Temperature field analysis of cryogenic propellant tanks with deep subcooling cycle
-
摘要:
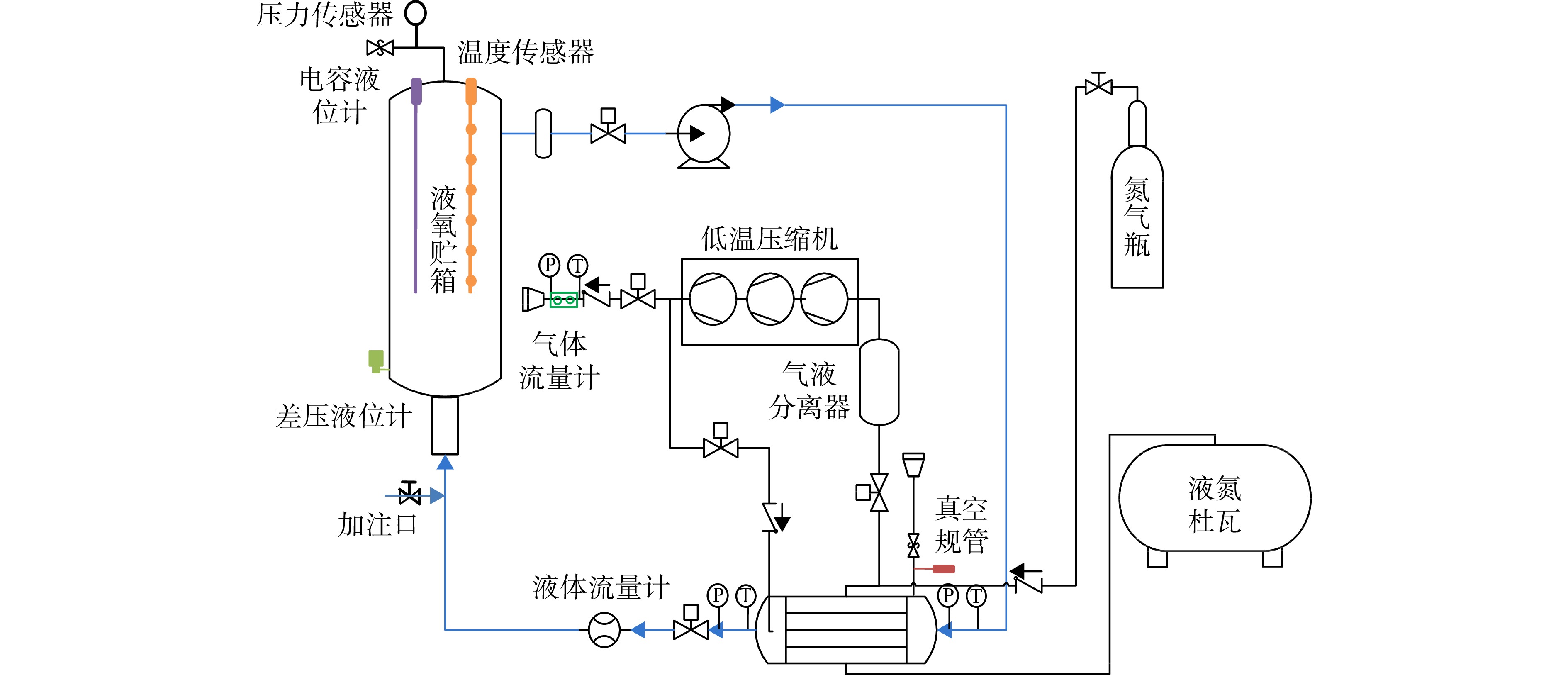
以某型号火箭液氧贮箱为例,对液氧在深度过冷循环过程中贮箱的降温特性进行仿真计算。以液氮为模拟工质,搭建低温推进剂过冷循环原理性缩比试验系统,通过实验数据验证数值模型的准确性。仿真分析了过冷循环流量及回流形式对贮箱降温速率及热分层特性的影响。研究表明:由于一级液氧贮箱筒段较长,贮箱内流体混合更加充分,液体温度均匀性良好;对于二级贮箱,由于其轴向长度较短,从输送管回流的部分深度过冷液氧直接通过贮箱上部抽液口被吸出,发生循环短路,导致贮箱温度始终无法降至70 K,贮箱内温度分层明显,温度均匀性较差,在对贮箱结构进行优化后,贮箱降温速率和温度均匀性提升明显。
Abstract:A rocket liquid oxygen tank was taken as an example to simulate the temperature-drop characteristics of the liquid oxygen tank with subcooled cycle. Using liquid nitrogen as the simulated working medium, the principle scaling cryogenic propellant subcooled cycle experimental system was established, and the accuracy of the numerical mode was verified by the experimental data. The effects of the subcooled cycle flow rate and return form on the temperature-drop rate and thermal stratification characteristics of the tank were simulated and analyzed. Results showed that, due to the long cylinder section of the first stage liquid oxygen tank, the fluid in the tank was more fully mixed and the temperature uniformity of the liquid was better. For the secondary tank, due to its short axial length, part of the subcooled liquid oxygen was directly sucked out through the upper suction port of the tank, such that the tank temperature cannot be reduced to 70 K. The temperature in the tank was obviously stratified, and the temperature uniformity was poor. After the optimization of the tank structure, the cooling rate and temperature uniformity of the tank were significantly improved.
-
Key words:
- cryogenic propellant /
- storage tank /
- deep subcooled /
- external loop /
- temperature-drop characteristics
-
表 1 液氧贮箱过冷循环阶段边界条件
Table 1. Boundary conditions of external loop sub-cooling of liquid oxygen tank
状态 一级液氧
贮箱二级液氧
贮箱加注容积/L 121000 20000 箱底至发动机输送管高/m 13 3 输送管/mm 320 120 绝热层或箱壁外表面辐射率ε 0.8 0.8 绝热结构厚度/mm 20 20 绝热层外表面对太阳的热辐射吸收率αs 0.3 0.3 绝热层表观导热系数/(W/(m·K)) 0.023 0.023 箱壁导热系数/(W/(m·K)) 170 170 环境温度/K 298 298 表 2 测量系统中传感器的精度
Table 2. Uncertainties in efficient cryogenic fluid storage test platform
测量仪表 量程 精度 PT100铂电阻 77~300 K ±0.1 K 压力传感器 0~0.8 MPa 0.25% FS 差压液位计 0~2 000 mm H2O ±0.075% -
[1] 谢福寿,雷刚,王磊,等. 过冷低温推进剂的性能优势及其应用前景[J]. 西安交通大学学报,2015,49(5): 16-23,127. XIE Fushou,LEI Gang,WANG Lei,et al. Performance advantages and application prospects of subcooled cryogenic propellants[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2015,49(5): 16-23,127. (in Chinese XIE Fushou, LEI Gang, WANG Lei, et al . Performance advantages and application prospects of subcooled cryogenic propellants[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2015 ,49 (5 ):16 -23, 127 . (in Chinese)[2] LAK T,WOOD C. Cryogenic fluid management technologies for space transportation: NASA-CR-193981[R]. Reston,US: AIAA,1994. [3] KUTTER B,ZEGLER F,LUCAS S,et al. Atlas centaur extensibility to long-duration In-space applications: AIAA-2005-6738[R]. Reston,US: AIAA,2005. [4] 符锡理. 运载火箭液氢液氧低温推进剂加注技术[J]. 低温工程,1995(6): 1-8. FU Xili. A keview of LH2,LO2 cryogenic propellant loading technology for launch vehicles[J]. Gryogenics,1995(6): 1-8. (in Chinese FU Xili . A keview of LH2, LO2 cryogenic propellant loading technology for launch vehicles[J]. Gryogenics,1995 (6 ):1 -8 . (in Chinese)[5] 王瑞铨. 国外运载火箭低温加注系统[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术,1997(2): 19-29. WANG Ruiquan. The cryogenic fueling systems of foreign launch vehicles[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles,1997(2): 19-29. (in Chinese WANG Ruiquan . The cryogenic fueling systems of foreign launch vehicles[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles,1997 (2 ):19 -29 . (in Chinese)[6] THOMAS M,MICHAEL L. Liquid oxygen propellant densification production and performance test results with a large-scale flight-weight propellant tank for the X33/RLV: NASA/TM-2010-216247[R]. Reston,US: AIAA,2010. [7] TOMSIK T. Performance tests of a liquid hydrogen propellant densification ground system for the X33/RLV: AIAA-1997-2976[R]. Reston,US: AIAA,1997. [8] WESLEY L,THOMAS M. A densified liquid methane delivery system for the Altair ascent stage: NASA/TM-2010-216246 [R]. Reston,US: AIAA,2010. [9] LAK T,LOZANO M,TOMSIK T. Advancement in cryogenic propulsion system performance through propellant densification: AIAA 1996-3123[R]. Reston,US: AIAA,1996. [10] 邵业涛,罗庶,王浩苏,等. 低温推进剂深度过冷加注技术研究及对运载火箭性能影响分析[J]. 宇航总体技术,2019,3(2): 18-25. SHAO Yetao,LUO Shu,WANG Haosu,et al. Research on the supercooling loading technology of cryogenic propellant and its effects on rocket performance[J]. Astronautical Systems Engineering Technology,2019,3(2): 18-25. (in Chinese SHAO Yetao, LUO Shu, WANG Haosu, et al . Research on the supercooling loading technology of cryogenic propellant and its effects on rocket performance[J]. Astronautical Systems Engineering Technology,2019 ,3 (2 ):18 -25 . (in Chinese)[11] 谢福寿,厉彦忠,王磊,等. 低温推进剂过冷技术研究[J]. 航空动力学报,2017,32(3): 762-768. XIE Fushou,LI Yanzhong,WANG Lei,et al. Study on subcooled technology for cryogenic propellants[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2017,32(3): 762-768. (in Chinese XIE Fushou, LI Yanzhong, WANG Lei, et al . Study on subcooled technology for cryogenic propellants[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2017 ,32 (3 ):762 -768 . (in Chinese)[12] 马原,高炎,高强,等. 液氧/液甲烷低温推进剂深度过冷加注实验研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报,2022,56(9): 134-141. MA Yuan,GAO Yan,GAO Qiang,et al. Deep subcooling filling of LO2/LCH4 cryogenic propellants[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2022,56(9): 134-141. (in Chinese MA Yuan, GAO Yan, GAO Qiang, et al . Deep subcooling filling of LO2/LCH4 cryogenic propellants[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2022 ,56 (9 ):134 -141 . (in Chinese)[13] 陶文铨. 数值传热学[M]. 2版. 西安: 西安交通大学,2001. TAO Wenquan. Numerical heat transfer[M]. 2nd ed. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University,2001. (in ChineseTAO Wenquan. Numerical heat transfer[M]. 2nd ed. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2001. (in Chinese) [14] ALIZADEHDAKHEL A,RAHIMI M,ALSAIRAFI A A. CFD modeling of flow and heat transfer in a thermosyphon[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer,2010,37(3): 312-318. doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2009.09.002 [15] DE SCHEPPER S C K,HEYNDERICKX G J,MARIN G B. Modeling the evaporation of a hydrocarbon feedstock in the convection section of a steam cracker[J]. Computers and Chemical Engineering,2009,33(1): 122-132. doi: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2008.07.013 [16] KARTUZOVA O V,KASSEMI M,MODER J P,et al. Self-pressurization and spray cooling simulations of the multipurpose hydrogen test bed (MHTB) ground-based experiment: AIAA2014-3578 [R]. Reston,US: AIAA,2014. [17] HIRT C W,NICHOLS B D. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics,1981,39(1): 201-225. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(81)90145-5 [18] BRACKBILL J U,KOTHE D B,ZEMACH C. A continuum method for modeling surface tension[J]. Journal of Computational Physics,1992,100(2): 335-354. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(92)90240-Y [19] 刘展,厉彦忠,王磊,等. 在轨运行低温液氢箱体蒸发量计算与增压过程研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报,2015,49(2): 135-140. LIU Zhan,LI Yanzhong,WANG Lei,et al. Evaporation calculation and pressurization process of on-orbit cryogenic liquid hydrogen storage tank[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2015,49(2): 135-140. (in Chinese LIU Zhan, LI Yanzhong, WANG Lei, et al . Evaporation calculation and pressurization process of on-orbit cryogenic liquid hydrogen storage tank[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2015 ,49 (2 ):135 -140 . (in Chinese) -








 下载:
下载: