Influence of tapered bridge holes on impingement double wall cooling for gas turbine blade
-
摘要:
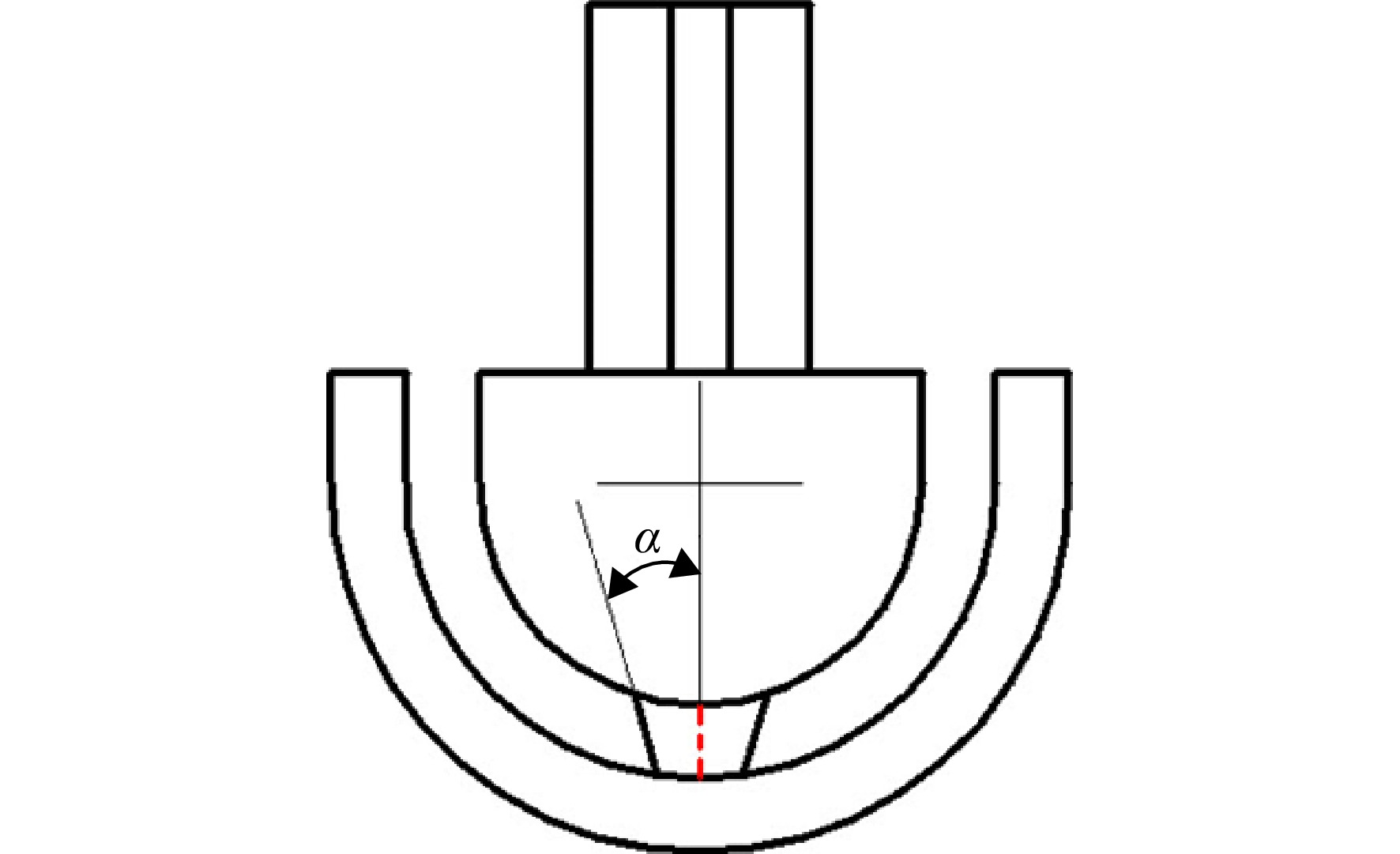
为探究叶片前缘双层壁冲击冷却中连接孔结构对整体流动和换热特性的影响,建立了具有0°、5°、10°、15°、20°倾角的5个渐缩型连接孔冲击冷却模型,采用ANSYS CFX进行数值模拟。结果表明:在双层壁冲击冷却结构中将连接孔调整为渐缩形态能显著提升综合换热能力。当连接孔倾斜角从0°增大到20°,其倾角变化对结构内、外腔室流动损失影响不大;内靶面平均努塞尔数随倾角的变化几乎不变,但外靶面换热强度随着倾角增大先增强后削弱。当连接孔倾角为15°时,外靶面平均努塞尔数最大,相比标准结构提升了19.7%;总综合换热因子随连接孔倾斜角的增大呈现先增大后减小的趋势,倾角为15°时,综合换热因子达到最高,相比于标准结构提升了12.15%。
Abstract:In order to investigate the influence of the bridge holes on flow and thermal behavior of impingement double-wall cooling for gas turbine leading blades, the impingement double-wall cooling configurations with 0°, 5°, 10°, 15° and 20° tapered bridge holes were calculated by using ANSYS CFX numerical simulation. Results indicated that the tapered bridge holes can significantly enhance the comprehensive heat transfer capacity. As the angle of bridge holes increased from 0° to 20°, the angle of holes did not have a significant influence on flow loss of inner and outer chambers for the blades. Likewise, the cooling performance of the inner chamber target wall was not sensitive to the change of the bridge hole angle. With the growing angle of bridge holes, the thermal behavior of the target wall for the outer chamber increased at first and then decreased, reaching the biggest value at 15°. When the angle of bridge holes increased to 15°, its average heat transfer intensity was 19.7% higher than the case with 0° bridge holes. Similarly, the thermal performance factor of the whole configuration also became larger at first and then became smaller. The largest thermal performance factor occurred at 15° too, which was 12.15% higher than the case with 0° bridge holes.
-
表 1 5种结构的各项参数对比
Table 1. Comparison of parameters for the five configurations
参数 α/(°) 0 5 10 15 20 Rein 5185 4767 4458 4393 4346 Reout 1515 1739 1875 1911 1937 Nu0,in 18.74 17.52 16.61 16.41 16.27 Nu0,out 7.00 7.82 8.30 8.43 8.52 fin 0.071 0.069 0.071 0.070 0.071 fout 0.031 0.030 0.030 0.030 0.030 ηin 5.63 6.14 6.45 6.53 6.56 ηout 2.38 2.29 2.23 2.36 2.24 ηt 4.28 4.54 4.69 4.80 4.77 -
[1] 杜长河,李森,李亮,等. 叶片前缘旋流蒸汽冷却流动和传热的数值研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报,2015,49(10): 72-78. DU Changhe,LI Sen,LI Liang,et al. Numerical study on characteristics of flow and heat transfer of steam vortex cooling for blade leading edges[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2015,49(10): 72-78. (in Chinese doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201510012DU Changhe, LI Sen, LI Liang, et al. Numerical study on characteristics of flow and heat transfer of steam vortex cooling for blade leading edges[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2015, 49(10): 72-78. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb201510012 [2] 王杰枫,杜长河,吴凡,等. 喷嘴周向位置和旋流腔拔模斜度对旋流冷却的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报,2018,52(11): 65-72. WANG Jiefeng,DU Changhe,WU Fan,et al. Effects of jet nozzle circumferential position and vortex chamber draft angle on the flow and heat transfer characteristics of vortex cooling[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2018,52(11): 65-72. (in ChineseWANG Jiefeng, DU Changhe, WU Fan, et al. Effects of jet nozzle circumferential position and vortex chamber draft angle on the flow and heat transfer characteristics of vortex cooling[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2018, 52(11): 65-72. (in Chinese) [3] LIAO Gaoliang,WANG Xinjun,LI Jun,et al. A numerical comparison of thermal performance of in-line pin–fins in a wedge duct with three kinds of coolant[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2014,77: 1033-1042. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.06.010 [4] 杨力. 基于冲击的燃气轮机透平叶片冷却结构研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学,2015. YANG Li. Research on the application of impingement cooling in gas turbineblades[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University,2015. (in ChineseYANG Li. Research on the application of impingement cooling in gas turbineblades[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2015. (in Chinese) [5] DEVORE M A,PAAUWE C S. Turbine airfoil with improved cooling: US20070166161[P]. 2007-07-19. [6] CHYU M K,SIW S C. Recent advances of internal cooling techniques for gas turbine airfoils[J]. Journal of Thermal Science and Engineering Applications,2013,5(2): 021008. doi: 10.1115/1.4023829 [7] HAN J C,DUTTA S,EKKAD S. Gas turbine heat transfer and cooling technology[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Taylor & Francis Group,2012: 14-67. [8] ZHANG Jingzhou,XIE Hao,YANG Chengfeng. Numerical study of flow and heat transfer characteristics of impingement/effusion cooling[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2009,22(4): 343-348. doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(08)60109-0 [9] STOAKES P,EKKAD S. Optimized impingement configurations for double wall cooling applications[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition. Vancouver,Canada: ASME ,2012: 1535-1543. [10] TAN Xiaoming,ZHANG Jingzhou,XU Huasheng. Experimental investigation on impingement/effusion cooling with short normal injection holes[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer,2015,69: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2015.09.005 [11] 郑杰,朱惠人,郭涛,等. 微尺度冲击冷却通道换热特性实验研究[J]. 推进技术,2015,36(1): 82-88. ZHENG Jie,ZHU Huiren,GUO Tao,et al. Experimental investigation on jet impingement heat transfer for micro-channel[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2015,36(1): 82-88. (in ChineseZHENG Jie, ZHU Huiren, GUO Tao, et al. Experimental investigation on jet impingement heat transfer for micro-channel[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2015, 36(1): 82-88. (in Chinese) [12] 李广超,蒋蔚,刘永泉,等. 粗糙度对不同尺度的双层壁结构冲击换热特性影响[J]. 推进技术,2017,38(7): 1563-1571. LI Guangchao,JIANG Wei,LIU Yongquan,et al. Effects of roughness on impacting heat transfer in different scale double-wall[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology,2017,38(7): 1563-1571. (in ChineseLI Guangchao, JIANG Wei, LIU Yongquan, et al. Effects of roughness on impacting heat transfer in different scale double-wall[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2017, 38(7): 1563-1571. (in Chinese) [13] RAO Yu,LIU Yuyang,WAN Chaoyi. Multiple-jet impingement heat transfer in double-wall cooling structures with pin fins and effusion holes[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences,2018,133: 106-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2018.07.021 [14] REN Zhong,VANGA S R,ROGERS N,et al. Internal and external cooling of a full coverage effusion cooling plate: effects of double wall configuration and conditions[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences,2018,124: 36-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.09.021 [15] 韦宏,祖迎庆. 双层壁冷却结构中多排射流冲击冷却的换热和流阻特性[J]. 航空动力学报,2021,36(8): 1621-1632. WEI Hong,ZU Yingqing. Heat transfer and flow resistance characteristics of multi-row jet impingement cooling in double-wall cooling structure[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power,2021,36(8): 1621-1632. (in ChineseWEI Hong, ZU Yingqing. Heat transfer and flow resistance characteristics of multi-row jet impingement cooling in double-wall cooling structure[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2021, 36(8): 1621-1632. (in Chinese) [16] KWON H,LIGRANI P M,VANGA S R,et al. Flow structure and surface heat transfer from numerical predictions for a double wall effusion plate with impingement jet array cooling[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2022,183: 122049. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.122049 [17] FAN X J,LI L,WANG J F,et al. Heat transfer enhancement for gas turbine blade leading edge cooling using curved double-wall/vortex cooling with various disturbing objects[C]//ASME Turbo Expo 2019: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition. 2019. [18] LIU Zhao,YE Lv,WANG C,et al. Numerical simulation on impingement and film composite cooling of blade leading edge model for gas turbine[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2014,73(2): 1432-1443. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.05.060 -








 下载:
下载: