动力学仿真,分析了发动机分级起动特性。采用Modelica语言开发了通用模块化液体动力系统动态特性仿真模型库(Tulips)。基于模型库,自底向上逐层构建和验证了发动机系统仿真模型。仿真结果表明:初级工况设置在推力高于额定值40%时起动品质较好;初级工况越低,进入初级工况的延迟时间越长;初级工况较低时,提前推力室点火和燃料节流阀转级时刻,有利于提高起动品质;涡轮泵转动惯量较大时,进入初级工况更平稳。
Abstract:The staged startup is an important measure to improve the startup quality and launch reliability of large thrust liquid-oxygen (LOX)/kerosene staged combustion rocket engines. The staged startup characteristics of the engine were studied by system dynamics simulation. The modular universal model library of transient simulation of liquid propulsion system (Tulips) was developed by using the Modelica language. Based on the model library, the system dynamics simulation models of the engine were built and validated layer-by-layer from bottom to top. The simulation results showed that, the startup quality was preferable when the prestage was set at the level where the thrust was higher than 40% of the rated value. The delay of entering the prestage was longer if the level of the prestage was lower. When the level of the prestage was low, the startup quality can be improved by advancing the moment of igniting the thrust chamber and the moment of transferring the resistance condition of the fuel throttle valve. If the turbopump rotational inertia was larger, the system became more stable when entering the prestage.
-
-
[1] KATORGIN B, CHELKIS F, LIMERICK C. The RD-170, a different approach to launch vehicle propulsion[R]. AIAA 93-2415, 1993 [2] BULK T A, FEDUN M H. RD-180 ATLAS IIIA stage tests-lessons learned[R]. AIAA 2000-3774, 2000. [3] RACHUK V, GONCHAROV N, MARTYNENKO Y, et al. Design, development, and history of the oxygen/hydrogen engine RD-0120[R]. AIAA 95-2540, 1995. [4] HULKA J, FORDE J, WERLING R, et al. Modification and verification testing of a Russian NK-33 rocket engine for reusable and restartable applications[R]. AIAA 98-3361, 1998. [5] 张晓光,高玉闪,马冬英,等. 大推力液氧煤油补燃发动机分级起动技术[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术,2020(4): 68-72.ZHANG Xiaoguang,GAO Yushan,MA Dongying,et al. Staged startup technology of high thrust staged combustion LOX/kerosene rocket engine[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles,2020(4): 68-72. (in Chinese) [6] 李元启,刘红军,徐浩海,等. 液体火箭发动机动态特性仿真技术研究进展[J]. 火箭推进,2017,43(5): 1-6.LI Yuanqi,LIU Hongjun,XU Haohai,et al. Research progress on numerical simulation technology of liquid rocket engine dynamic characteristics[J]. Journal of Rocket Propulsion,2017,43(5): 1-6. (in Chinese) [7] BINDER M P, TOMSIK T, VERES J. RL10A-3-3A rocket engine modeling project[R]. NASA-TM-107318, 1997 [8] DURTESTE S. A transient model of the VINCI cryogenic upper stage rocket engine[R]. AIAA 2007-5531, 2007. [9] KUROSU A, YAMANISHI N, TANI N, et al. Study of next booster engine LE-X in JAXA[R]. AIAA 2006-4700, 2006. [10] DI MATTEO F, DE ROSA M, ONOFRI M. Start-up transient simulation of a liquid rocket engine[R]. AIAA 2011-6032, 2011. [11] YAMANISHI N, KIMURA T, TAKAHASHI M, et al. Transient analysis of the LE-7A rocket engine using the rocket engine dynamic simulator (REDS) [R]. AIAA 2004 3850, 2004. [12] 黄敏超,王新建,王楠. 补燃循环液体火箭发动机启动过程的模块化仿真[J]. 推进技术,2001,22(2): 101-103.HUANG Minchao,WANG Xinjian,WANG Nan. Modular simulation on the start process for staged combustion cycle liquid propellant rocket engine[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2001,22(2): 101-103. (in Chinese) [13] 刘昆,张育林,程谋森. 液体火箭发动机系统瞬变过程模块化建模与仿真[J]. 推进技术,2003,24(5): 401-405.LIU Kun,ZHANG Yulin,CHENG Mousen. Modularization modeling and simulation for the transients of liquid propellant rocket engines[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2003,24(5): 401-405. (in Chinese) [14] 张黎辉,李伟,段娜. 液体火箭发动机模块化通用仿真[J]. 航空动力学报,2011,26(3): 687-691.ZHANG Lihui,LI Wei,DUAN Na. General simulation on modularization of liquid rocket engine[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2011,26(3): 687-691. (in Chinese) [15] 陈宏玉,刘红军,陈建华. 补燃循环发动机强迫起动过程[J]. 航空动力学报,2015,30(12): 3010-3016.CHEN Hongyu,LIU Hongjun,CHEN Jianhua. Forced start-up procedure of a staged combustion cycle engine[J]. Journal of Aero-space Power,2015,30(12): 3010-3016. (in Chinese) [16] BRADLEY M, BRADLEY M. Start with off-nominal propellant inlet pressures[R]. AIAA 1997-2687, 1997. [17] 管杰,刘上,刘志让. 补燃发动机完全自身起动过程富氧燃气温度控制[J]. 火箭推进,2020,46(3): 33-40.GUAN Jie,LIU Shang,LIU Zhirang. Temperature control of oxygen-riched gas during complete self start-up process for staged combustion cycle engine[J]. Journal of Rocket Propulsion,2020,46(3): 33-40. (in Chinese) [18] 李程,杨永强,徐浩海,等. 500 t级液氧煤油补燃发动机起动过程仿真研究[J]. 火箭推进,2014,40(6): 1-7.LI Cheng,YANG Yongqiang,XU Haohai,et al. Numerical simulation of start-up process for 500 t thrust LOX/kerosene staged combustion cycle rocket engine[J]. Journal of Rocket Propulsion,2014,40(6): 1-7. (in Chinese) [19] 李程,刘站国,徐浩海. 双推力室起动同步性研究[J]. 火箭推进,2014,40(4): 16-21,56.LI Cheng,LIU Zhanguo,XU Haohai. Study on synchronous ignition of dual-thrust chamber engine[J]. Journal of Rocket Propulsion,2014,40(4): 16-21,56. (in Chinese) [20] KOPTILYY D, MARCHAN R, DOLGOPOLOV S, et al. Mathematical modeling of transient processes during startup of main liquid propellant engine under hot test conditions[C]//Proceedings of the 8th European Conference for Aeronautics and Space Sciences. Brussels: European Research Council, 2019: 1-15. [21] 郑大勇,王弘亚,胡骏. 大推力氢氧发动机瞬态特性研究[J]. 推进技术,2021,42(8): 1761-1769.ZHENG Dayong,WANG Hongya,HU Jun. Transient characteristics of high-thrust oxygen/hydrogen rocket engine[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2021,42(8): 1761-1769. (in Chinese) [22] 汪洪波, 吴海燕, 谭建国. 推进系统动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018. [23] 张淼,徐浩海,李斌,等. 流量调节器管路系统自激振荡特性研究[J]. 推进技术,2021,42(7): 1493-1500. doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.200395ZHANG Miao,XU Haohai,LI Bin,et al. Auto oscillation of flow regulator pipe system[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2021,42(7): 1493-1500. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13675/j.cnki.tjjs.200395 -








 下载:
下载: