Fretting wear behavior considering the contact of third body particles
-
摘要:
基于有限元方法建立带有第三体颗粒接触作用的球-平面三维仿真模型,研究在部分滑移状态下第三体对微动磨损的影响。分析了线弹性和弹塑性材料本构下第三体颗粒与第一体之间接触行为,确定研究对象材料本构;分析了不同尺寸条件下的第三体颗粒接触行为;研究了不同加载条件下第三体颗粒对微动磨损的影响。结果表明,弹塑性材料更能体现第三体的接触特性,第三体颗粒受到较大的接触压力发生塑性变形,减小了接触面之间的接触压力;直径0.8 μm的第三体颗粒所承受接触压力最大,0.2 μm时接触压力最小,且随着直径增大塑性变形增大;部分滑移状态下,在微动初始阶段第三体颗粒的存在会降低磨损,较小的接触宽度或较大的位移幅值会导致第三体颗粒承受的接触压力减小,摩擦耗散能增大,微动磨损加剧。
Abstract:Based on the finite element method, a ball-plane three-dimensional simulation model with the contact of the third body particles was established. The influence of the third body on fretting wear under partial slip condition was mainly studied. The contact behavior between the third body and the joint surface under the action of linear elastic material and elastic-plastic material was analyzed. The influences of different sizes on the contact behavior of the third body particles were studied. Finally, the effect of third body particles on fretting wear under different loading conditions was studied. The results showed that the elastic-plastic material can better reflect the contact characteristics of the third body. The third body particles were plastically deformed by the larger contact pressure, which reduced the contact pressure between the contact surfaces. The contact pressure of the third body particles with a diameter of 0.8 μm was the largest, and the contact pressure was the smallest at 0.2 μm, and the plastic deformation increased with the increase of diameter. In the initial stage of fretting, the existence of the third body particles could reduce the wear. For partial slip fretting wear, a smaller contact width or a larger displacement amplitude could lead to a decrease in the contact pressure of the third body particles, and an increase in friction dissipation energy and wear.
-
Key words:
- third body particles /
- fretting wear /
- partial slip /
- contact width /
- displacement amplitude
-
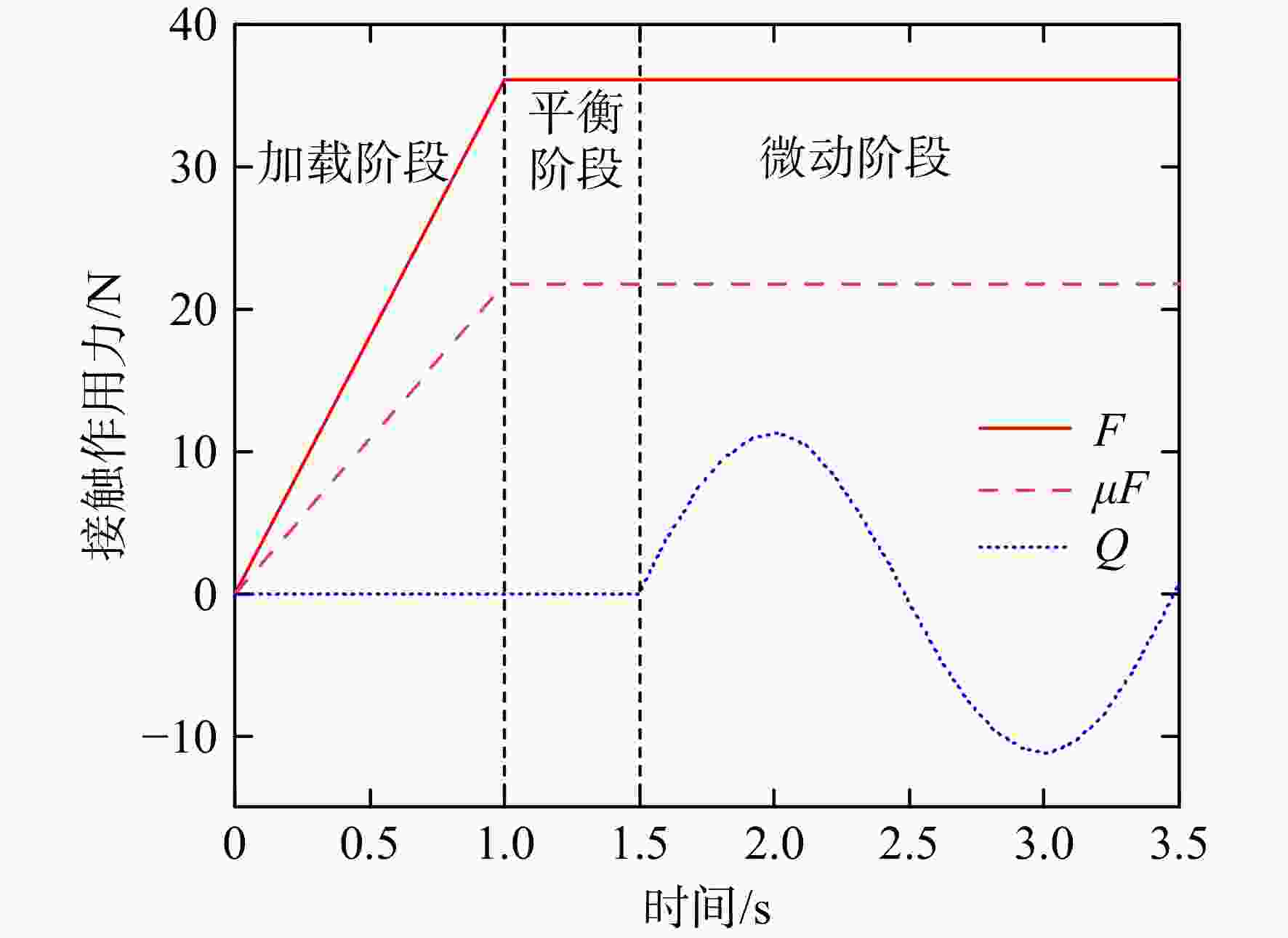
表 1 微动磨损模型中的相关参数
Table 1. Parameters used in the fretting wear analysis
参数 值 最大赫兹接触压力Pmax/GPa 1.2 赫兹接触半宽a/μm 120 黏着区域尺寸/c/μm 92 位移幅值S/μm 0.5 摩擦因数μ 0.6 -
[1] 周仲荣,Leo Vincent. 微动磨损[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2002. ZHOU Zhongrong,Leo Vincent. Fretting wear[M]. Beijing: Science Press,2002. (in ChineseZHOU Zhongrong, Leo Vincent. Fretting wear[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002. (in Chinese) [2] AHMADI A,SADEGHI F. A three-dimensional finite element damage mechanics model to simulate fretting wear of hertzian line and circular contacts in partial slip regime[J]. Journal of Tribology,2022,144(5): 051602. doi: 10.1115/1.4051814 [3] GHOSH A,WANG W,SADEGHI F. An elastic–plastic investigation of third body effects on fretting contact in partial slip[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2016,81: 95-109. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2015.11.013 [4] YUE Tongyan,ABDEL WAHAB M. Finite element analysis of fretting wear under variable coefficient of friction and different contact regimes[J]. Tribology International,2017,107: 274-282. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2016.11.044 [5] XIN L,YANG B B,LI J,et al. Wear damage of Alloy 690TT in partial and gross slip fretting regimes at high temperature[J]. Wear,2017,390/391: 71-79. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2017.07.006 [6] 范娜,王云霞,王秋凤,等. 载荷对304不锈钢微动磨损性能的影响[J]. 摩擦学学报,2016,36(5): 555-561. FAN Na,WANG Yunxia,WANG Qiufeng,et al. Effects of load on fretting wear behaviors of 304 stainless steels[J]. Tribology,2016,36(5): 555-561. (in ChineseFAN Na, WANG Yunxia, WANG Qiufeng, et al. Effects of load on fretting wear behaviors of 304 stainless steels[J]. Tribology, 2016, 36(5): 555-561. (in Chinese) [7] 袁新璐,李根,张晓宇,等. 位移幅值对铜镁合金微动磨损行为的影响[J]. 摩擦学学报,2021,41(1): 125-136. YUAN Xinlu,LI Gen,ZHANG Xiaoyu,et al. Effect of displacement amplitude on fretting wear behavior of copper-magnesium alloy[J]. Tribology,2021,41(1): 125-136. (in ChineseYUAN Xinlu, LI Gen, ZHANG Xiaoyu, et al. Effect of displacement amplitude on fretting wear behavior of copper-magnesium alloy[J]. Tribology, 2021, 41(1): 125-136. (in Chinese) [8] ODFALK M,VINGSBO O. Influence of normal force and frequency in fretting©[J]. Tribology Transactions,1990,33(4): 604-610. doi: 10.1080/10402009008981995 [9] PEARSON S R,SHIPWAY P H,ABERE J O,et al. The effect of temperature on wear and friction of a high strength steel in fretting[J]. Wear,2013,303(1/2): 622-631. [10] GODET M. The third-body approach: a mechanical view of wear[J]. Wear,1984,100(1/2/3): 437-452. [11] ARNAUD P,FOUVRY S,GARCIN S. A numerical simulation of fretting wear profile taking account of the evolution of third body layer[J]. Wear,2017,376/377: 1475-1488. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2017.01.063 [12] ZMITROWICZ A. Wear debris: a review of properties and constitutive models[J]. Journal of theoretical and applied mechanics,2005,43(1): 3-35. [13] WATERHOUSE R B,TAYLOR D E. Fretting debris and the delamination theory of wear[J]. Wear,1974,29(3): 337-344. doi: 10.1016/0043-1648(74)90019-2 [14] 王剑飞,薛伟海,高禩洋,等. 表面织构下钛合金不同周次的微动磨损行为[J]. 中国表面工程,2022,35(3): 73-83. WANG Jianfei,XUE Weihai,GAO Siyang,et al. Fretting wear behavior of Ti alloy under different cycles with surface texture[J]. China Surface Engineering,2022,35(3): 73-83. (in ChineseWANG Jianfei, XUE Weihai, GAO Siyang, et al. Fretting wear behavior of Ti alloy under different cycles with surface texture[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2022, 35(3): 73-83. (in Chinese) [15] BIAN W W,HONG C,XIN L,et al. Effect of the cycle number on fretting wear behavior of alloy 690TT tube in high-temperature pressurized water[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials,2022,567: 153828. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2022.153828 [16] LINCK V,BAILLET L,BERTHIER Y. Modeling the consequences of local kinematics of the first body on friction and on third body sources in wear[J]. Wear,2003,255(1/2/3/4/5/6): 299-308. [17] KABIR M A,LOVELL M R,HIGGS C F. Utilizing the explicit finite element method for studying granular flows[J]. Tribology Letters,2008,29(2): 85-94. doi: 10.1007/s11249-007-9285-y [18] AHMADI A,SADEGHI F. A novel three-dimensional finite element model to simulate third body effects on fretting wear of hertzian point contact in partial slip[J]. Journal of Tribology,2021,143(4): 041502. doi: 10.1115/1.4048386 [19] YAN Xiaoyu,WANG Wei,LIU Xiaojun,et al. Using a coupled FEM-DEM method to study the nonlinear phenomena of third-body behavior[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers,Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology,2021,235(5): 975-988. [20] HU Jianqiao,YUAN Fuping,LIU Xiaoming,et al. Effect of plasticity on nanoscale wear of third-body particles[J]. Tribology International,2021,155: 106739. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106739 [21] ARNAUD P,FOUVRY S. A dynamical FEA fretting wear modeling taking into account the evolution of debris layer[J]. Wear,2018,412/413: 92-108. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2018.07.018 [22] HILLS D A,SACKFIELD A,PAYNTER R J H. Simulation of fretting wear in halfplane geometries: part 1 the solution for long term wear[J]. Journal of Tribology,2009,131(3): 1. [23] BRINK T,MILANESE E,MOLINARI J F. Effect of wear particles and roughness on nanoscale friction[J]. Physical Review Materials,2022,6(1): 013606. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.6.013606 [24] 惠阳,刘贵民,杜建华,等. 基于第三体的制动材料摩擦磨损行为研究进展[J]. 材料导报,2021,35(19): 19153-19160. HUI Yang,LIU Guimin,DU Jianhua,et al. Research progress on friction and wear behavior of brake materials based on the third body[J]. Materials Reports,2021,35(19): 19153-19160. (in Chinese doi: 10.11896/cldb.20080194HUI Yang, LIU Guimin, DU Jianhua, et al. Research progress on friction and wear behavior of brake materials based on the third body[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(19): 19153-19160. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11896/cldb.20080194 [25] 王剑飞,薛伟海,高禩洋,等. 磨屑对TC4钛合金微动磨损行为的影响[J]. 摩擦学学报,2022,42(5): 1012-1023. WANG Jianfei,XUE Weihai,GAO Siyang,et al. Effect of debris on fretting wear behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Tribology,2022,42(5): 1012-1023. (in ChineseWANG Jianfei, XUE Weihai, GAO Siyang, et al. Effect of debris on fretting wear behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Tribology, 2022, 42(5): 1012-1023. (in Chinese) [26] 黄琳,崔昊,尹剑,等. 基于制动器摩擦副销-盘试验的第三体摩擦磨损特性研究[J]. 润滑与密封,2022,47(6): 59-64. HUANG Lin,CUI Hao,YIN Jian,et al. Study on the friction and wear characteristics of the third body based on pin-disc test of brake friction pairs[J]. Lubrication Engineering,2022,47(6): 59-64. (in Chinese doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2022.06.008HUANG Lin, CUI Hao, YIN Jian, et al. Study on the friction and wear characteristics of the third body based on pin-disc test of brake friction pairs[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2022, 47(6): 59-64. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2022.06.008 [27] KAPOOR A,JOHNSON K L. Plastic ratchetting as a mechanism of metallic wear[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences,1994,445(1924): 367-384. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1994.0066 [28] BAYDOUN S,FOUVRY S,DESCARTES S. Modeling contact size effect on fretting wear: a combined contact oxygenation - third body approach[J]. Wear,2022,488/489: 204168. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2021.204168 -








 下载:
下载: